Running a growing tech company means handling sensitive data every day. Customer information, intellectual property, financial records, and confidential communications all flow through your systems. One breach can cost millions, destroy customer trust, and derail your growth trajectory.
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) gives you a structured way to protect what matters most. It's not just about buying security tools or checking compliance boxes. An ISMS is a comprehensive framework of policies, processes, and controls that systematically manages information risks across your entire organization.
If you're preparing for your first security audit, responding to customer security questionnaires, or building a compliance program from scratch, this guide will show you exactly how to implement an effective ISMS in 2025.
What Is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An Information Security Management System is a holistic framework that defines how your organization protects its information assets and manages security risks. Think of it as your company's comprehensive playbook for keeping data confidential, maintaining its integrity, and ensuring it's available to the right people at the right time.
At its core, an ISMS is driven by continuous risk management. You assess threats and vulnerabilities, implement controls to address them, monitor how well those controls work, and improve them over time. This isn't a one-time project you finish and forget. It's an ongoing cycle that evolves with your business and the threat landscape.
An effective ISMS covers three fundamental security principles (the CIA triad):
Confidentiality means ensuring data is accessed only by authorized people. This includes everything from password policies and access controls to encryption and secure file sharing. If your customer database or trade secrets leak to unauthorized parties, you've failed confidentiality.
Integrity prevents unauthorized changes to data. Whether it's financial records, source code, or customer orders, you need assurance that information hasn't been tampered with. Controls like version control, change management, and audit logging help maintain integrity.
Availability ensures information is accessible when authorized users need it. Ransomware attacks, server failures, or natural disasters can all disrupt availability. Your ISMS addresses this through backups, disaster recovery plans, and redundant systems.
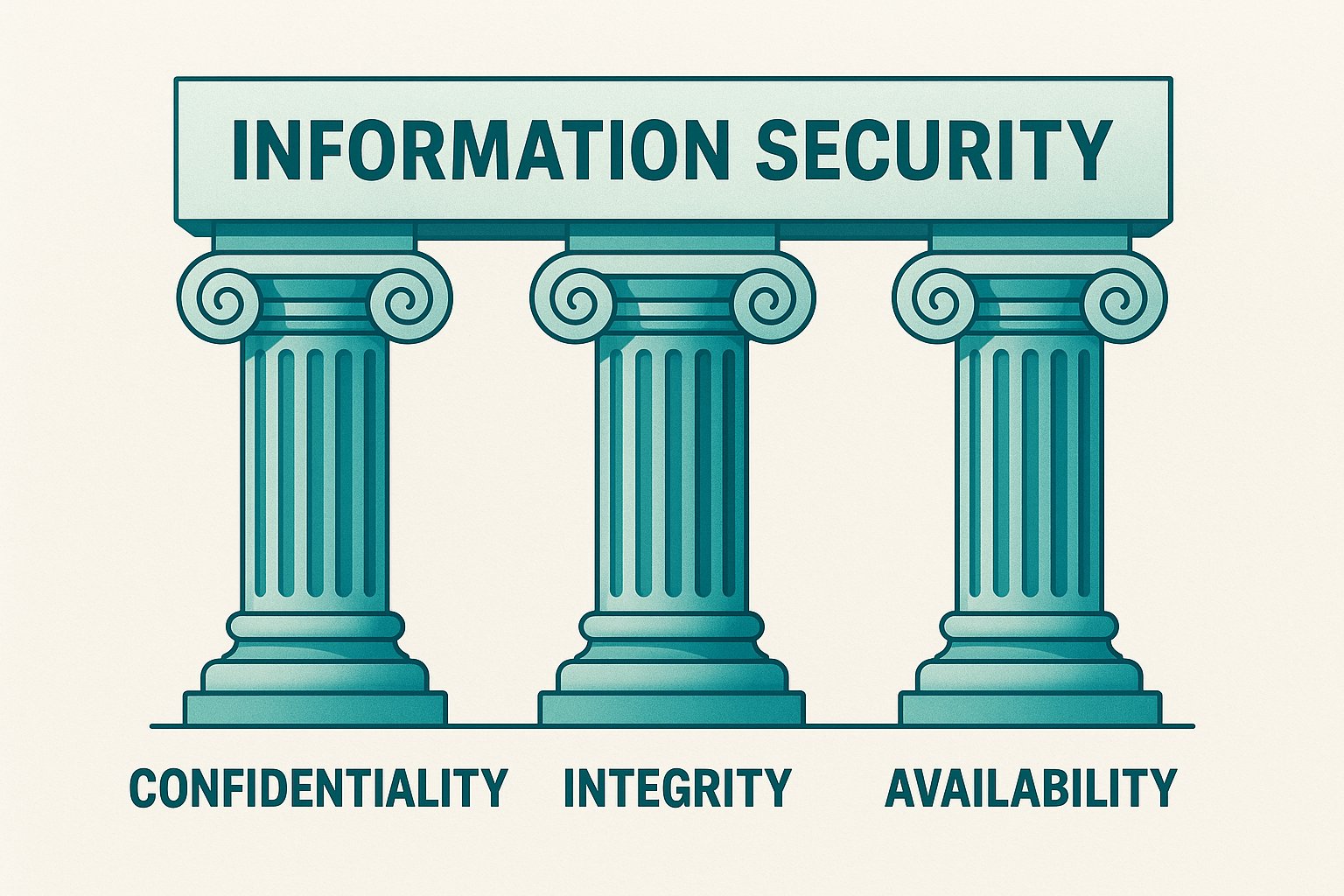
Many frameworks also emphasize authenticity (verifying user identities through mechanisms like multi-factor authentication) and accountability (maintaining audit logs so actions can be traced and users can't deny their activities).
What makes an ISMS different from just "doing security" is the systematic approach. You're not randomly implementing security controls based on what seems important. You're following a structured methodology that ensures nothing falls through the cracks. An ISMS isn't just about technology. It's equally about people and processes.
Your system will cover how employees are trained on security practices, how third-party vendors are assessed and monitored, how incidents are detected and responded to, and how leadership stays involved through regular reviews. Security becomes woven into your company culture rather than existing as a separate IT concern.
Why Information Security Management Systems Matter More Than Ever in 2025
The stakes for information security have never been higher. Cyber threats are more sophisticated, data breach costs continue climbing, and customers demand proof of strong security practices before they'll trust you with their data.
What Are the Rising Costs of Data Breaches?
Data breaches hit record costs in 2024, with the average breach costing $4.88 million, a 10% increase over the previous year. Globally, cybercrime damage is projected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025. For many companies (especially startups and growth-stage firms), a single major breach can be financially devastating or even business-ending.
An ISMS helps you prevent breaches through proactive risk management. By systematically identifying vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate controls, you reduce both the likelihood and potential impact of security incidents.
The numbers tell a compelling story about the value of strong security programs:
- Organizations extensively using security AI and automation saved an average of $2.2 million per breach compared to those that didn't
- Companies with robust incident response capabilities shaved more than two months off their breach response time
- That speed translates to significantly limited damage and lower total costs

Why Compliance Is No Longer Optional for Your Business
Regulatory requirements around data protection are tightening worldwide. The EU's GDPR, industry-specific regulations like HIPAA for healthcare, and emerging frameworks like NIS2 all demand demonstrable security controls and processes.
An ISMS provides a structured way to meet these requirements. For B2B SaaS companies especially, having an ISO 27001 certified ISMS or equivalent has become a prerequisite for enterprise deals. Customers want to see proof that you've implemented a verified security management system before they'll entrust you with their data.
In many scenarios, you can't even get in the door without ISO 27001 certification or a strong ISMS. Your sales team has likely already heard:
- "Send us your ISO certificate before we move forward"
- "Do you have SOC 2 Type 2 compliance?"
- "What's your current security posture and certification status?"
That's not an unusual request anymore. It's becoming standard operating procedure for enterprise buyers, especially in regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and insurance.
How Do Complex Digital Environments Demand Systematic Management?
Modern businesses operate in highly complex digital environments. You've got cloud infrastructure, SaaS applications, mobile devices, remote workers, and interconnected systems spanning multiple vendors and geographies. The attack surface has expanded dramatically.
Every new cloud service, software integration, or digital workflow introduces potential vulnerabilities. Your company probably uses dozens of SaaS tools. Each one represents a potential security risk if not properly managed. An ISMS helps you maintain visibility and control across this complexity.
A good ISMS forces you to:
- Inventory all your assets (including digital services and vendor relationships)
- Classify them based on sensitivity and criticality
- Implement appropriate controls for each asset category
- Monitor continuously for configuration drift or emerging threats
It addresses supply chain security by requiring due diligence on third-party services and continuous monitoring of vendor relationships.
As your systems and data sprawl across cloud and on-premises environments, an ISMS ensures security practices scale with operational complexity. You're not left wondering if you've secured everything. You have a systematic process for managing risk across your entire technology stack.
What Role Does an ISMS Play in Business Continuity and Recovery?
Security incidents cause massive business disruption. Beyond the financial cost, breaches lead to system downtime, data loss, reputational damage, customer churn, and regulatory investigations.
An ISMS integrates incident response planning, business continuity procedures, and disaster recovery processes into your security program. You don't just try to prevent incidents. You also prepare for rapid detection, containment, and recovery when something goes wrong.
Organizations with strong incident response capabilities built into their ISMS can detect and respond to breaches significantly faster. That speed matters tremendously. The difference between containing a breach in days versus months can mean:
- Millions of dollars in saved costs
- Preserved customer trust and reduced churn
- Avoided regulatory fines and legal exposure
- Faster business recovery and resumed operations
How Can Security Become a Competitive Advantage?
Here's something many founders miss: a strong ISMS isn't just about defense. It's a competitive differentiator.
When your ISMS is ISO 27001 certified, you can confidently answer customer security questionnaires, pass vendor assessments, and demonstrate your commitment to protecting sensitive data. Your sales team can move deals forward faster because you've already proven your security posture.
Compare that to competitors who are scrambling to answer basic security questions or who can't produce evidence of systematic security management. You win those deals. You close enterprise customers who have strict security requirements. You avoid the painful scenario where a promising deal stalls because you can't demonstrate adequate security controls.
An ISMS elevates security from a cost center to a growth enabler. It opens doors to enterprise customers, satisfies regulatory requirements, and builds the trust necessary for long-term customer relationships.
ISMS vs ISO 27001: What's the Relationship?
When people talk about implementing an ISMS, ISO/IEC 27001 inevitably comes up. Understanding the relationship between an ISMS and ISO 27001 is crucial.
What Is ISO 27001 and How Does It Work?
ISO/IEC 27001 is the internationally recognized standard for information security management systems. It provides requirements and a model for building, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS. Essentially, ISO 27001 is the blueprint for creating an effective ISMS.
The standard has two main components:
Management system clauses (Sections 4-10) define the organizational requirements:
- Establishing security context and scope
- Securing leadership commitment
- Planning risk assessment and treatment
- Providing necessary resources
- Operating the ISMS day-to-day
- Monitoring performance and effectiveness
- Conducting internal audits
- Driving continual improvement
These clauses tell you what processes you need to have in place to manage security systematically.
Annex A controls provide a catalog of specific security controls organizations should consider. The latest ISO 27001:2022 version streamlined this to 93 controls grouped into four categories:
- Organizational controls (governance, policies, frameworks)
- People controls (training, background checks, awareness)
- Physical controls (facilities, equipment, environmental)
- Technological controls (encryption, access management, logging)
These controls cover everything from access management and encryption to incident response and supplier security.
You're expected to assess which Annex A controls are relevant to your organization based on your risk assessment. You document your selections in a Statement of Applicability (SoA), explaining which controls you've implemented, which don't apply to you, and the justification for each decision.

Why Does ISO 27001 Certification Matter for Your Business?
You can build an ISMS without pursuing ISO 27001 certification. Many companies do exactly that. They use ISO 27001 as a framework but don't go through formal certification.
However, certification provides third-party verification that your ISMS meets the standard. An accredited certification body audits your ISMS and, if it conforms to ISO 27001 requirements, issues a certificate. This certificate is powerful proof for customers, partners, and regulators that you've implemented a robust security management system.
For B2B SaaS companies, ISO 27001 certification has become increasingly essential. Here's why:
- Enterprise customers frequently require it as a prerequisite for even considering your solution
- Government contracts often mandate it
- Insurance companies may offer better rates if you're certified
- Investors see it as evidence of mature operational practices
- Sales cycles accelerate when you can immediately prove your security posture
Comp AI specializes in helping companies achieve ISO 27001 certification rapidly. Traditional approaches can take 3-6 months or longer. Comp AI's automated evidence collection and expert guidance can compress that timeline to weeks, getting you certified and closing deals faster.
What Changed in ISO 27001:2022 That You Need to Know?
If you're familiar with the older ISO 27001:2013 version, be aware of significant changes in the 2022 revision.
The number of controls changed from 114 organized into 14 categories to 93 controls in 4 high-level categories. This wasn't just reorganization. The update consolidated some controls, removed outdated ones, and added 11 new controls addressing modern security challenges.
The new controls cover areas like:
- Threat intelligence gathering and sharing
- Secure coding practices for software development
- Cloud security configuration and management
- Data leakage prevention technologies
- Enhanced monitoring and detection capabilities
These additions reflect the evolving threat landscape and the reality that most companies now operate in cloud and hybrid environments.
Organizations with existing ISO 27001:2013 certifications had until October 31, 2025 to transition to the 2022 version. If you're starting fresh in 2025, you'll be implementing the 2022 standard from day one.
Plus, in 2024, ISO added mandatory climate-change considerations to all management systems standards (including ISO 27001). You must consider climate-related issues (like severe weather disrupting data centers or supply chains) when determining organizational context and assessing risks. Even if you conclude the impact is low for your specific situation, you need to document that you considered it.
Which Other ISMS Frameworks Should You Know About?
While ISO 27001 is the most widely recognized ISMS standard globally, other frameworks exist:
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is popular in the United States, especially for government contractors and organizations in regulated industries. NIST CSF 2.0, released in February 2024, emphasizes governance and supply chain risk management. Many companies map their ISMS controls to both ISO 27001 and NIST CSF to satisfy different customer requirements.
SOC 2 is an audit framework focused on service organizations. It's complementary to ISO 27001 rather than competing. Many SaaS companies pursue both: ISO 27001 for international recognition and enterprise requirements, SOC 2 for U.S.-based customers who specifically request it.
The practical reality: ISO 27001 provides the most globally recognized certification for an ISMS. If you had to pick one standard to implement, ISO 27001 would give you the broadest market acceptance.
What Are the Core Components of an Effective ISMS?
A comprehensive ISMS addresses multiple security domains systematically. Let's break down the key components you need to implement.

How Do Security Policies and Governance Drive Your ISMS?
Your ISMS starts with clearly documented security policies that establish rules and expectations for managing information security. These aren't one-time documents you write and forget. They're living policies that guide daily decisions and behaviors.
At minimum, you need an overarching Information Security Policy approved by senior leadership. This sets the tone that security is a priority and outlines your approach to managing risk. You'll also need specific policies covering areas like:
- Access control (who can access what)
- Acceptable use of systems and data
- Data classification and handling requirements
- Incident response procedures
- Change management processes
Governance means clearly defining roles and responsibilities. Who's accountable for information security? Who makes risk decisions? Who implements controls? In many organizations, there's a designated Information Security Officer or team responsible for the ISMS, but security responsibilities should be distributed appropriately throughout the organization.
Leadership involvement is critical. An ISMS can't succeed if it's purely an IT initiative. Senior management must demonstrate commitment through active participation in reviews, resource allocation, and enforcement of accountability.
How Do You Conduct Effective Risk Assessment and Treatment?
Risk management sits at the heart of every ISMS. You can't protect everything equally, so you need a systematic way to identify and prioritize risks.
Start with an asset inventory. What information assets does your organization have? This includes:
- Data stores (databases, file shares, cloud storage)
- Applications (SaaS tools, custom software, APIs)
- Infrastructure (servers, network devices, cloud resources)
- Devices (laptops, mobile devices, IoT)
- Facilities (offices, data centers)
- People (who have access to sensitive information)
For each asset, determine its value and sensitivity.
Next, identify threats and vulnerabilities for each asset. What could go wrong? Customer databases face risks from hacking, insider misuse, or accidental exposure. Laptops risk theft or loss. Cloud services risk misconfiguration. Third-party vendors risk security breaches that affect your data.
Assess the likelihood and potential impact of each risk materializing. This helps you prioritize. A high-likelihood, high-impact risk (like a lack of multi-factor authentication on administrator accounts) demands immediate attention. A low-likelihood, low-impact risk might be accepted as-is.
For significant risks, determine how you'll treat them:
- Mitigate by implementing controls to reduce likelihood or impact
- Transfer through insurance or contractual agreements
- Accept if the risk is within your risk tolerance
- Avoid by not engaging in the risky activity
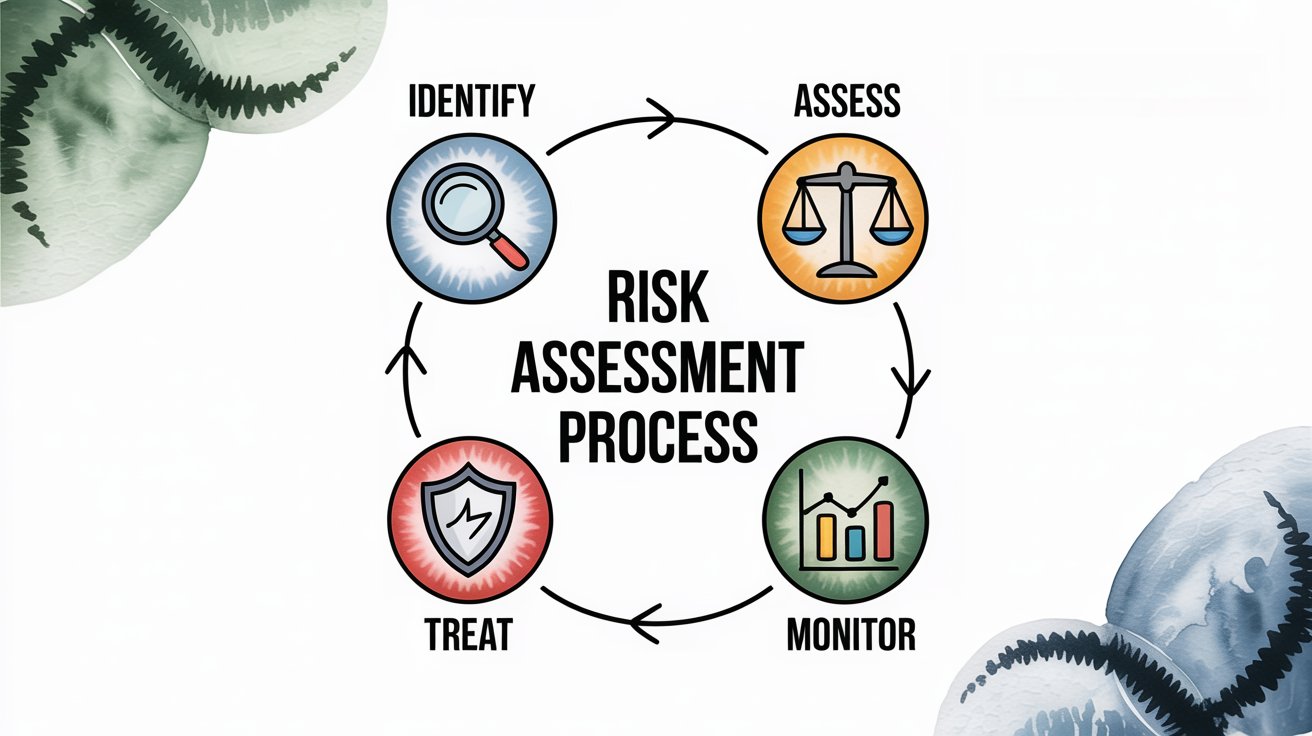
Document your risk assessment results and treatment plan. This becomes a living document you review and update regularly as your business and threat landscape evolve.
What Access Control and Identity Management Do You Need?
Controlling who can access what is fundamental to information security. Strong access control prevents unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) where users receive only the permissions necessary for their job functions. This "principle of least privilege" minimizes the damage if an account is compromised.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory, especially for:
- Administrative accounts with elevated privileges
- Remote access to corporate systems
- Access to sensitive data (customer records, financial data)
- Cloud service consoles and management interfaces
MFA dramatically reduces the success rate of credential-based attacks.
User account lifecycle management ensures accounts are created properly, permissions are reviewed periodically, and access is revoked immediately when employees leave or change roles. Many breaches happen through former employee accounts that weren't deactivated.
Privileged access management (PAM) gives you extra controls around high-risk administrative accounts. These accounts can make system-wide changes or access any data, so they need enhanced monitoring, approval workflows, and session recording.
Comp AI automates evidence collection for access control practices, making it simple to demonstrate to auditors that you're properly managing user accounts and permissions across your systems.
Which Technical Security Controls Should You Implement?
These are the concrete security measures you implement to protect systems and data:
Encryption protects data confidentiality. Encrypt data at rest (in databases, file storage, backups) and in transit (network communications, API calls). Proper key management ensures encryption keys themselves are protected.
Endpoint protection means ensuring all devices:
- Have security software installed and updated
- Are configured securely according to hardening standards
- Are kept up to date with security patches
- Are managed through mobile device management (MDM) or endpoint management platforms
Network security includes:
- Firewalls controlling traffic flow
- Network segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems monitoring for threats
- Secure configuration of network devices
Vulnerability management means regularly scanning for security vulnerabilities, prioritizing them based on risk, and patching or remediating them according to defined service level agreements. Critical vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems need immediate attention. Lower-risk issues can be addressed on a longer timeline.
Logging and monitoring provide visibility into what's happening in your environment:
- Centralized logging from all critical systems
- Real-time alerting on suspicious activities
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools helping you detect and respond to threats quickly
Backup and recovery ensures you can restore operations after data loss or ransomware:
- Regular backups on appropriate schedules
- Immutable backup storage (so attackers can't delete backups)
- Periodic restore testing verifying your recovery capabilities work when you need them
How Do You Implement Secure Development Practices?
If you're developing software, security needs to be built in from the start, not bolted on afterward.
Implement secure coding practices and train developers on common vulnerabilities. Use version control for all code. Require peer code reviews before changes are deployed. Implement automated security testing in your CI/CD pipeline to catch vulnerabilities early.
Manage secrets (API keys, database credentials, encryption keys) properly:
- Never hardcode them in source code
- Use dedicated secrets management tools
- Rotate secrets regularly according to policy
Dependency scanning identifies known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and frameworks you use. The supply chain attack surface has grown dramatically as modern applications rely on hundreds of open-source dependencies.
How Should You Manage Third-Party Risk?
Your security is only as strong as your weakest vendor. Third-party service providers, cloud platforms, and SaaS applications all introduce risk to your environment.
Maintain an inventory of all third-party services and vendors that:
- Access your data
- Provide critical services
- Process customer information
- Host your infrastructure
Assess their security posture before you engage them. This might include:
- Reviewing their security documentation
- Requiring them to complete security questionnaires
- Verifying their own ISO 27001 or SOC 2 compliance
- Conducting on-site assessments for critical vendors
Include security requirements in vendor contracts:
- Data breach notification obligations
- Right to audit security controls
- Data handling and deletion requirements
- Subprocessor approval processes
Continuously monitor third-party risk, especially for critical providers. Vendor risk isn't a one-time assessment. Vendors get breached, change their practices, or introduce new subprocessors. Your ISMS should include periodic vendor reviews.
What Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning Do You Need?
Despite your best preventive controls, incidents will happen. How you respond determines whether an incident becomes a minor blip or a catastrophic breach.
Develop and document an incident response plan that covers:
- Detection of security incidents
- Analysis to understand scope and impact
- Containment to limit damage
- Eradication of the threat
- Recovery to normal operations
- Post-incident review to learn and improve
Define roles and responsibilities. Establish communication protocols (internal escalation and external notification requirements).
Run tabletop exercises or simulations periodically to test your plan. People need practice to respond effectively under pressure.
Business continuity and disaster recovery planning ensure your organization can continue operating (or quickly resume) after a major disruption. This includes documented recovery procedures, designated alternate work locations, and tested backup and recovery capabilities.
How Do Training and Awareness Programs Support Your ISMS?
Technology controls fail if people don't know how to use them properly or if they fall for social engineering attacks.
Every employee should receive security awareness training covering basics like:
- Recognizing phishing attempts
- Creating strong passwords
- Reporting security incidents
- Handling sensitive data properly
Role-specific training provides additional depth for:
- Developers (secure coding, threat modeling)
- IT staff (system hardening, incident response)
- Anyone with privileged access (elevated security responsibilities)
Make training ongoing, not a one-time checkbox. Quarterly refreshers, security newsletters, and simulated phishing campaigns help keep security top of mind.
A security-conscious culture means security practices become second nature. Employees instinctively question suspicious emails, lock their screens when stepping away, and think about data security when making decisions.
How Do You Measure and Monitor ISMS Effectiveness?
How do you know if your ISMS is working? You need metrics and monitoring.
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect your security posture:
- Endpoint compliance: Percentage of endpoints with security software installed and up to date
- Patching speed: Average time to patch critical vulnerabilities
- Access hygiene: Failed login attempts investigated
- Offboarding time: Time to revoke access for departing employees
- Backup verification: Successful backup restoration tests
- Incident handling: Security incidents detected and resolved
Regularly review these metrics. Trends tell you whether your security is improving, degrading, or holding steady. Anomalies indicate potential issues needing investigation.
Continuous monitoring through automated tools provides real-time visibility. You can't rely solely on quarterly reviews. You need to know immediately if something suspicious happens.
What Are Internal Audits and Management Reviews?
ISO 27001 requires periodic internal audits of your ISMS. These audits verify that:
- You're following your documented policies and procedures
- Controls are operating effectively
- You're meeting the standard's requirements
Internal audits should be conducted by someone independent of the area being audited to ensure objectivity. They generate findings (conformities and non-conformities) and recommendations for improvement.
Management review is a formal process where senior leadership reviews the ISMS's performance at least annually. This review examines:
- Audit results and corrective actions
- Security metrics and trends
- Risk assessment updates and new threats
- Security incidents and lessons learned
- Resource needs and budget requirements
Leadership then makes decisions about strategic direction, priorities, and resource allocation.
These reviews close the continuous improvement loop. You're not just implementing an ISMS and letting it run on autopilot. You're actively monitoring, evaluating, and improving it over time.
How to Implement an ISMS: Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Building an ISMS from scratch can seem overwhelming. Breaking it into discrete phases makes the process manageable.
How Do You Define Scope and Secure Leadership Buy-In?
Start by defining what your ISMS will cover. Which business units, locations, systems, and processes are in scope? For many companies, it makes sense to cover the entire organization. For others with distinct business lines, you might scope the ISMS to specific products or services initially.
Document your scope clearly. This becomes part of your certification if you pursue ISO 27001.
Secure executive sponsorship and commitment. An ISMS requires resources (people, time, budget, tools) and organizational change. It won't succeed without visible leadership support.
Establish an ISMS team or designate an ISMS manager responsible for driving implementation. This person needs sufficient authority and dedicated time.
How Do You Assess Current State and Identify Gaps?
Before you start building, understand where you are today. Conduct an informal assessment of your current security practices against ISO 27001 requirements (or whatever framework you're following).
What controls do you already have in place? Where are the gaps? This gap analysis helps you prioritize effort and estimate the work ahead.
For example, you might find you already have:
- Strong access controls and encryption ✓
- But lack formal incident response procedures ✗
- Regular vulnerability scanning ✓
- But no supplier risk assessments ✗
How Do You Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment?
Implement a risk assessment methodology. ISO 27005 provides guidance on information security risk management, but you don't need to overcomplicate this. The goal is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks.
Create your asset inventory. For each asset, identify threats (what could go wrong) and vulnerabilities (weaknesses that make threats more likely to succeed). Assess likelihood and impact. Calculate risk levels.
Document everything in a risk register. This becomes your living document for tracking and managing risks over time.
How Do You Design Risk Treatment and Select Controls?
For each significant risk, determine your treatment approach. Most risks will be mitigated through controls.
This is where you map to ISO 27001 Annex A controls. Which of the 93 controls are relevant to addressing your identified risks? Some controls will be required for all organizations (like access control and incident response). Others might not apply to your specific context.
Create your Statement of Applicability. For each Annex A control, document:
- Whether it's implemented, not applicable, or planned
- Your justification for the decision
- References to where evidence can be found
What Policies and Procedures Should You Develop?
Formalize your security requirements in documented policies and procedures. Start with your high-level Information Security Policy, then develop specific policies for key areas:
Required policies:
- Access Control Policy
- Data Classification and Handling Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Change Management Policy
- Incident Response Plan
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans
- Backup Policy
- Vendor Risk Management Policy
- Secure Development Policy
Procedures provide step-by-step instructions for implementing policies. For example, your Access Control Policy might state that departing employees must have access revoked within 24 hours. The accompanying procedure details exactly who does what: HR notifies IT, IT disables accounts in order of sensitivity, badges are deactivated, etc.
Keep policies concise and high-level. Procedures can be more detailed but shouldn't be so prescriptive that they become impractical to follow.
How Do You Implement Technical and Organizational Controls?
Now comes the hard work: actually implementing the controls you've selected.
This typically involves:
Technical controls: Configuring systems to meet security requirements:
- Deploy MFA across all critical systems
- Implement endpoint protection on all devices
- Set up centralized logging and SIEM
- Configure backup systems with immutable storage
- Harden server configurations
- Deploy vulnerability scanning
- Enable encryption at rest and in transit
Organizational controls: Establish processes and workflows:
- Create the incident response team structure
- Implement the change approval process
- Set up the vendor risk assessment workflow
- Design the access request and review process
People controls: Focus on human elements:
- Launch security awareness training programs
- Conduct background checks for new hires in sensitive roles
- Establish security responsibilities in job descriptions
Prioritize based on risk. Tackle high-impact controls first. You don't need to implement everything perfectly before moving forward. You need enough controls in place that your ISMS is genuinely reducing risk and operating as a management system.
How Do You Run the ISMS and Collect Evidence?
Your ISMS needs to operate for a period before certification auditors will feel confident it's embedded in your organization. This doesn't mean waiting months. It means showing that controls are actually working and generating evidence.
Evidence includes:
- Logs showing monitoring is active
- Training records showing employees completed security awareness
- Access review records showing periodic reviews occurred
- Incident tickets showing incidents were detected and resolved
- Change tickets showing the approval process was followed
- Vulnerability scan reports showing scanning is happening and issues are remediated
Comp AI automates continuous evidence collection from your systems, making this process dramatically faster and less manual than traditional approaches. Instead of spending weeks gathering screenshots and exporting logs, Comp AI connects to your tools and collects evidence automatically.
How Do You Conduct an Internal Audit?
Before engaging an external certification body, run an internal audit of your ISMS. This simulates the certification audit and helps you identify issues before they become formal non-conformities.
Internal auditors:
- Review your ISMS documentation
- Interview staff about security practices
- Examine evidence of control operation
- Test whether controls are operating as documented
They generate a report identifying conformities, non-conformities (gaps requiring correction), and opportunities for improvement.
Address any non-conformities before proceeding to certification. This might mean updating policies, implementing missing controls, or fixing configuration gaps.
How Do You Conduct an Effective Management Review?
Conduct a formal management review where leadership examines ISMS performance. This review should cover:
- Internal audit results and corrective actions
- Metrics and KPIs showing security posture
- Incidents and their resolution
- Changes in context or risk landscape
- Resource needs for continued operation
- Opportunities for improvement
Document the meeting minutes. Management should make decisions about any needed changes, resource allocation, or strategic direction.
How Do You Schedule Certification Audits?
If you're pursuing ISO 27001 certification, select an accredited certification body (CB). Ask for proposals from multiple CBs to compare costs and approaches.
Ensure your CB is:
- Accredited by a recognized accreditation body (like ANAB in the US or UKAS in the UK)
- Using the latest standards (ISO/IEC 27006-1:2024 audit guidelines and IAF MD 29:2024 audit time calculations)
Schedule your Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits:
- Stage 1 is a documentation review (often conducted remotely) where auditors verify your ISMS is properly designed and you're ready for Stage 2
- Stage 2 is the comprehensive audit where auditors test whether your ISMS operates effectively in practice
What Happens After Certification?
After passing your Stage 2 audit, you receive your ISO 27001 certificate (typically valid for three years). Congratulations! But the work doesn't stop.
You'll have surveillance audits in years two and three. A full recertification audit occurs at year three.
More importantly, you need to keep operating and improving your ISMS:
- Continue monitoring metrics
- Assessing new risks as they emerge
- Updating policies as your business evolves
- Conducting regular internal audits
- Holding management reviews
An ISMS is a living system, not a static achievement. The continuous improvement cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) keeps your security posture current and effective.
ISMS Best Practices for 2025
Implementing an ISMS in 2025 means accounting for modern threats, regulatory changes, and technological realities that didn't exist when earlier ISMS were built.
Why Should You Embrace Automation in Your ISMS?
Manual ISMS management is painfully slow and error-prone. Gathering evidence, tracking controls, managing documentation, and coordinating audits consumes enormous time when done manually.
Modern compliance automation platforms drastically reduce this overhead:
- Continuously collect evidence from your systems automatically
- Automatically map controls to frameworks (ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA)
- Generate compliance reports on demand
- Maintain audit trails without manual documentation
What used to take months can now happen in weeks.
Comp AI is purpose-built for this challenge. The platform integrates with your existing infrastructure (cloud providers, SaaS tools, identity systems) and automatically collects the evidence auditors need. When you're ready for certification, Comp AI coordinates with certification bodies and provides white-glove support through the audit process.
Companies using automation report saving hundreds of hours and reducing their time to certification from 3-6 months to just weeks.
How Do You Address Cloud Security Comprehensively?
Most companies now operate primarily or entirely in cloud environments. Your ISMS must address cloud-specific risks.
Misconfigurations are one of the top causes of cloud breaches. Implement infrastructure-as-code practices with security reviews built in. Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to continuously monitor your cloud configuration against security benchmarks.
Shared responsibility models mean:
- You're accountable for securing what you put in the cloud
- The cloud provider secures the underlying infrastructure
- Understand exactly which security controls are your responsibility versus the cloud provider's
Multi-cloud and hybrid environments introduce complexity. Your ISMS should provide consistent security policies and controls regardless of where systems run.
How Do You Integrate DevSecOps?
If you're building software, security can't be a stage gate that happens after development. It needs to be integrated throughout the development lifecycle.
DevSecOps practices embed security into CI/CD pipelines:
- Automated security testing on every build
- Dependency scanning for vulnerable libraries
- Secrets scanning to catch hardcoded credentials
- Infrastructure-as-code security analysis before deployment
- Container scanning for image vulnerabilities
This shift-left approach catches vulnerabilities early when they're cheaper and easier to fix. It also provides continuous evidence that secure development practices are being followed.
Why Should You Prioritize Identity as the Perimeter?
In cloud and remote work environments, the traditional network perimeter doesn't exist. Identity becomes your primary security control.
Invest in strong identity and access management:
- Single sign-on (SSO) centralizes authentication and gives you visibility into who's accessing what
- MFA protects against credential theft
- Just-in-time access limits standing permissions
Zero Trust architectures assume no user or device should be implicitly trusted, even inside your network. Every access request is verified based on identity, device posture, and context.
How Do You Address Climate and Environmental Risks?
The 2024 climate change amendment to ISO 27001 requires considering climate-related risks. Don't overlook this.
Think about how extreme weather could affect your operations:
- If your data centers or cloud regions are in areas prone to hurricanes, flooding, wildfires, or extreme heat, document those risks and your mitigation strategies
- Supply chain disruptions due to climate events can affect vendors and logistics
- Business continuity planning should account for these scenarios
Even if you conclude climate risks are low for your specific situation, document your analysis. Auditors will ask.
How Can You Map to Multiple Frameworks Simultaneously?
Your customers don't all speak the same compliance language. Some want ISO 27001. Others ask for SOC 2. U.S. government contractors need NIST CSF compliance. EU customers care about GDPR and NIS2.
Design your ISMS to satisfy multiple frameworks simultaneously. The good news: these frameworks overlap significantly. The access controls you implement for ISO 27001 also satisfy SOC 2 criteria and map to NIST CSF functions.
Maintain cross-walks showing how your controls map to different framework requirements. This accelerates security questionnaire responses and vendor assessments. When a customer asks for your SOC 2 report or NIST CSF alignment, you can quickly demonstrate coverage.
How Do You Build for Continuous Compliance?
Traditional point-in-time audits create a cycle where organizations scramble before audits and then let things slide afterward. That's reactive and risky.
Build continuous compliance into your ISMS:
- Automated monitoring and evidence collection mean you're always audit-ready
- Regular internal audits (quarterly rather than just annually) catch issues early
- Monthly or quarterly reviews keep leadership engaged
Continuous compliance reduces audit stress and provides better ongoing risk management. You're not preparing for audits. You're operating a system that happens to generate audit evidence as a byproduct.
How Comp AI Accelerates Your ISMS Implementation
Building an ISMS traditionally takes 3-6 months or longer and requires significant manual effort. Comp AI changes that equation.
Comp AI's platform combines automated evidence collection, AI-powered policy generation, and white-glove expert support to compress traditional 3-6 month timelines into weeks. The platform integrates directly with your existing infrastructure to continuously collect audit evidence without manual work.
How Does Automated Evidence Collection Work?
Comp AI integrates with your cloud infrastructure, identity providers, SaaS applications, and security tools to automatically collect the evidence auditors need. Instead of manually taking screenshots, exporting logs, and tracking down documentation, evidence flows automatically into Comp AI.
This isn't just faster. It's more accurate and continuous. Manual evidence collection is a point-in-time snapshot that quickly becomes outdated. Automated collection provides ongoing proof that controls are operating effectively.
How Does AI-Powered Policy Generation Save Time?
Writing comprehensive security policies from scratch is time-consuming and requires expertise many teams lack. Comp AI's AI agents generate policies tailored to your environment and requirements. You review and approve them rather than writing from a blank page.
How Does Expert Guidance Speed Up Certification?
Comp AI provides white-glove support through the entire certification process. The team helps you:
- Scope your ISMS appropriately
- Select appropriate controls based on your risk assessment
- Prepare documentation that auditors expect
- Coordinate with certification bodies for scheduling
When you're ready for certification, Comp AI works directly with accredited certification bodies to schedule audits and ensure you have everything auditors need. No surprises, no delays.
What Happens After Certification?
After certification, Comp AI continues:
- Monitoring your environment for configuration changes
- Collecting evidence automatically and continuously
- Alerting you to drift from compliance requirements
- Preparing for surveillance audits proactively
The platform generates dashboards showing your security posture at a glance:
- Which controls are operating effectively
- Where gaps exist that need attention
- Trending metrics over time
- Readiness status for upcoming audits
Leadership can see ISMS performance without digging through documents.
For companies that need to move fast (particularly those facing customer-driven compliance deadlines or preparing for funding rounds), Comp AI compresses the timeline from months to weeks while maintaining the rigor needed to pass certification.
Frequently Asked Questions About Information Security Management Systems
How long does ISMS implementation take?
It depends on your starting point, organizational complexity, and resources. Traditional approaches typically take 3-6 months from initial planning to certification audit. With automation platforms like Comp AI, that timeline can compress to weeks for well-prepared organizations.
Factors affecting timeline include: current security maturity, size and complexity of your environment, availability of internal resources, whether you use automation, and certification body scheduling.
What does ISO 27001 certification cost?
Certification body fees for initial certification (Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits) typically range from $10,000 to $20,000 for small organizations. Larger or multi-site organizations can expect higher costs. These fees cover the audit itself.
Internal implementation costs vary widely. Traditional consulting-driven approaches might cost $10,000 to $25,000 or more. Automation platforms offer different pricing models but generally reduce total cost through dramatically lower labor requirements.
Annual surveillance audits (required in years two and three to maintain certification) typically cost less than initial certification, often $5,000 to $10,000.
Can we get certified quickly if we're under a customer deadline?
Yes, with the right approach and tools. Comp AI specializes in rapid certification for companies facing tight deadlines. The platform automates evidence collection and provides expert guidance to compress what normally takes months into weeks.
The key is:
- Prioritizing high-impact controls first
- Leveraging automation for evidence collection
- Getting expert help from experienced consultants
- Coordinating closely with your certification body to schedule audits as soon as you're ready
Do we need ISO 27001 if we already have SOC 2?
SOC 2 and ISO 27001 serve different purposes and markets. SOC 2 is popular in North America, especially for SaaS companies. ISO 27001 has stronger international recognition, particularly in Europe and regulated industries.
Many B2B SaaS companies eventually pursue both. The good news is significant overlap. The security controls you implement for one framework largely satisfy the other.
If you're primarily serving U.S. customers who specifically request SOC 2, you might start there. If you're selling internationally or to enterprise customers who require ISO 27001, prioritize that. Many companies find ISO 27001 provides broader market value.
What happens if we fail an audit?
Certification audits identify non-conformities (areas where your ISMS doesn't meet requirements). Minor non-conformities typically need to be addressed within a defined timeframe (often 90 days) but don't necessarily prevent certification.
Major non-conformities generally need to be resolved before certification is granted. The auditor will want to see evidence that you've corrected the issue before issuing the certificate.
Failing to maintain your ISMS between audits can result in certification suspension or withdrawal. That's why continuous operation and monitoring matter.
How much ongoing maintenance does an ISMS require?
An ISMS isn't a one-time project. It requires ongoing operation and improvement. Typical recurring activities include:
- Continuous monitoring of security controls
- Regular review and update of risk assessments (at least annually or when significant changes occur)
- Internal audits (annually at minimum, more frequently for high-risk areas)
- Management reviews (at least annually)
- Policy updates as business or technology changes
- Employee training refreshers and updates
- Responding to and learning from security incidents
- Surveillance audits (annually for ISO 27001 certification)
With automation like Comp AI provides, the ongoing burden is substantially lower than manual approaches. Many activities happen automatically rather than requiring dedicated manual effort.
Can we implement an ISMS for a specific product or service rather than the whole company?
Yes. Your ISMS scope is up to you. Many organizations start with a specific product line, service offering, or business unit. This can make initial implementation more manageable.
The scope must be clearly defined and make business sense. You can't arbitrarily exclude areas to avoid implementing controls. If certain systems process customer data for your in-scope product, those systems need to be in scope even if they're used by other business units too.
Over time, many organizations expand their ISMS scope to cover the entire company as security maturity increases.
What's the relationship between ISMS and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA?
An ISMS provides the foundation for regulatory compliance. Many regulations require specific security controls and practices. Implementing an ISO 27001-based ISMS typically covers a significant portion of what regulations require.
For example, GDPR has detailed security requirements. ISO 27001 Annex A controls align well with these requirements. Having an ISO 27001 certified ISMS demonstrates to regulators that you're systematically managing information security.
However, an ISMS alone might not cover all aspects of specific regulations. GDPR includes requirements around data subject rights, consent management, and privacy impact assessments that go beyond pure security controls. HIPAA has specific requirements around business associate agreements and breach notification.
Think of your ISMS as the security foundation. Layer additional compliance-specific requirements on top for comprehensive regulatory coverage.
Take the Next Step Toward ISMS Implementation
Information security isn't optional. It's a fundamental requirement for building a trustworthy, sustainable business. The question isn't whether you need an ISMS. It's how quickly you can implement one that actually works.
Start by assessing where you are today. What security controls and practices do you already have? Where are the gaps? What are your customers, investors, or partners asking for?
If you're facing pressure to achieve ISO 27001 certification, respond to complex security questionnaires, or simply demonstrate that you take security seriously, Comp AI can help you get there faster than traditional approaches.
The Comp AI platform automates the heavy lifting of ISMS implementation and maintenance. Automated evidence collection, AI-powered policy generation, continuous monitoring, and white-glove expert support mean you can achieve certification in weeks rather than months.
More importantly, you'll build a security management system that actually reduces risk and scales with your business. Not just a compliance checkbox, but a foundation for operational excellence and customer trust.
Visit trycomp.ai to see how Comp AI accelerates ISMS implementation and certification. Or schedule a demo to discuss your specific situation and timeline.
Security management done right becomes a competitive advantage. Get started today.
Share this article
Help others discover this content