Your 8-Point HIPAA Compliance Audit Checklist for 2025
Prepare for your OCR audit with our definitive HIPAA compliance audit checklist. Covers administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure success.
- Home
- Compliance HubHub
- Your 8-Point HIPAA Compliance Audit Checklist for 2025
Facing a HIPAA audit from the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) can be a daunting prospect for any healthcare organization or business associate. However, with systematic preparation, an audit transforms from a source of anxiety into an opportunity to validate and strengthen your data protection framework. A successful audit isn't just about avoiding hefty fines; it's about demonstrating a deep commitment to protecting patient privacy and maintaining the trust of those you serve. This comprehensive hipaa compliance audit checklist breaks down the complex regulatory landscape into eight manageable, actionable areas.
We will move beyond generic advice to provide specific, practical steps for reviewing your administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. This ensures you have the precise documentation and evidence needed to prove due diligence when auditors arrive. Each section is designed to function as a self-assessment tool, allowing you to proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities in your compliance posture.
By using this guide, you can confidently prepare your organization, find potential gaps before auditors do, and build a more resilient compliance program for the long term. To grasp the broader importance of these efforts, consider the benefits of meeting security compliance in your business , which extend far beyond passing a single audit. This checklist will guide you through crucial topics including Business Associate Agreements, breach notification protocols, employee training, and patient rights documentation, setting you on a clear path to audit readiness.
1. Administrative Safeguards and Policies
Administrative safeguards are the foundational policies and procedures that steer your organization's entire HIPAA compliance program. Think of them as the blueprint for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI). These aren't just abstract rules; they are the documented actions, policies, and protocols governing how you manage the security, development, and implementation of measures protecting electronic PHI (ePHI). A key part of any HIPAA compliance audit checklist involves verifying these administrative controls are not only documented but also actively implemented.
This foundational layer includes critical functions like performing a thorough security risk analysis, appointing designated Security and Privacy Officers, and establishing robust workforce training. It also covers developing contingency plans for emergencies and managing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs). Effective administrative safeguards often involve well-defined processes that leave no room for ambiguity. Creating a formal Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for handling PHI requests, for instance, ensures every team member follows the exact same verified steps, minimizing human error and demonstrating a commitment to compliance.

Real-World Implementation Examples
- Kaiser Permanente showcases a strong model by establishing dedicated compliance teams at both regional and facility levels, ensuring policies are enforced consistently across a large, complex organization.
- Cleveland Clinic formed a HIPAA governance committee that meets quarterly. This proactive group reviews policies, analyzes recent security incidents, and addresses potential compliance gaps before they become major issues.
- Anthem Health tackled the challenge of policy dissemination for its 50,000+ employees by developing a centralized policy management system. This system includes version control and acknowledgment tracking to ensure every employee has read and understood the latest policies.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To ensure your administrative safeguards stand up to scrutiny, focus on documentation and continuous improvement. Your goal is to create a living, breathing compliance program, not a "set it and forget it" document.
- Conduct and Document Annual Risk Assessments: Make this a non-negotiable annual task. Document every identified risk, the potential impact, and your mitigation plan. Auditors will ask for this documentation first.
- Establish a Policy Review Schedule: Regulations change. Set a recurring calendar reminder (quarterly or semi-annually) to review and update all policies to reflect new laws or organizational changes.
- Use Scenario-Based Training: Move beyond generic presentations. Use real-world examples of potential breaches or PHI mishandling in training to help staff understand how policies apply to their daily work.
- Maintain BAA Diligence: Don't just sign and file Business Associate Agreements. Review them annually to ensure your vendors still meet your security requirements and that the scope of work hasn't changed.
2. Physical Safeguards and Facility Security
Physical safeguards are the tangible, real-world measures taken to protect your facilities, equipment, and electronic information systems from unauthorized physical access, theft, and environmental hazards. While cyber threats get much of the attention, a physical breach can be just as devastating. This part of your HIPAA compliance audit checklist focuses on controlling access to buildings where Protected Health Information (PHI) is stored or accessed, securing workstations, and managing the physical devices and media that hold electronic PHI (ePHI). Auditors will verify that you have implemented policies and procedures to prevent unauthorized individuals from simply walking in and accessing sensitive data.
These controls form a critical defense layer, ensuring that even if digital defenses are bypassed, the physical hardware containing PHI remains secure. This includes everything from door locks and alarm systems to policies governing workstation placement and the secure disposal of old hard drives. Effective physical safeguards protect against both malicious intrusions and natural disasters, ensuring the continued availability and integrity of patient information. A robust security plan addresses who has access, where they have access, and how that access is monitored and controlled.

Real-World Implementation Examples
- Mayo Clinic implemented biometric access controls in its data centers and other areas housing patient data servers. This move drastically reduced unauthorized access attempts by over 95%, creating a highly secure and auditable environment.
- Johns Hopkins Hospital addressed visual privacy by deploying privacy screens on all workstations in public-facing areas. They also enforce a strict clean desk policy, conducting random audits to ensure no PHI is left unattended.
- Mass General Brigham established a comprehensive media disposal program, installing secure shredding bins for paper records and contracting with certified vendors for the destruction of electronic media like hard drives and backup tapes.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To prove your physical safeguards are effective, you need to show auditors a combination of implemented technology and rigorously enforced policies. Focus on creating multiple layers of security and documenting everything.
- Conduct Regular Physical Security Audits: Perform walk-throughs during and after business hours to check for unlocked doors, unattended workstations, and improperly stored documents. Document these checks and any corrective actions taken.
- Secure All Workstations: Implement automatic screen locks that activate after a short period of inactivity (e.g., 2-5 minutes). Use privacy screens on monitors in high-traffic areas where screens could be viewed by unauthorized individuals.
- Control Facility Access: Use visitor logs for all non-employees and require them to be escorted in areas where PHI is accessible. Deploy security cameras in strategic, non-sensitive locations like entrances and server rooms, and define a clear policy for footage retention.
- Establish Secure Disposal Procedures: Create a formal process for decommissioning and disposing of all devices and media containing ePHI. This should include methods like degaussing or physical destruction, with documented certificates of destruction from vendors.
3. Technical Safeguards and Data Encryption
Technical safeguards represent the technology and the associated policies that protect electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) and control who can access it. This domain covers the digital defenses of your organization, including access controls, audit logs, data integrity, and transmission security. A central pillar of this defense is encryption, which renders data unreadable and unusable to unauthorized individuals, both when it's stored (at rest) and when it's being sent (in transit). In a digital healthcare landscape where cyber threats are sophisticated and relentless, strong technical safeguards are non-negotiable for any HIPAA compliance audit checklist.
These measures are crucial because they form the last line of defense against a breach. If physical or administrative safeguards fail, robust technical controls like encryption can prevent a security incident from becoming a catastrophic data breach. Auditors will rigorously inspect your IT infrastructure, access policies, and data protection protocols to ensure they meet HIPAA's stringent requirements for confidentiality, integrity, and availability.

Real-World Implementation Examples
- University of California Health deployed end-to-end encryption across all its email systems, a massive undertaking that now protects over 15 million patient communications annually from interception.
- Intermountain Healthcare implemented granular, role-based access controls for its electronic health record (EHR) system. This initiative reduced inappropriate ePHI access by a reported 78% within the first year by ensuring staff could only view data essential to their job function.
- Geisinger Health System fortified its remote access security by mandating multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users. This simple yet powerful control has effectively eliminated breaches stemming from stolen or compromised login credentials for its remote workforce.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To validate your technical safeguards, you must demonstrate both implementation and consistent monitoring. Proving that your technology works as intended is key to passing an audit.
- Encrypt Everything: Implement full-disk encryption on all devices that store or access ePHI, including laptops, servers, and mobile devices. This is a critical control that auditors specifically look for.
- Secure Remote Access: Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) with strong, modern encryption protocols for all remote access to networks containing PHI. Ensure split-tunneling is disabled to prevent security bypasses.
- Review Access Controls Quarterly: Don't let access permissions become stale. Implement a formal process to review and update user access rights every quarter and immediately upon a change in an employee's role or termination.
- Automate Log Monitoring: Manually reviewing audit logs is impractical. Use automated tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to monitor logs in real-time and alert you to suspicious access patterns or potential threats.
4. Business Associate Agreements and Third-Party Risk Management
Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) are legally binding contracts required between covered entities and any third-party vendors, known as business associates, that create, receive, maintain, or transmit Protected Health Information (PHI) on their behalf. This item on your HIPAA compliance audit checklist ensures all vendor relationships involving PHI are properly documented and that these third parties implement appropriate safeguards. As organizations increasingly rely on vendors for services from cloud hosting to billing, this has become a critical compliance focal point.
Effective third-party risk management extends beyond just signing the BAA. It involves a continuous cycle of vetting, monitoring, and reassessment to ensure vendors consistently protect the PHI entrusted to them. An auditor will not only ask for your BAAs but will also probe your process for managing vendor risk throughout the relationship lifecycle, from initial onboarding to contract termination.
The following infographic illustrates the fundamental workflow for establishing and managing compliant vendor relationships.
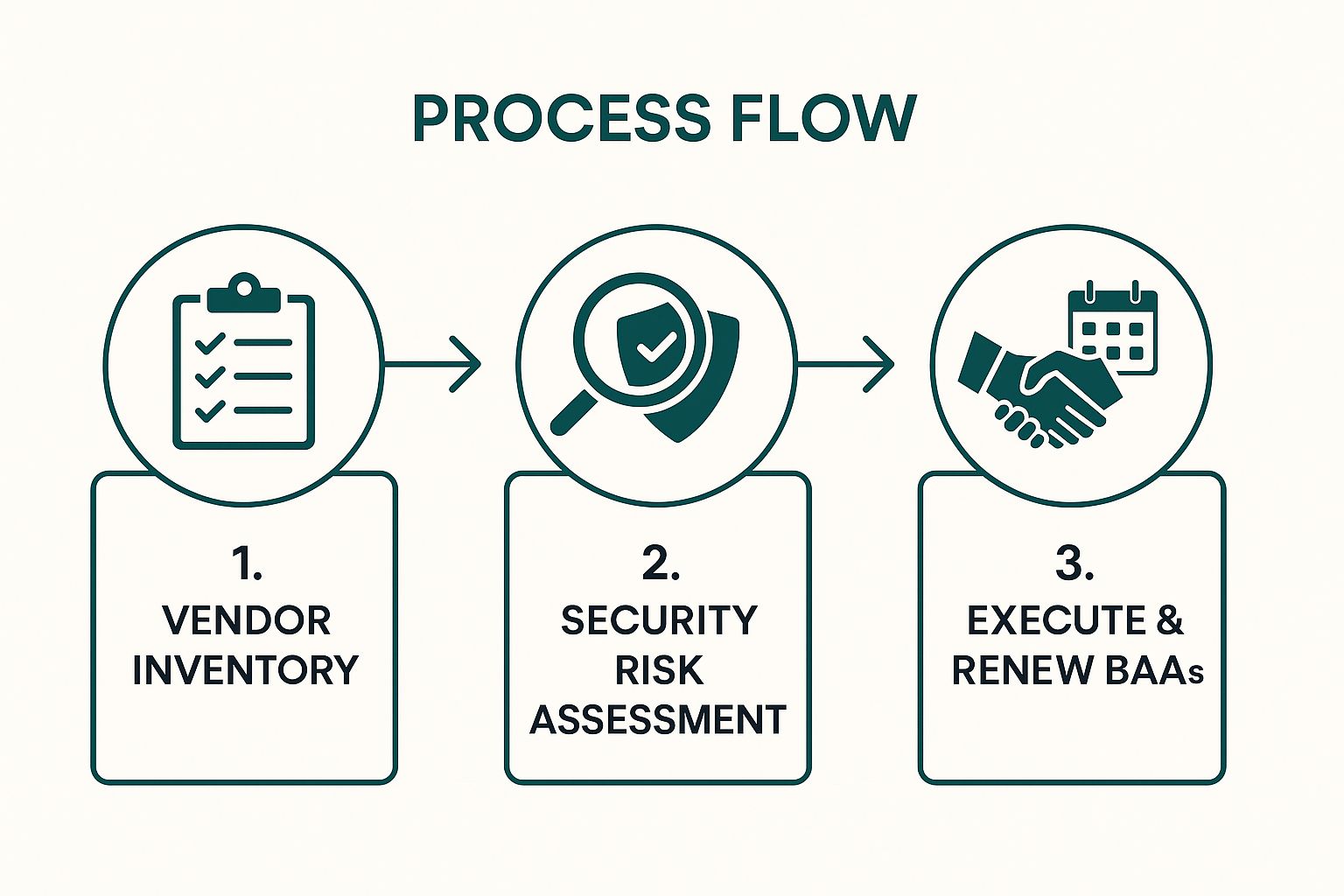
This simple yet crucial process flow establishes a clear, auditable trail for every business associate relationship.
Real-World Implementation Examples
- HCA Healthcare responded to rising vendor threats by developing a robust risk management program that assesses over 500 business associates annually using standardized security questionnaires and risk-tiering.
- Memorial Hermann Health System streamlined its vendor oversight by implementing a dedicated management platform. This system actively tracks BAA status, security assessment results, and renewal dates for its 300+ business associates.
- Scripps Health enhances its BAAs with additional contractual requirements, mandating that all vendors maintain specific levels of cyber liability insurance and provide certificates of compliance upon request.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To demonstrate robust vendor management, you must go beyond having signed BAAs and prove you have an active oversight program. Your goal is to show auditors that you treat vendor risk as an extension of your own security posture.
- Maintain a Centralized Vendor Inventory: Create and maintain a comprehensive, up-to-date inventory of all business associates and their subcontractors who handle PHI. This is often the first document an auditor requests.
- Implement a Pre-Contract Risk Assessment: Before signing any BAA, conduct a formal security risk assessment of the potential vendor. Document your findings and the vendor's remediation of any identified gaps.
- Standardize Your BAA Templates: Work with legal counsel to develop a standardized BAA template that includes all required HIPAA provisions and any stronger, organization-specific security clauses.
- Establish a BAA Review Schedule: Set a recurring annual or biennial schedule to review and update all active BAAs to ensure they align with any regulatory changes or changes in the vendor service scope.
- Verify Subcontractor Compliance: Ensure your BAAs require your business associates to have their own BAAs in place with any of their subcontractors that will handle your PHI.
5. Breach Notification and Incident Response Procedures
The HIPAA Breach Notification Rule mandates that covered entities and business associates provide notification following a breach of unsecured PHI. This component of a HIPAA compliance audit checklist verifies that your organization has a robust, documented incident response plan. Auditors will scrutinize your ability to detect potential breaches, conduct timely risk assessments to determine if notification is necessary, and execute notification protocols within strict timeframes. An effective response plan is not just about reaction; it is a proactive strategy to minimize harm and maintain trust.
A well-defined incident response procedure is critical because failure to properly handle and report breaches has led to some of the largest HIPAA penalties. The process involves more than just sending an email; it includes notifying affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and sometimes the media. Having a clear, actionable plan ensures a systematic, rather than chaotic, response during a high-stress security event. For comprehensive guidance, you can reference a data breach response plan template to build or refine your own procedures.
Real-World Implementation Examples
- Premera Blue Cross faced a $6.85 million settlement partly due to delayed breach notification after an incident affecting 11 million individuals, highlighting the severe financial consequences of an inadequate response.
- Banner Health, following a 2016 breach, successfully leveraged its incident response plan to notify 2.81 million affected individuals within the mandatory 60-day window, demonstrating effective crisis management.
- UCLA Health developed a tiered incident response system that categorizes security events by severity. This model assigns appropriate pre-defined response teams, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently based on the incident's impact.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To prove your incident response readiness to an auditor, you must show that your plan is documented, tested, and ready for immediate activation. Preparation is the key to mitigating damage and meeting regulatory deadlines.
- Conduct Tabletop Exercises: Run simulated breach scenarios at least annually with your response team. This helps identify gaps in your plan and ensures everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Create Pre-Approved Templates: Develop notification letters and communication scripts for individuals, regulators, and the media in advance. Having these templates pre-approved by legal and compliance teams dramatically speeds up the notification process.
- Document All Incidents: Maintain a detailed log of every security incident, even minor ones that do not qualify as a notifiable breach. This documentation demonstrates a mature security monitoring and assessment process to auditors.
- Formalize Your Risk Assessment: Use the four-factor test specified by HHS (nature of the PHI, unauthorized person, whether PHI was acquired or viewed, and mitigation extent) to formally assess every potential breach and document your conclusions.
6. Minimum Necessary Standard and Access Controls
The Minimum Necessary Standard is a cornerstone principle of HIPAA that requires covered entities to make reasonable efforts to limit the use or disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI) to the minimum necessary to accomplish the intended purpose. This isn't just a suggestion; it's a mandate that governs every interaction with sensitive data. During a HIPAA compliance audit, investigators will scrutinize whether your organization has policies and technical controls in place to ensure workforce members only access the specific PHI required to perform their jobs.
This principle is both an administrative policy requirement and a technical implementation challenge. It involves creating a framework that limits PHI access based on specific job roles and functions. An effective implementation means moving beyond a one-size-fits-all access model to a granular, role-based system. Developing a formal access control policy is the first step in demonstrating that you have defined who can access what information and under what circumstances, creating a clear audit trail for compliance.
Real-World Implementation Examples
- Texas Health Resources implemented context-aware access controls that adjust permissions based on established patient-provider relationships, which reportedly reduced inappropriate access incidents by 82%.
- Mount Sinai Health System uses advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze access logs in real-time. This system flags anomalous access patterns that may violate minimum necessary principles, allowing for immediate investigation.
- Providence St. Joseph Health implemented a "break-the-glass" protocol for emergency access to patient records. This allows providers urgent access but requires a mandatory, documented justification post-access, which is then reviewed by a privacy officer.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To prove your adherence to the Minimum Necessary Standard, focus on systematic role definition, regular reviews, and robust technical enforcement. Your audit preparation should highlight a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to access management.
- Conduct a Job Role Analysis: Don't guess what access people need. Work with department heads to formally document the specific types of PHI each job role legitimately requires to function. This analysis becomes the blueprint for your access controls.
- Implement Automated Access Provisioning: Tie your access control system directly to your HR system. This ensures that when an employee is hired, changes roles, or is terminated, their access rights are automatically adjusted or revoked, minimizing security gaps.
- Establish a Formal Access Request Process: Create a documented workflow for any access requests that fall outside of standard role permissions. This process must include management approval and a clear justification for the need.
- Review Access Permissions Quarterly: Make access reviews a mandatory quarterly task. Managers should be required to recertify that their direct reports' access levels are still appropriate for their current job duties.
7. Employee Training and Workforce Security
Since human error is a primary cause of data breaches, effective employee training and robust workforce security protocols are non-negotiable components of any HIPAA compliance program. This safeguard addresses the "human element" of security, ensuring that every person with access to PHI understands their role in protecting it. A thorough HIPAA compliance audit checklist will heavily scrutinize how an organization trains, monitors, and manages its workforce, from onboarding to termination.
This area covers everything from initial and ongoing training on security policies to the procedures for authorizing access, supervising staff, and applying sanctions for violations. Auditors look for evidence that training is not just a one-time event but a continuous, evolving program. They will verify that training content is relevant to specific job roles, updated to reflect new threats, and that completion is meticulously documented for every single workforce member. Strong workforce security is demonstrated by having a formal awareness training policy that integrates security into the company culture.
Real-World Implementation Examples
- Ochsner Health System transformed its training by developing a gamified HIPAA program. This innovative approach boosted completion rates from 78% to 97% and improved knowledge assessment scores by a remarkable 23%.
- Virginia Mason Medical Center supplements its annual comprehensive training with monthly five-minute security awareness videos. These quick-hit videos address current and relevant threats, keeping security top-of-mind for staff throughout the year.
- Sutter Health enhances its training by incorporating real breach case studies from HHS enforcement actions. This method powerfully illustrates the severe, real-world consequences of non-compliance and HIPAA violations.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To prove your workforce is a security asset, not a liability, focus on creating a comprehensive and measurable training program. Your goal is to build a culture of security awareness that is both documented and demonstrable.
- Tailor Training to Job Roles: Conduct a training needs assessment to identify knowledge gaps. A front-desk receptionist needs different, more focused training on patient interactions than a database administrator managing ePHI servers.
- Implement Microlearning: Break away from long, annual training sessions. Use short, frequent modules like quizzes, videos, or email tips to keep security concepts fresh and engaging.
- Conduct Phishing Simulations: Regularly test your employees with simulated phishing campaigns. Use the results to provide targeted, immediate follow-up training for individuals who click malicious links, turning a potential weakness into a learning opportunity.
- Document Everything: Track not just training completion but also assessment scores. Maintain detailed records of sanction policies and any disciplinary actions taken for HIPAA violations, as auditors will ask for this evidence.
8. Patient Rights and Privacy Practices Documentation
HIPAA grants patients specific rights concerning their Protected Health Information (PHI) and mandates that covered entities establish clear processes to honor these rights. This component of a HIPAA compliance audit checklist verifies that your organization has implemented and documented procedures for managing patient requests. These include the right to access records, request amendments, receive an accounting of disclosures, and request restrictions on PHI use. This area is the patient-facing front line of compliance, directly impacting trust and carrying significant regulatory risk if mishandled.
Your audit preparation must demonstrate that you not only have a written Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP) but also concrete workflows for every patient right. This includes tracking requests and responses, adhering to strict timelines, and ensuring staff can recognize and properly route these requests. Auditors will scrutinize the entire lifecycle of a patient request, from initial submission to final resolution, to confirm your documented policies are being followed in practice. Failure here is a highly visible compliance gap that can lead to patient complaints and HHS investigations.
Real-World Implementation Examples
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center pioneered the OpenNotes program, giving patients full, transparent access to their clinical notes, which has been shown to improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
- Kaiser Permanente leveraged its EHR system to automate the accounting of disclosures process. This innovation drastically reduced the average response time for these requests from a potential 45 days down to just seven days.
- Cigna streamlined its handling of amendment requests by developing standardized response templates. This ensured consistent and compliant communication while reducing the average processing time for each request by 40%.
Actionable Tips for Your Audit
To prove your patient rights management is robust and compliant, you must blend clear documentation with efficient, technology-enabled processes. Your goal is to make exercising these rights a straightforward and transparent process for patients.
- Implement a Patient Portal: A secure portal that allows patients to self-service access their records is one of the most effective ways to meet access requirements and reduce administrative workload.
- Use Standardized Request Forms: Create simple, clear forms for each type of patient right (access, amendment, etc.). This ensures you collect all necessary information upfront and standardizes the intake process.
- Establish a Response Timeline Tracker: Use a ticketing system or spreadsheet to track every request, its deadline (typically 30 days), and its current status. This is critical evidence for an audit.
- Train Your Front-Line Staff: Receptionists and schedulers are often the first point of contact. Train them to recognize a patient rights request and know the exact procedure for routing it to the designated privacy team.
8-Point HIPAA Compliance Checklist Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative Safeguards and Policies | High - requires comprehensive policy development and regular updates | Significant time and possible external expertise needed | Organizational accountability and proactive compliance | Establishing compliance foundations across organization | Clear responsibility chains, consistent PHI handling, audit readiness |
| Physical Safeguards and Facility Security | Moderate - involves physical changes and facility management | Investment in physical security devices and monitoring | Reduced unauthorized physical access to PHI | Securing facilities and physical devices storing PHI | Tangible security barriers, deterrence of breaches, complements technical measures |
| Technical Safeguards and Data Encryption | High - complex software and system integration | Skilled IT resources, ongoing management of encryption keys | Strong protection against data breaches | Protecting electronic PHI across digital systems | Data rendered useless if stolen, audit trails, scalable across organizations |
| Business Associate Agreements and Third-Party Risk Management | Moderate to High - legal contracts and ongoing vendor oversight | Legal and compliance resources for negotiations and monitoring | Clear third-party responsibilities and reduced vendor risk | Managing external vendors handling PHI | Extends compliance to vendors, legal recourse, accountability throughout data chain |
| Breach Notification and Incident Response Procedures | Moderate - requires cross-department coordination and rapid processes | Incident management resources and communications capability | Timely breach detection and regulatory notification | Responding to and managing PHI breaches | Rapid response, reduces penalties, maintains trust and transparency |
| Minimum Necessary Standard and Access Controls | High - requires detailed role analysis and ongoing access management | IT systems with RBAC and audit capabilities, administrative effort | Restricted PHI access minimizing insider risk | Limiting PHI access strictly to job functions | Reduces insider threats, enforces compliance, aligns with governance best practices |
| Employee Training and Workforce Security | Moderate - ongoing training development and delivery needed | Training development resources, documentation systems | Enhanced workforce awareness and reduced human error | Educating staff on HIPAA privacy and security | Creates compliance culture, reduces liability, empowers employees |
| Patient Rights and Privacy Practices Documentation | Moderate - process and documentation systems required | Administrative staff for processing and responding to requests | Improved patient trust and regulatory compliance | Managing patient PHI access, amendments, and communications | Empowers patients, builds transparency, ensures regulations met |
From Checklist to Culture: Embedding Continuous Compliance
Navigating the intricate landscape of HIPAA is a formidable challenge, but the comprehensive hipaa compliance audit checklist detailed in this guide provides a clear and actionable roadmap. You've walked through the critical domains: from establishing robust Administrative Safeguards and securing physical locations to implementing sophisticated Technical Safeguards that protect ePHI in transit and at rest. We have dissected the importance of watertight Business Associate Agreements, a rapid-response Breach Notification plan, and the strict enforcement of the Minimum Necessary Standard.
The journey doesn't end here. Completing a checklist is a milestone, not the final destination. True, sustainable compliance transcends periodic audits and becomes embedded in the very fabric of your organization’s culture. It’s about creating an environment where every team member, from the C-suite to the front lines, understands their role in safeguarding sensitive patient information. This cultural shift transforms compliance from a reactive, often stressful, scramble into a proactive, continuous state of readiness.
Key Takeaways: From Reactive to Proactive
Your primary goal should be to move beyond a "check-the-box" mentality. The most successful organizations treat compliance as a living, breathing part of their operations.
- Compliance is Continuous: An annual audit is just a snapshot in time. Threats evolve, regulations change, and internal processes shift. Your compliance program must be dynamic, with regular risk assessments, policy updates, and ongoing training sessions to match.
- Documentation is Your Defense: In an audit, undocumented actions are considered undone. Thorough, organized, and accessible documentation is your most critical evidence. This includes everything from risk analysis reports and BAA inventories to employee training logs and incident response post-mortems.
- Automation is Your Ally: Manually tracking every control, collecting evidence from disparate systems, and managing policy updates is not just inefficient; it's a recipe for human error. Leveraging technology to automate these repetitive tasks frees up your team to focus on strategic risk management rather than administrative burdens.
Actionable Next Steps: Building a Resilient Compliance Program
With the insights from our hipaa compliance audit checklist fresh in your mind, it's time to take decisive action. The path forward involves turning this knowledge into institutional practice.
- Formalize a Compliance Committee: Designate a cross-functional team responsible for overseeing the HIPAA program. This group should meet regularly to review risks, incidents, and policy effectiveness, ensuring accountability is distributed and maintained.
- Schedule a Mock Audit: Don't wait for an OCR official to knock on your door. Conduct a full-scale internal mock audit at least annually. This exercise will reveal gaps in your controls and documentation in a low-stakes environment, giving you time to remediate issues before they become critical findings.
- Integrate Compliance into Daily Workflows: Make security a seamless part of operations. For example, integrate access control reviews into your employee onboarding and offboarding processes. Make privacy impact assessments a mandatory step in the procurement process for any new software that will handle PHI.
By adopting this mindset, you not only prepare to pass an audit with confidence but also build a foundation of trust with your patients and partners. An effective compliance program is a powerful business enabler, demonstrating a deep commitment to integrity and data stewardship that resonates in today's security-conscious market.
***
Ready to transform your approach from manual checklists to automated, continuous compliance? Discover how Comp AI can streamline your entire HIPAA audit preparation process, from evidence collection to real-time monitoring. Schedule a demo with Comp AI today and see how you can achieve a perpetual state of audit readiness with confidence and ease.
Share this article
Help others discover this content
More from Compliance Hub
Explore more insights and stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
Top 12 HIPAA Risk Assessment Tools for 2025
Explore our expert review of the top 12 HIPAA risk assessment tools. Find the right platform to simplify compliance and protect your organization in 2025.
12 Best Vulnerability Management Tools of 2025
Discover the 12 best vulnerability management tools for 2025. Our in-depth review covers features, pros, cons, and use cases to secure your assets.
Your Essential Data Breach Response Plan Template
Build a robust data breach response plan template with our expert guide. Learn to manage incidents, protect your business, and maintain customer trust.