Getting ISO 27001 certified can feel overwhelming. You're looking at hundreds of controls, mountains of documentation, and an audit process that seems designed to find every gap in your security posture. But with a structured approach and the right checklist, you can streamline the entire process.
Whether you're a startup preparing for your first enterprise deal or an established company expanding into regulated markets, this guide walks you through exactly what you need to do. We'll break down the ISO 27001 compliance checklist into manageable steps, show you what auditors actually look for, and share how Comp AI helps companies get certified in just 14 days instead of the typical 6-12 months.
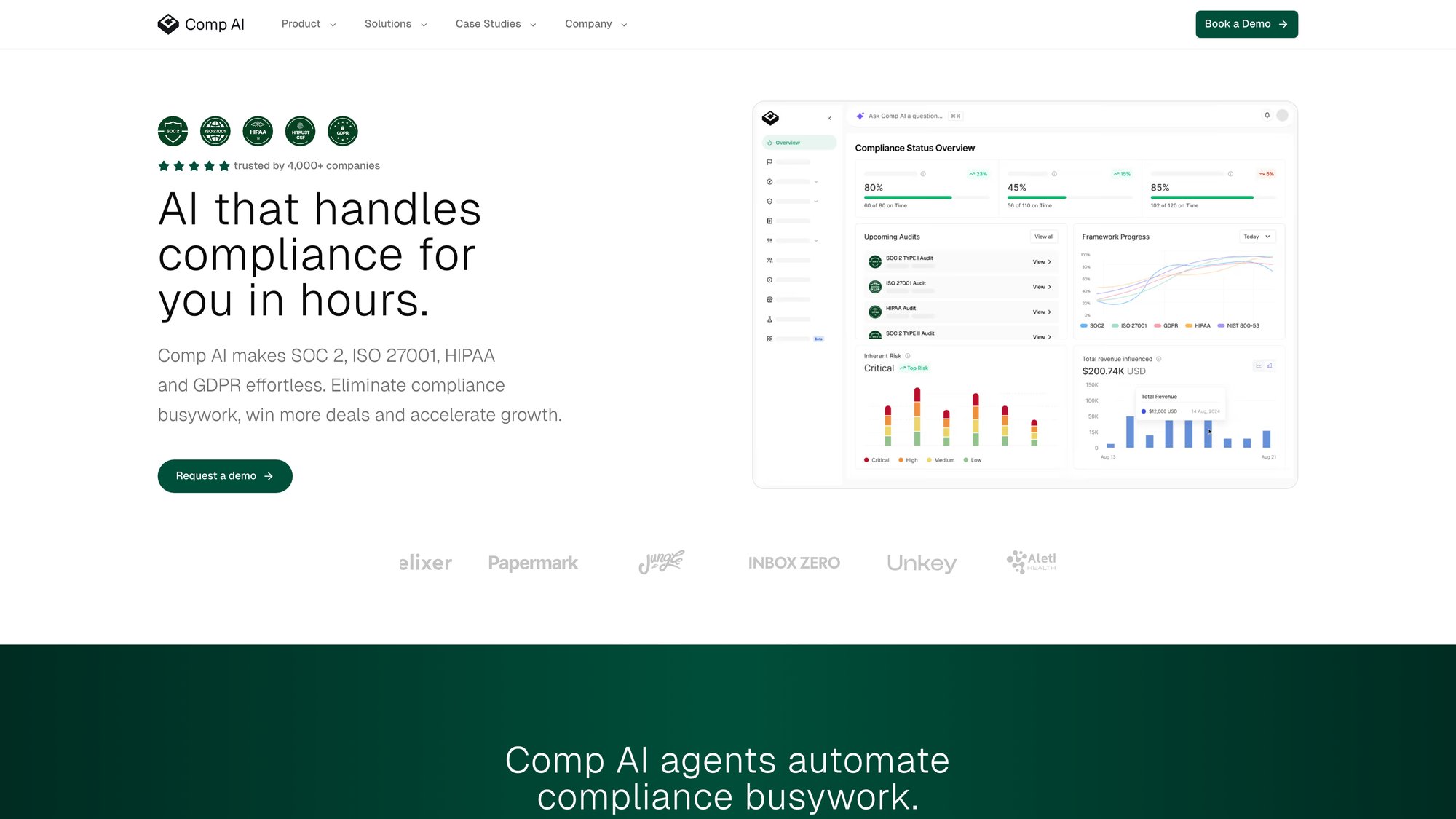
Comp AI's platform uses AI agents to automate evidence collection, policy generation, and continuous monitoring, transforming what used to be a 6-12 month manual process into a streamlined 14-day certification journey.
What is ISO 27001 Certification and Why Does It Matter in 2025?
ISO 27001 is the international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring it stays secure through people, processes, and technology controls.
Think of it as a framework that proves to customers, partners, and regulators that you're serious about security. The standard includes 114 controls across 14 domains, from access control to cryptography to supplier relationships. You won't need every single control, but you'll need to justify why each one is or isn't relevant to your business.
For tech startups, ISO 27001 certification opens doors. Enterprise clients often require it before they'll even consider your product. It signals maturity, reduces their risk, and gives procurement teams the documentation they need to justify buying from you.
The traditional certification process is slow and expensive. Most companies spend 6-12 months and tens of thousands of dollars preparing for their audit. But with compliance automation platforms like Comp AI, you can compress that timeline dramatically while maintaining the same level of security rigor.
Modern automation platforms centralize your compliance controls, automatically gather evidence from your existing tools, and keep you audit-ready year-round, eliminating the frantic scramble that typically precedes certification audits.
ISO 27001 Implementation Checklist: 8 Essential Phases for Success
Let's break down the certification journey into eight manageable phases. Each builds on the previous one, creating a structured path to certification.
Phase 1: How to Define Your ISMS Scope for ISO 27001
Before you write a single policy, you need to define what you're protecting and why. This is your ISMS scope, and it's the foundation everything else builds on.
Start by identifying:
- Which systems store or process sensitive data
- Which teams need access to what information
- Where data flows between systems and third parties
- What your biggest security risks actually are
Most startups make their scope too broad at first. You don't need to include every system on day one. Focus on the systems that handle customer data, intellectual property, and anything that touches regulated information. You can always expand the scope later.
Document your boundaries clearly. If you're using Comp AI, this process gets automated through AI agents that map your infrastructure and identify what needs protection. Otherwise, you'll need to manually inventory systems, interview stakeholders, and document data flows.
Your scope statement should answer:
- What assets are included (applications, data, infrastructure)
- What organizational units are covered (engineering, customer success, etc.)
- What physical locations apply (offices, data centers, cloud regions)
- What exclusions exist and why
Phase 2: ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Process (Complete Step-by-Step Guide)
Risk assessment is where you identify what could go wrong and how bad it would be. ISO 27001 doesn't prescribe a specific methodology, but it requires you to systematically identify, analyze, and evaluate information security risks.
The process looks like this:
1. Identify threats: What could compromise your data? Think ransomware, insider threats, third-party breaches, data loss.
2. Identify vulnerabilities: Where are you exposed? Unpatched systems, weak access controls, lack of encryption, poor vendor management.
3. Assess likelihood and impact: For each risk, estimate how likely it is to happen and how much damage it would cause. Use a simple scale like Low/Medium/High or a numerical scoring system.
4. Determine risk levels: Combine likelihood and impact to prioritize risks. High-likelihood, high-impact risks need immediate attention.
5. Document everything: Your risk register becomes a living document you'll reference throughout certification and beyond.
Traditional risk assessments take weeks. You're scheduling meetings with department heads, reviewing system architectures, and manually documenting hundreds of potential risks. Comp AI accelerates this by using AI to automatically identify risks based on your tech stack and industry, then helps you prioritize them based on actual threat intelligence.
Phase 3: How to Create Your ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability (SoA)
The Statement of Applicability is your roadmap for which of the 114 ISO 27001 controls you'll put in place and why. For each control in Annex A, you need to declare whether it's applicable and justify your decision.
Here's what that looks like in practice:
| Control Area | Number of Controls | Common Exclusions |
|---|---|---|
| Information Security Policies | 2 | Rarely excluded |
| Organization of Information Security | 7 | May exclude some for small teams |
| Human Resource Security | 6 | May simplify for small companies |
| Asset Management | 10 | Usually all applicable |
| Access Control | 14 | Usually all applicable |
| Cryptography | 2 | May exclude if no encryption needed |
| Physical and Environmental Security | 15 | May exclude for fully remote teams |
| Operations Security | 14 | Usually all applicable |
| Communications Security | 7 | Usually all applicable |
| System Acquisition, Development, Maintenance | 13 | May exclude some for SaaS companies |
| Supplier Relationships | 5 | Usually all applicable |
| Information Security Incident Management | 7 | Usually all applicable |
| Business Continuity | 4 | Usually all applicable |
| Compliance | 8 | Usually all applicable |
Don't just exclude controls to make your life easier. Auditors will scrutinize every exclusion. You need solid justification like "We don't have physical offices, so physical access controls don't apply" or "We use only managed cloud services, so we don't maintain server rooms."
Your SoA also needs to explain how you'll address each applicable control. This doesn't mean you need perfect setup right away, but you need a plan. With Comp AI, you get AI-generated control suggestions tailored to your tech stack, so you're not starting from scratch.
Phase 4: ISO 27001 Policies and Procedures (Essential Templates and Requirements)
Policies and procedures are the written rules that govern how your ISMS operates. You need documentation for every applicable control in your SoA.
Core policies you'll need:
- Information Security Policy: Your overarching security philosophy and management commitment
- Access Control Policy: Who gets access to what and how
- Acceptable Use Policy: What employees can and can't do with company systems
- Incident Response Policy: What happens when something goes wrong
- Business Continuity Policy: How you keep running during disruptions
- Data Classification Policy: How you categorize data sensitivity
- Change Management Policy: How you safely make system changes
- Vendor Management Policy: How you assess and monitor third parties

Each policy needs supporting procedures that explain the step-by-step process. For example, your Incident Response Policy needs procedures for detection, triage, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident review.
Writing policies from scratch is tedious. You're either hiring expensive consultants or spending weeks adapting templates that don't quite fit your organization. Comp AI generates customized policies based on your business model, tech stack, and risk profile in minutes instead of weeks. The policies are complete, audit-ready, and actually reflect how your company operates.
Phase 5: How to Implement ISO 27001 Security Controls (Technical, Administrative, and Physical)
This is where policy meets reality. You need to actually put in place the controls you've committed to in your SoA.
Your priorities should be:
1. Technical controls: Set up multi-factor authentication, encrypt data at rest and in transit, get logging and monitoring working, configure firewalls and intrusion detection, patch systems regularly.
2. Administrative controls: Conduct security awareness training, perform background checks, define roles and responsibilities, document procedures, set up change management processes.
3. Physical controls: Secure office access if applicable, protect hardware, manage visitor access, dispose of equipment securely.
Don't try to get everything perfect in one sprint. Use a risk-based approach. Focus first on high-risk areas and controls that auditors will definitely check. You can iterate on lower-priority controls after your initial certification.
Track your progress systematically. Create a spreadsheet or use a GRC tool to map controls to status. Comp AI automates this tracking and provides evidence collection in real-time, so you always know where you stand and what's left to do.
Phase 6: ISO 27001 Security Awareness Training Requirements (What You Need to Know)
Your ISMS only works if people actually follow it. That means training everyone on security policies, their responsibilities, and how to report incidents.
Training requirements:
Onboarding training: Every new employee needs security awareness training during onboarding. Cover password policies, phishing recognition, data handling, acceptable use, and incident reporting.
Annual refresher training: At least once a year, everyone needs updated training. Use this to cover new threats, policy changes, and lessons learned from incidents.
Role-specific training: People with elevated access need additional training on their specific responsibilities. Developers need secure coding training. IT admins need privilege management training. HR needs data privacy training.
Documentation: Keep records of who completed training and when. Auditors will ask for proof.
Most companies struggle with making security training engaging. Generic videos put people to sleep, and completion rates suffer. You need training that's relevant to your specific risks and actually changes behavior.
Comp AI includes role-based security training that's tailored to your tech stack and integrates with your onboarding process. Completion tracking is automatic, so you're not chasing people for certificates.
Phase 7: ISO 27001 Internal Audit Process (Complete Guide to Self-Assessment)
Before you face your certification audit, you need to audit yourself. Internal audits help you find gaps while there's still time to fix them.
Internal audit process:
1. Plan the audit scope: Which controls and processes will you review? Usually you'll audit all controls annually, but you might do it in phases.
2. Select auditors: Use someone independent of the process being audited. If you're auditing IT, don't use your IT team.
3. Review documentation: Check that policies exist, procedures are documented, and evidence is available.
4. Interview staff: Verify that people understand their responsibilities and are following procedures.
5. Test controls: Don't just ask if controls exist. Actually test them. Try to access systems without proper authorization. Check if logs capture the right information. Verify backups can be restored.
6. Document findings: Create a report of what you found, including any gaps or areas for improvement.
7. Track corrective actions: Fix what's broken and verify the fixes work.
Internal audits take time if you're doing them manually. You're scheduling interviews, reviewing documentation, testing controls, and writing reports. Comp AI automates evidence collection and continuously monitors control effectiveness, so you can identify gaps immediately instead of waiting for an annual audit.
Phase 8: ISO 27001 Management Review Requirements (Leadership Responsibilities)
Senior leadership needs to formally review the ISMS at least annually. This isn't a rubber stamp exercise. Management review ensures your ISMS stays relevant as your business changes.
Your management review should cover:
- Results from internal audits and any external assessments
- Status of corrective actions from previous reviews
- Changes in external and internal issues that affect the ISMS
- Feedback on information security performance
- Results from risk assessments and changes to the risk profile
- Opportunities for continual improvement
- Resource needs and adequacy
Document the review meeting, decisions made, and action items assigned. Auditors will want to see that leadership is engaged and providing resources for security improvements.
This is also where you show that your ISMS isn't just a paper exercise. Share metrics on incident response times, training completion rates, vulnerability remediation, and control effectiveness. Prove that you're actually managing security, not just checking boxes.
How to Prepare for Your ISO 27001 Certification Audit
Once you've put your ISMS in place and completed internal audits, you're ready for certification. The audit happens in two stages.
Stage 1: ISO 27001 Documentation Review (What Auditors Check First)
The auditor reviews your documentation remotely to verify completeness. They're checking that you have all required policies, procedures, and your SoA is properly structured.
What they're looking for:
- Your ISMS scope is clearly defined
- Your risk assessment is thorough and logical
- Your SoA justifies all control decisions
- Your policies address all applicable controls
- Your procedures are detailed enough to actually follow
This stage is pass/fail. If you're missing critical documentation or your SoA doesn't make sense, you'll need to fix it before moving forward. Most companies pass Stage 1 on the first try if they've been thorough.
Typical Stage 1 findings:
- Missing or incomplete procedures for certain controls
- Risk assessment doesn't cover all assets in scope
- SoA justifications are too vague for excluded controls
- Policies reference processes that aren't documented
Fix any findings before Stage 2. You usually have 90 days to address them.
Stage 2: ISO 27001 On-Site Assessment (How Auditors Verify Your Controls)
Stage 2 is the real audit. The auditor comes onsite (or remote, depending on your setup) to verify you're actually doing what your documentation says.
Expect them to:
- Interview staff at all levels to verify understanding
- Review access logs to confirm access controls work
- Test technical controls by attempting unauthorized access
- Review incident response records to see how you handle issues
- Inspect evidence for multiple controls across different time periods
- Verify training records are complete and current
Auditors use sampling. They can't check every employee or every system, so they'll select representative samples. If your samples look good, they'll extrapolate that the rest probably does too.
Common Stage 2 findings:
- Procedures aren't being followed consistently
- Evidence is incomplete for certain controls
- Staff lack awareness of their security responsibilities
- Technical controls aren't configured according to policy
- Change management records are missing or incomplete
Minor findings can usually be addressed with corrective action plans. Major gaps require fixing before certification is granted.
ISO 27001 Audit Evidence Requirements (What Documentation You Need)
Auditors live on evidence. You can have the best security program in the world, but if you can't prove it, it doesn't count.
Essential evidence types:
| Control Area | Evidence Examples |
|---|---|
| Access Control | Access review logs, MFA authentication reports, user provisioning tickets, role definitions |
| Incident Management | Incident tickets with timestamps, post-incident reviews, lessons learned documents |
| Asset Management | Asset inventory with owners, software inventory, hardware tracking records |
| Change Management | Change tickets, approval records, testing documentation, rollback procedures |
| Vendor Management | Vendor contracts with security requirements, vendor assessments, due diligence records |
| Training | Training completion records, quiz results, training materials, attendance logs |
| Backup/Recovery | Backup logs, restoration test results, DR exercise records |
| Vulnerability Management | Scan results, patching records, vulnerability tracking, risk acceptance forms |
| Physical Security | Access logs, visitor registers, badge issuance records (if applicable) |
| Monitoring | System logs, SIEM alerts, monitoring dashboards, log retention policies |
The evidence needs to cover a representative time period. If you're auditing in December, don't just show them November's logs. They'll want to see evidence from across the entire year.
Organization matters too. If you're scrambling to find evidence during the audit, it signals poor control. Have everything organized by control domain before the auditor arrives.
Comp AI automatically collects and organizes evidence in real-time through integrations with your existing tools. When audit time comes, everything's ready. You're not spending weeks searching through Slack, Jira, AWS, and Google Workspace trying to assemble proof.

Top ISO 27001 Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Having helped thousands of companies get certified, we've seen patterns in what trips people up. Here's what to watch out for.
Mistake 1: Making Your ISO 27001 Scope Too Broad
New companies often try to include everything in their initial scope. They want to show ambition and comprehensive security. But a broader scope means more controls, more documentation, and more audit scrutiny.
Start focused. Include the systems and processes that actually matter for your business. You can expand the scope after initial certification once you've got your ISMS running smoothly.
Mistake 2: Using Generic ISO 27001 Policy Templates Without Customization
Templates are tempting. Download some ISO 27001 policies, change the company name, and you're done, right? Wrong.
Auditors can spot generic policies immediately. They'll ask questions about specific procedures mentioned in your policies, and if you haven't actually set them up, you'll fail. Write policies that reflect what you actually do, not what some template says you should do.
Mistake 3: Treating ISO 27001 as Just an IT Project
ISO 27001 is an organizational standard, not just an IT certification. If only your IT team is involved, you're doing it wrong.
You need input from HR for employee security policies, from legal for compliance requirements, from operations for business continuity, and from leadership for resource allocation. Make it a cross-functional effort from day one.
Mistake 4: Not Planning for Continuous Improvement After Certification
Getting certified is just the beginning. You need to maintain and improve your ISMS continuously. That means regular risk assessments, internal audits, management reviews, and updating controls as threats evolve.
Companies that treat ISO 27001 as a one-time project often fail their recertification audits three years later. Build maintenance into your operations from the start.
Mistake 5: Poor ISO 27001 Evidence Collection and Organization
You did the work, but you can't prove it. This is surprisingly common. Teams put controls in place but don't document them properly. When the audit comes, they're stuck.
Build evidence collection into your normal workflow. If you're doing access reviews, save the review results somewhere retrievable. If you're responding to incidents, document the response process. Make evidence collection automatic wherever possible.
How Long Does ISO 27001 Certification Take? (Timeline Breakdown)
The timeline varies dramatically based on your approach and current maturity.
Traditional timeline (6-12 months):
- Months 1-2: Scope definition, risk assessment, SoA development
- Months 3-5: Policy and procedure documentation
- Months 6-8: Control setup and evidence collection
- Months 9-10: Internal audits and management review
- Months 11-12: Certification audit and corrective actions
This assumes you're starting from scratch and doing everything manually. Add more time if you have a complex infrastructure, large team, or limited security maturity.
With Comp AI (14 days):
- Days 1-3: Automated scope analysis and risk assessment powered by AI
- Days 4-7: Auto-generated policies and procedures customized to your tech stack
- Days 8-10: Automated evidence collection from existing tools
- Days 11-12: AI-assisted internal audit and gap remediation
- Days 13-14: Audit preparation and final review
The acceleration comes from automation. Instead of manually writing policies, mapping controls, and collecting evidence, AI agents do the heavy lifting. You're reviewing and approving rather than creating from scratch.
Comp AI works with your existing tools like AWS, Google Workspace, GitHub, Jira, and Slack to automatically gather evidence and maintain compliance. The platform continuously monitors control effectiveness, so you're always audit-ready.
The 14-day timeline assumes you can dedicate resources to the project and have basic security hygiene in place. If you're starting with significant security gaps, you'll need more time to fix issues before audit. But even then, you're looking at weeks instead of months.
ISO 27001 Certification Cost Breakdown (Complete Budget Guide)
Certification isn't free. Here's what you're looking at for costs.
Certification audit fees:
- Small organizations (under 25 people): $8,000-$15,000
- Medium organizations (25-100 people): $15,000-$25,000
- Large organizations (100+ people): $25,000-$50,000+
Audit costs depend on your scope size, number of sites, and complexity. Recertification audits every three years cost roughly the same, with smaller surveillance audits in between.
Getting ready costs:
| Approach | Cost Range | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| DIY | $20,000-$50,000 in staff time plus tools | 6-12 months |
| Consultant-led | $50,000-$150,000 depending on scope | 3-6 months |
| Comp AI | Starting at $3,000, typically $8,000/year | 14 days |
The DIY approach looks cheap but often costs more when you factor in opportunity cost. Your engineering team spending three months on compliance isn't building product. Consultants are expensive but know the process. They can help you avoid costly mistakes.
Compliance automation platforms like Comp AI offer the best ROI for most startups. You get the speed of DIY with the expertise of consultants at a fraction of the cost. The platform handles policy generation, evidence collection, and continuous monitoring, so your team stays focused on building.
Ongoing maintenance costs:
- Annual internal audits: $5,000-$15,000 if outsourced
- Training programs: $2,000-$10,000 annually
- GRC software: $10,000-$50,000 annually for traditional tools
- Surveillance audits: $5,000-$10,000 per year
- Comp AI all-inclusive: $8,000/year typically
Don't forget the hidden costs: time spent in audit meetings, fix-it work after findings, policy updates as your business changes. These add up quickly without automation.
ISO 27001 vs SOC 2: Which Compliance Framework Should You Choose?
This question comes up constantly. Both are security certifications, but they serve different purposes.
SOC 2 is better when:
- Your primary market is the United States
- You're selling to SaaS companies and tech startups
- You need certification fast (24 hours with Comp AI for Type I)
- Your customers specifically ask for SOC 2
ISO 27001 is better when:
- You're selling internationally, especially in Europe
- Your customers are in regulated industries
- You need a comprehensive security framework
- You want a certification that's globally recognized
Get both when:
- You're selling to enterprises globally
- Different customers require different certifications
- You want to maximize market opportunities
The good news? There's significant overlap. Both require risk assessments, policies, access controls, incident response, and continuous monitoring. If you do one well, you're 60-70% of the way to the other.
Comp AI supports both certifications with a unified ISMS. You set up controls once, and they count toward both frameworks. The platform automatically maps evidence to each framework's requirements, so you're not duplicating work. Learn more about ISO 27001 vs SOC 2 differences.
How to Maintain ISO 27001 Certification (Ongoing Compliance Requirements)
Getting certified is one milestone. Staying certified is the real challenge.
Annual surveillance audits:
Years one and two after certification involve smaller surveillance audits. The auditor samples a subset of controls to verify you're maintaining your ISMS. These are less intensive than full recertification but still require preparation.
Three-year recertification:
Every three years, you go through full recertification. It's similar to your initial certification audit but focuses more on improvements and how you've adapted to changing risks.
Continuous monitoring requirements:
Between audits, you need to keep your ISMS running:
- Conduct internal audits at least annually
- Hold management reviews at least annually
- Update risk assessments when major changes occur
- Maintain evidence collection continuously
- Keep policies current as your business evolves
- Train new employees and refresh existing staff
This ongoing work is where most companies struggle without automation. Someone needs to own ISMS maintenance, coordinate audits, collect evidence, and prepare reports. It's a part-time to full-time job depending on organization size.
Comp AI handles continuous monitoring automatically. The platform tracks control effectiveness in real-time, alerts you to issues before they become audit findings, and maintains your evidence repository without manual work. You stay audit-ready 365 days a year instead of scrambling before surveillance audits.
ISO 27001 Compliance FAQs (Expert Answers to Common Questions)
How long does ISO 27001 certification take?
Traditional setup takes 6-12 months from start to certification. With compliance automation platforms like Comp AI, you can complete the process in just 14 days. The timeline depends on your current security maturity, organization size, and resource availability. Smaller companies with basic security controls in place can move faster than larger organizations starting from scratch.
Can you get ISO 27001 certified as a startup?
Absolutely. Startups often pursue ISO 27001 to win enterprise deals and enter regulated markets. The standard scales to any organization size. Small companies actually have an advantage because they have fewer systems to secure and simpler processes to document. Comp AI was built specifically for early-stage startups that need certification fast without dedicating months of engineering time.
What's the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27001 is the certifiable standard that defines ISMS requirements. It tells you what you need to do to set up, run, maintain, and improve an information security management system. ISO 27002 is a supporting guideline that provides best practice recommendations for putting in place the security controls referenced in ISO 27001's Annex A. You get certified to 27001, but you might use 27002 for setup guidance.
Do you need a consultant for ISO 27001?
Not necessarily. Many companies successfully achieve certification without consultants by using comprehensive guides, templates, and automation tools. However, consultants can accelerate the process if you lack internal security expertise. Modern compliance automation platforms like Comp AI provide an alternative that combines expert guidance with automation at a fraction of consultant costs. You get the expertise without the hefty fees.
How much does ISO 27001 certification cost?
Total costs typically range from $30,000-$100,000 for traditional approaches, including audit fees ($8,000-$25,000), consultant fees ($50,000-$150,000), and ongoing maintenance. With automation, costs drop significantly. Comp AI starts at $3,000 with typical annual costs around $8,000, including continuous monitoring and maintenance. This makes certification accessible to startups that couldn't afford traditional routes.
Can you fail an ISO 27001 audit?
Yes, though it's uncommon if you've prepared properly. Major gaps that indicate your ISMS isn't functioning can result in certification denial. You'll need to fix the issues and reschedule your audit. Minor findings can usually be addressed with corrective action plans without delaying certification. Good preparation, including thorough internal audits, minimizes the risk of significant findings.
How often do you need to renew ISO 27001?
The certification is valid for three years. You'll have annual surveillance audits in years one and two, then a full recertification audit in year three. Between audits, you must maintain your ISMS through continuous monitoring, internal audits, management reviews, and evidence collection. Let the certification lapse, and you'll need to go through the full certification process again from scratch.
Does ISO 27001 require penetration testing?
The standard doesn't explicitly mandate penetration testing, but it does require you to test technical controls regularly. Most organizations include penetration testing as part of their security testing program because it's an effective way to verify control effectiveness. Auditors expect to see evidence of security testing appropriate to your risk level. If you handle sensitive data or face significant cyber threats, penetration testing is basically expected.
Get ISO 27001 Certified in 14 Days with Comp AI

The traditional certification process is broken. Six months is too long when you're trying to close enterprise deals. $100,000 is too much when you're watching your runway. Manual evidence collection is too fragile when you're scaling fast.
Comp AI makes ISO 27001 certification fast, affordable, and painless. Comp AI's AI-powered platform automates everything from policy generation to evidence collection to continuous monitoring. You get certified in 14 days instead of 6-12 months, starting at just $3,000 instead of $50,000+.
Here's how it works:
Comp AI connects to your existing tools like AWS, Google Workspace, GitHub, Jira, and Slack. Comp AI's AI agents analyze your infrastructure, identify applicable controls, generate customized policies, and continuously collect evidence. You review and approve rather than creating from scratch.
When audit time comes, everything's organized and ready. Your auditor gets exactly what they need without you spending weeks assembling documentation. After certification, Comp AI maintains your ISMS automatically, keeping you audit-ready 365 days a year.
The result?
- 100% audit success rate across 4,000+ companies
- 14-day average time to certification
- White-glove support including Slack access to compliance experts
- Money-back guarantee if you don't get certified
Stop letting compliance slow down your business. Book a demo with Comp AI and see how we can get you ISO 27001 certified in just two weeks. Your next enterprise deal is waiting.
Share this article
Help others discover this content