SOC 2 Compliance Checklist: Certification Guide (2025)
Your step-by-step SOC 2 compliance checklist for 2025. Covers policies, controls, evidence collection, and how to achieve certification fast.
- Home
- Compliance HubHub
- SOC 2 Compliance Checklist: Certification Guide (2025)
Achieving SOC 2 compliance has become virtually non-negotiable for B2B companies handling customer data. In 2025, enterprise clients routinely require a SOC 2 report before signing contracts, treating it as baseline proof of security. SOC 2 isn't a simple box-checking exercise. It's an in-depth audit of your organization's security controls, policies, and processes.
Preparing for a SOC 2 audit can feel daunting, especially for startups with limited resources. But a structured checklist makes the process manageable and ensures nothing critical slips through the cracks.
This guide provides a comprehensive SOC 2 compliance checklist to help you prepare for a successful audit. We'll break down the key steps (from defining your audit scope to gathering evidence) so you can navigate SOC 2 with clarity and confidence. By following these steps and using modern compliance automation platforms, you can save time and avoid common pitfalls, turning SOC 2 compliance into an achievable project instead of a mysterious hurdle.
What is SOC 2 Compliance and Why Does It Matter?
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) is an auditing framework developed by the AICPA that evaluates how well an organization protects customer data across five principles: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Unlike a pass/fail certification, a SOC 2 audit produces an attestation report from an independent CPA auditor, offering detailed assurance about your internal controls. SOC 2 compliance isn't mandated by law, but it's effectively become the gold standard for demonstrating trust to customers.
Why Enterprise Customers Require SOC 2 Certification
In practice, technology and SaaS companies face strong pressure to get SOC 2 compliant. Security-conscious clients often won't do business without it. The sales cycle impact represents one of the most tangible costs of not having SOC 2 certification.
One important thing to understand: SOC 2 is a flexible framework, not a prescriptive checklist of controls. The framework doesn't dictate exactly which controls you must set up. The official criteria define what you need to achieve (like controlling access to systems and monitoring for threats), but each organization decides how to handle and document those controls.
This means your exact compliance to-do list will be tailored to your systems and risks. However, industry best practices and common requirements give us a clear picture of the essential steps and controls almost every company needs for SOC 2.
10 Essential Steps to Achieve SOC 2 Compliance
Preparing for SOC 2 typically involves a series of project steps that build on each other. From scoping out what will be audited to setting up controls and collecting evidence, it's a progression that can take months if done manually (a full SOC 2 Type II process often spans 6-12 months).
The good news? With the right approach and automated compliance software, many companies compress this timeline dramatically. Here are the 10 essential steps to achieve SOC 2 compliance:
1. How to Define Your SOC 2 Audit Scope and Objectives
Begin by clarifying the scope of your SOC 2 audit and what you aim to achieve. SOC 2 is not one-size-fits-all, so you'll need to decide: Which systems and services will be included? Which Trust Services Criteria (TSC) will you cover?
Start by identifying all the locations, applications, cloud services, and processes where customer data is stored or processed in your business. Those will form the boundary of your audit scope. Most companies focus the scope on their primary product or service platform rather than every internal system.
Choosing Your Trust Services Criteria
Next, determine which of the five SOC 2 TSC categories apply:
- Security (also called "Common Criteria") is mandatory for any SOC 2 report
- Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, Privacy are optional based on your business needs
For example, a typical SaaS company might include Security, Availability, and Confidentiality if uptime and data handling are important to customers, but exclude Processing Integrity if it's not relevant.
Type I vs Type II: What You Need to Know
Also choose whether you need a SOC 2 Type I or Type II report. Your prospective clients or partners may have a preference.
| Report Type | What It Evaluates | Timeline | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Design of controls at a point in time | Can be completed as soon as controls are in place | Quick compliance proof, faster market entry |
| Type II | Both design and operating effectiveness over 3-12 months | Requires observation period of at least 3 months | Stronger assurance, enterprise customer requirements |
Type II provides stronger assurance since it proves your controls actually work consistently. It's the version most enterprise customers ultimately expect. If you're in a hurry to show compliance, you might do a Type I first (to get a report in hand quickly) and then follow up with a Type II.

Many startups, however, skip Type I and go straight for Type II to meet customer demands, accepting that the full process will take longer. Be realistic about timelines here: a Type II will require maintaining controls and evidence gathering for at least 3 months (the observation period), whereas a Type I can be audited immediately once you set up your controls.
Pro tip: It can be helpful to engage a SOC 2 expert or your auditor early on to assist with scoping. A formal scoping session can confirm you're including the right systems and criteria and not biting off unnecessary scope. Use our SOC 2 Readiness Assessment tool to get started.
For a deeper comparison of SOC 2 Type I vs Type II and guidance on choosing the right report for your situation, see our detailed guide on SOC 2 Type 1 vs Type 2.
2. How to Choose the Right SOC 2 Auditor for Your Company
Only specific professionals are authorized to perform a SOC 2 audit: namely, a licensed Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or a firm that is an AICPA-affiliated CPA organization. Selecting your independent auditor is a crucial step, and it's wise to do it early in your compliance journey.
A good auditor will not only execute the formal audit but can also provide guidance as you prepare (without compromising their independence). Many organizations find that the auditor's involvement from the start smooths out the entire process. Keep in mind that auditor firms often have lead times. If you wait until you're "ready" to book an audit, you might face scheduling delays of several weeks or more.
What to Look for in a SOC 2 Auditor
When evaluating SOC 2 audit firms, consider these key factors:
→ Experience and knowledge: Do they have experience with companies of your industry and size? An auditor familiar with cloud software companies will understand your AWS/Azure environment quickly. They should confidently answer technical questions and have a clear process to share with you.
→ Approach and support: Some auditors offer extensive pre-audit support (checklists, readiness reviews), while others expect you to be fully prepared. Determine what level of guidance you need. Ideally, choose an auditor who is willing to collaborate and communicate with your team throughout, not just appear at the end.
→ Reputation and compatibility: Ask for references or check reviews if available. It's also a good idea to meet the actual audit team (not just the sales rep) before signing, to ensure you feel comfortable with them and they are transparent about their process and timelines. Since the auditors will be combing through your systems and policies, trust is key.
Once you've picked an auditor, you don't need them on site right away, but do stay in touch as you prepare. Agree on the audit timeframe (for a Type II, this includes the start and end of the observation period) and ask if they have any checklists or tools to help you prep evidence. Knowing the audit schedule will create a target for your team to be ready. As you near the audit, the auditor might do an informal pre-audit review to catch any glaring issues. Take advantage of that if offered, since it's better to fix gaps before the official audit begins.
3. SOC 2 Readiness Assessment: How to Identify Compliance Gaps
With your scope defined and auditor in mind, it's time to take stock of where you stand. A readiness assessment (or gap analysis) is essentially a practice run audit you conduct on yourself. The goal is to compare your current security controls and practices against SOC 2 requirements and identify any gaps or weaknesses.
Start by reviewing the Trust Services Criteria and the specific controls they imply. For each area (security, availability, etc.), ask: What controls do we already have in place, and do we have evidence for them? What required controls or policies are we missing entirely?
Common Gaps Organizations Discover
Common gaps that organizations discover include:
- Missing formal security policies
- Loose or undocumented access controls
- Lack of a defined incident response plan
- No regular risk assessments
- Incomplete vendor due diligence
It's also very common to find gaps in evidence and documentation, even for controls you are doing informally.

Many companies find it useful to use a compliance management tool or automation platform at this stage to accelerate the gap analysis. For instance, compliance platforms can scan your systems and map out which SOC 2 controls you meet and where the gaps are.
Comp AI, for example, integrates with your infrastructure to automatically identify control gaps and generate a detailed readiness report. These tools often come with a library of controls and can auto-generate a gap report, saving you from combing through the criteria line by line. Our SOC 2 Readiness Assessment can identify your gaps in minutes, not weeks.
Prioritizing Remediation
The outcome should be a clear list of remediation tasks: a set of things you need to set up, fix, or improve to satisfy SOC 2. Prioritize the identified gaps by risk and difficulty.
For example, if you discover that multi-factor authentication (MFA) is not enabled everywhere it should be, that's typically a high-priority fix for Security criteria. If you're missing a formal change management process, you'll need to define and document that. The readiness assessment essentially generates the to-do list for your SOC 2 project. The remaining steps on this checklist will be all about addressing those to-dos one by one.
Tip: Document the findings of your gap analysis thoroughly. Create a spreadsheet or use your compliance automation platform to list each required control, whether you meet it, and what the remediation plan is if not. This becomes your project tracker. Auditors appreciate when companies have this mapped out, and it ensures you don't overlook anything critical before the audit.
4. Essential Security Policies and Documentation Requirements
"If it's not documented, it doesn't exist." That's a mantra to adopt for SOC 2. A huge part of compliance is proving to an auditor that you have formalized processes and policies in place. So, documentation work is a major early step.
Essential Security Policies
You will need a complete set of written policies covering these critical areas:
| Policy Type | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Define who can access what systems and data | Template |
| Acceptable Use | Set rules for appropriate use of company systems | Template |
| Change Management | Control how changes to systems are made | Template |
| Incident Response | Define how security incidents are handled | Template |
| Data Classification | Categorize data by sensitivity level | Template |
| Encryption | Specify encryption requirements | Template |
| Backup and Recovery | Document backup procedures | Template |
| Vendor Management | Control third-party risk | Template |
These policies outline your rules and procedures for safeguarding data and systems. If you don't have them, you'll need to draft them (using templates can help as a starting point). If you do have policies, ensure they are up-to-date and align with SOC 2 compliance requirements. For example, a policy should state that employees must use MFA and strong passwords, that you conduct employee background checks, that customer data is encrypted at rest and in transit, matching the controls you intend to set up.

Procedures and Processes
In addition to high-level policies, document the operational procedures that show how you handle security in practice. This can include:
- Employee onboarding/offboarding process (how you assign and revoke access)
- Vulnerability management process (how you patch systems and manage flaws)
- Deployments/change management process (how code or infrastructure changes are reviewed and approved)
- Incident handling procedures
Be specific. Auditors look for evidence that you follow consistent processes. Diagrams and flowcharts can help illustrate processes, but make sure there's written explanation too.
Logs, Reports, and Records
Start collecting evidence artifacts as you go. Set up a repository (like a dedicated folder structure in Google Drive, Confluence page, or a compliance platform) to store all documents and evidence that an auditor might request. Examples include:
- System logs and alerts
- Screenshots of security settings
- Lists of user accounts and their roles
- Training completion records
- Vendor risk assessments
For every control in your gap list, think about "what proof could an auditor examine to verify this?" and then ensure you have that proof stored. Establish a habit of saving things like access reviews, policy sign-offs, and backup logs in your repository going forward. It's much easier to gather evidence continuously than in a last-minute scramble.
Staying Organized
To stay organized, many teams create a master compliance folder or wiki that serves as the single source of truth for all SOC 2 documentation. Consider maintaining an index or table of contents of all your compliance documents so you (and the auditor) can quickly find everything.
The goal is that by the time the audit starts, all your documentation is centralized and easily accessible to demonstrate your compliance efforts. This not only impresses auditors but also helps your internal team stay on the same page.
How Comp AI Accelerates Documentation
If you use a compliance automation platform like Comp AI, it can actually generate many documents for you, such as creating baseline policies tailored to your tech stack or providing a pre-formatted "System Description" (the section of a SOC 2 report where you describe your system and controls) ready for you to customize.
Such platforms also often include a built-in evidence repository that auto-collects logs, screenshots, and reports from your integrated systems. Comp AI integrates with 50+ platforms to automatically collect and organize evidence. Using these features can save dozens of hours and ensure nothing is missed when it comes to documentation.
5. How to Implement and Test Critical Security Controls
With policies written and gaps identified, the core work is to execute on those remediations. In other words, set up the security controls that SOC 2 requires and make sure they're working effectively.
This step will likely be the most time-consuming, as it may involve technical changes, new tools, or process improvements across your organization. Focus on the fundamental controls that almost every SOC 2 auditor will expect to see:
Critical Security Controls Breakdown
| Control Category | What It Covers | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| *Access Controls* | Who can access systems and data | MFA, RBAC, least privilege, provisioning/deprovisioning |
| *Encryption* | Data protection at rest and in transit | Database encryption, HTTPS/TLS, secure configurations |
| *Monitoring & Logging* | Security event detection | SIEM, alerts, log aggregation, suspicious activity tracking |
| *Change Management* | How system changes are controlled | Code reviews, version control, CI/CD pipelines, approvals |
| *Vulnerability Management* | Finding and fixing security flaws | Regular scans, patch management, penetration testing |
| *Backup & Recovery* | Data resilience | Backup schedules, tested restoration, disaster recovery |
Access Controls
Ensure you have strong identity and access management in place. This means setting up role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege (each user only has the minimal access they need).
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be enabled on all critical accounts and systems (especially VPNs, admin consoles, cloud accounts, Git repositories). Lack of MFA is a common audit finding to avoid. Set up a process for user provisioning and deprovisioning so that when people join, change roles, or leave, their access is adjusted promptly and logged. Review our Access Control Policy template for guidance.
Secure Configurations and Monitoring
Lock down your systems according to best practices. For example, configure cloud services (AWS/Azure/GCP) securely: no open S3 buckets, proper network security, encryption settings enabled.
Encryption is key: use encryption for data in transit and at rest wherever feasible (enable database encryption, enforce HTTPS/TLS for web traffic).
Deploy logging and monitoring solutions to track security events. This could involve aggregating logs in a SIEM or using cloud-native monitoring, and setting up alerts for things like multiple failed logins, suspicious network traffic, or changes to critical configurations. Auditors will ask for evidence of monitoring, such as logs or screenshots showing your alerting in action.
Change Management
Set up a formal change management process for your technology environment. If you're a software company, this means having code changes reviewed (via pull requests) and tested before deployment, and using version control and CI/CD pipelines that log changes.
For infrastructure, use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) or documented procedures for modifying configurations. The idea is to show that changes are tracked, approved, and don't happen arbitrarily. Make sure you document any emergency change process as well (for urgent fixes) and log when it's used.
Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Management
Conduct a formal risk assessment if you haven't already: identify your top risks and how your controls mitigate them (some auditors will ask for a risk assessment document). Also, set up a vulnerability management process to regularly scan for vulnerabilities (using a tool or service) and apply patches/updates in a timely manner.
If you haven't done so, consider running a penetration test before the audit and fixing any high-risk findings. This demonstrates due diligence in testing your security.
Backups and Recovery
Ensure that all critical data is backed up and that you have the ability to restore from backups. Document your backup schedule and test the restoration process.
SOC 2 auditors often want to see that you not only back up data but have verified those backups actually work (for example, by performing a test restore).
Physical and Environmental Security
If any in-scope systems are hosted on-premises or in co-location, address physical security controls: things like badge access, CCTV, fire suppression, climate control, and visitor logs for data centers or offices. Many startups are fully cloud-based and can largely refer to their cloud provider's physical security, but don't ignore any office network or device protections (keep an inventory of laptops, ensure disk encryption on endpoints, secure your office Wi-Fi).
Testing Your Controls
As you set up each control, perform some basic testing or verification yourself. For example, once you enforce MFA, try logging in without it to confirm it's truly required. If you set up alerting, trigger a test alert to see that it's captured and responded to.
This internal testing gives confidence that when the auditor tests your controls (which they will, especially for a Type II), everything will function as intended. It's better to catch and fix a misconfiguration now than during the audit.
Throughout this step, maintain documentation of changes. Keep change tickets, meeting notes, or emails that show approvals for significant updates. Save configuration screenshots before and after where relevant. By the end of this phase, you want to have all critical controls in place and evidence of their operation.
As a milestone, many organizations target reaching a point where they can say: "If an auditor came tomorrow to do a Type I, we would pass." That means the design of controls is solid. Then you focus on operating them over time for a Type II.
6. Security Awareness Training: Building a Compliant Culture
People and culture are an often underestimated part of SOC 2 compliance. Even the best written policies won't be effective if your team isn't aware of them or following them. Auditors know this, so they look for both training records and signs of a security-conscious culture.
Security Awareness Training
Provide formal security training for all employees, especially those in technical and sensitive roles. This is typically done annually (at minimum) and should cover topics like phishing prevention, data handling procedures, incident reporting, and key company policies.
If you have developers, include secure coding practices. There are many online training modules available that you can use. Document when training is completed: maintain logs or certificates of completion for each employee. Auditors may request evidence that your staff underwent security training within the audit period.

Policy Attestation
When you roll out new or updated security policies (from step 4), have employees read and sign off on them. This can be done via an HR system, electronic signature, or even an email acknowledgement. The point is to show that everyone has been informed of the rules (especially critical policies like acceptable use, clean desk). Save these acknowledgments as evidence.
Incident Response Drills
Educate the team on what to do if something goes wrong. Make sure employees know how to report a security incident and who to contact. Conduct a tabletop exercise or drill for your incident response plan involving key team members, and document the results. This not only tests your plan (as required by SOC 2) but also reinforces everyone's understanding of it.
Role-Specific Training
Certain roles might need extra training. For example, if you have system administrators, they should be trained on secure configuration and management of those systems. Developers might need training on OWASP Top 10 (web app vulnerabilities) if software security is in scope. If you handle credit cards or health data, make sure folks are aware of those compliance obligations too (even though SOC 2 itself is broad, overlapping concerns like PCI or HIPAA often coexist).
Build Security into Onboarding/Offboarding
Make security orientation a part of every new hire's onboarding. This way, compliance remains an ongoing effort, not a one-time push. Likewise, have a strong offboarding process (remove access immediately, retrieve equipment) and consider including an exit interview question on whether they followed security policies, as an extra measure.
By instilling a "security-first" culture, you reduce the chance of human errors that could lead to incidents, and you make compliance sustainable beyond just the audit. Auditors may actually interview a few employees or managers during a SOC 2 (especially for Type II) to gauge if the policies are truly understood and in use.
You want your team to be able to answer basic questions like "What would you do if you suspect a phishing email?" or "Do you know what our company's incident response plan is?" correctly. A well-trained staff that can confidently talk about security is a strong signal that your controls aren't just paper exercises.
7. Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning
Even with great preventative controls, incidents happen. SOC 2 expects organizations to be prepared to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents or disruptions. Two important documents (and practices) to have in place are an Incident Response Plan and a Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery Plan (BCP/DR).
Incident Response (IR) Plan
This is a playbook outlining how you handle security incidents (data breaches, malware infections, service outages). It should define the steps of incident handling:
- Detection - How incidents are identified and reported
- Analysis - Initial assessment and severity determination
- Containment - Immediate actions to limit damage
- Eradication - Removing the threat from your environment
- Recovery - Restoring normal operations safely
- Lessons Learned - Post-incident review and improvements
And assign roles/responsibilities to team members for each step. Important elements include: a clear definition of what constitutes an "incident" and how employees should report one, an internal communication plan (who gets alerted, how escalation works), and a post-incident review process.
Create an incident log template as well to record details of any incidents. Once your plan is written, test it: run a scenario (simulate a ransomware attack or data leak) and have the team walk through their actions. Document the outcome of this drill as evidence that your incident response process is not just theoretical.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCP/DR)
This plan focuses on how you keep operations running (or restore them) during a serious disruption, be it a natural disaster, cyber-attack, cloud outage, etc.
It will include your data backup and restoration procedures, acceptable downtime targets, and alternate procedures if primary systems are unavailable. Key components are:
- A list of critical systems and their recovery time objectives
- Contact information for crisis management
- Backup site or cloud failover details if applicable
- Steps for communicating with customers or stakeholders during extended outages
Test your DR plan at least annually. For instance, perform a backup restore test (recover data from backup and verify integrity) or simulate a scenario where you have to fail over to a secondary system. Also consider a tabletop exercise for a business continuity scenario (like "office inaccessible due to hurricane" or "cloud provider down for 24 hours") and discuss how you'd maintain customer support. These tests should be documented with date, what was done, and outcomes.
Having these plans and tests addresses the Availability and Security criteria in SOC 2 and demonstrates a mature posture. Auditors will typically ask for copies of the IR plan and BCP/DR plan, and evidence of tests (meeting notes, test reports, or after-action summaries). Make sure to update the plans if there are major changes in your environment, and store them where the team can easily find them in an emergency (consider an offline copy as well, in case your network is down).
By completing this step, you show that your organization can quickly react to incidents and continue operating under adverse conditions, which is critical for trust. It's not just about having these documents. It's about operational readiness. As a bonus, being prepared here can significantly limit damage and downtime if an incident ever does occur for real.
8. Third-Party Vendor Risk Management for SOC 2
Your SOC 2 compliance is only as strong as its weakest link, and sometimes that weak link could be an external vendor. Most companies rely on third-party services (cloud hosts, SaaS tools, contractors) that might handle or affect the security of customer data.
SOC 2's criteria include requirements for vendor management, so a thorough compliance checklist must address how you assess and monitor your vendors.
Inventory Your Vendors
Make a list of all third-party vendors and service providers that are in scope for SOC 2. Focus on those that either store/process customer data or could impact the security of your systems (like an IT MSP, data center provider, payment processor). Common in-scope vendors include your cloud infrastructure provider (AWS, Azure, GCP), identity provider (Okta), critical SaaS apps that house customer data, and any subcontractors who have access to sensitive info.
Obtain SOC 2 Reports (or Equivalents)
For each critical vendor, especially those handling customer data, request a recent SOC 2 report from them. Many big providers publish SOC 2 reports or ISO 27001 certificates in their trust portals (for example, AWS, Azure, and GCP all have SOC 2 reports available).
If a vendor doesn't have a SOC 2, you might rely on ISO 27001 certification or ask them to fill out a security questionnaire. The idea is to evaluate their security posture. When you get these reports, review them for any noted weaknesses and ensure those don't pose a risk to you or have been addressed.
Vendor Risk Assessments
Perform a vendor risk assessment for significant vendors. This can be a checklist or questionnaire where you evaluate the vendor on criteria like: Do they encrypt data? Do they have up-to-date security certifications? What is their uptime SLA? Have they had breaches? Document your assessment and any risk rating (low/medium/high risk vendor). If any vendor is high risk, consider mitigation steps (maybe finding an alternative or requiring additional controls in the contract).
Learn more about effective third-party risk management and explore top risk management software solutions.
Update Contracts with Security Clauses
Work with your legal team to ensure that vendor contracts include appropriate security and compliance clauses. For instance, you may require that the vendor notifies you of any breach, that they maintain certain minimum security practices, or that they assist you in compliance efforts as needed.
If existing contracts lack such clauses, you might not fix that immediately (contract changes can take time), but at least note it as a risk or plan to address on renewal.
Track Vendor Compliance Over Time
Establish an owner internally for vendor management. This person or team should review vendor compliance at least annually. That could mean checking for updated SOC 2 reports each year and seeing if any findings were addressed. Also, keep an eye on news: if a key vendor suffers a data breach or outage, be ready to evaluate the impact on your control environment and communicate to your auditor if needed.
During your SOC 2 audit, the auditor will expect to see that you've taken a diligent approach to third-party risk. Evidence to prepare includes: a list of vendors in scope, copies of their SOC 2 reports or certifications, and possibly your internal vendor risk assessments or a policy on vendor management.
They may also check that you're requiring SOC 2 from your subservice organizations where appropriate. For example, if you use a data subprocessor, you should be vetting their security.
By completing this step, you demonstrate that you're not overlooking supply chain security. Remember, a security incident at a vendor can be just as devastating (or more) than one in your own environment, so this is a critical part of the checklist.
9. How to Prepare Evidence for Your SOC 2 Audit
As your planned controls and processes fall into place, the final preparation step is to get everything ready for the auditor's examination. In practice, this means two things: collecting and organizing your evidence for each control, and optionally doing a mock audit or readiness review to ensure confidence.
Collect and Organize Evidence
By now, you should have a repository full of documentation and logs. Now make sure it's complete and well-organized. Go back to your list of SOC 2 requirements and verify you have evidence for each control.
Typical evidence an auditor will want to see includes:
- Screenshots of security settings (MFA enforced in AWS, password policy in your IDP)
- System configuration files or reports (a listing of user accounts and permissions from your production system)
- Policy documents and revision history (to show policies were in effect during the period)
- Training records (dates and completion status)
- Incident logs (if any incidents occurred, show how they were handled)
- Backup logs and test reports
- Vendor SOC reports

Audit trails are important. For example, if you say "we review user access quarterly," have the meeting notes or tickets from those quarterly reviews as proof. Ensure that evidence items are labeled or named in a clear way so an auditor can easily map them to the respective control or criterion.
Create an Evidence Index
It's very helpful to create an evidence index or matrix: essentially a spreadsheet or table that lists each control or criteria and references the evidence files that satisfy it. Some compliance software will auto-generate this, but you can do it manually.
For instance: "Control: MFA is enabled on all customer-facing systems. Evidence: Screenshot of AWS IAM MFA settings (file X), screenshot of GitHub SSO settings (file Y), CSV export of MFA enforcement report from Okta (file Z)."
This kind of mapping will massively speed up the audit fieldwork, as you can hand this index to the auditor and they can find everything they need.
Conduct a Mock Audit (Optional but Recommended)
If time permits, consider doing an internal audit or third-party readiness review just before the real audit. This could be done by a consultant or even by someone on your team not directly involved in the process (for objectivity).
The idea is to simulate the audit: go through each control and have them verify the evidence and compliance, just like an auditor would. They might perform sample tests, such as checking a random user in your system to see if they indeed have the correct access level and corresponding documentation.
A "fresh eyes" review can catch issues that the core team might have overlooked due to familiarity. Any findings from this mock audit can be fixed in the nick of time. While this step may cost a bit (if using an external reviewer) or use internal hours, it often pays off by preventing costly delays or failures in the actual audit.
If you engaged your chosen auditor early, you might alternatively ask them to do a pre-audit workshop or walkthrough of your evidence. Some auditors will offer a readiness check (sometimes for an additional fee, sometimes as part of the service) where they look at your controls without officially judging them and give feedback. Take advantage of that if available. It's like getting hints before the test.
Final Administrative Items
As you complete final prep, double-check a few administrative items too:
- Is your "system description" document ready? (This is usually part of the SOC 2 report where you describe your company, scope, and controls in narrative form)
- Has management prepared a formal assertion letter stating that you believe you meet the SOC 2 criteria?
These are pieces the auditor will include in the report, and they often expect you to draft them. Your auditor can provide templates for both. Also, ensure that key staff will be available during the audit period to answer questions or provide any ad-hoc info the auditor requests.
At this stage, if you've diligently followed the checklist, you should feel audit-ready. All policies should be enacted, controls operating, and evidence neatly collected. Take a deep breath. You're about to cross the finish line.
10. What to Expect During Your SOC 2 Audit (And How to Maintain Compliance After)
With everything in place, it's time for the actual SOC 2 audit. This is where the independent auditor (CPA) will evaluate your controls and evidence, perform tests, and ultimately issue the SOC 2 report attesting to your compliance.
Kickoff and Documentation Review
The audit usually begins with a kickoff meeting where the auditor confirms the scope (systems, trust criteria, audit period) and requests all your documentation and evidence. Since you've prepared meticulously, you can hand over your organized evidence repository and mapping document.
The auditor will spend some time reviewing documentation first. They might ask clarifying questions about your system or request additional evidence if something is missing or unclear. Be responsive to these questions. A quick clarification or providing an extra screenshot can keep things moving smoothly.
Testing of Controls
For a Type I audit, the auditor is mainly checking that controls are designed and set up as of the audit date. They will likely inspect configurations, read policies, and perhaps interview personnel to verify design.
For a Type II audit, they will do more extensive testing. This can include sampling activities over the period. For example, they might select a random sample of helpdesk tickets to see if access removals were done when employees left, or sample days from log monitoring to see if any incidents were noted. They could interview team members to confirm that procedures were followed throughout the period.
Be prepared for the auditors to request things on the fly, like "Show me the user access list as of three months ago and as of today" or "demonstrate how you restore a backup." This is normal. It's how they verify operating effectiveness. Since you've been maintaining evidence and practicing drills, you should be able to comply with these requests.
Keep a cooperative attitude and provide whatever is needed (within reason) as promptly as possible.
Audit Duration
A SOC 2 audit can range from a couple of weeks to a couple of months in elapsed time. The Type II audit process often takes several weeks of evidence gathering and testing, especially if the audit period was six or more months long.
The auditors might do some work off-site, then come back with follow-up queries. Don't be alarmed if the process isn't continuous. Auditors often juggle multiple engagements. The key is to maintain communication. If they ask for something, clarify the deadline and deliverable. If an item will take time to gather, let them know you're working on it. It's also wise to schedule periodic check-ins (say twice a week) during the fieldwork to address any questions timely.
Issue Resolution
If the auditors find exceptions or issues (maybe one of your controls didn't operate perfectly during the period) you will have a chance to discuss it. If it's something you can quickly remediate, do so and provide evidence.
For example, if they find 1 out of 25 new hires didn't get security training within the expected timeframe, you might give a rationale or show that the person eventually did it and how you improved the process to avoid future slips. Auditors will note exceptions in their report if significant, but minor isolated incidents often don't derail an overall favorable opinion. The goal is no "material" exceptions.
Use your compliance team or consultant to advocate and explain context to the auditor if needed.
The SOC 2 Report
After testing, the auditor will compile the SOC 2 report. This includes your system description, the auditor's opinion letter (which states if your controls met the criteria, and for Type II if they were operating effectively over the period), and details of tests and any exceptions.
An unqualified opinion (no major exceptions) is what you want. It means you passed. Before finalizing, you typically get to review a draft for factual accuracy (ensuring your company name and system description are correct). Review it carefully.
Once finalized, congrats! You are now SOC 2 compliant. The report will be delivered to you and you can share it with clients under NDA as needed.
Maintaining Ongoing Compliance
At this point, you might be ready to celebrate, and you should. But remember: SOC 2 is an ongoing commitment, not a one-time checkbox. Your report is typically valid for 12 months.
To maintain compliance, you'll need to repeat the audit annually (for Type II, each audit covers the prior 6-12 months of activity, so they overlap if you want continuous coverage). That means the security controls and processes you set up must continue to operate consistently.
In other words, the best way to prepare for next year's audit is to never stop "being SOC 2 compliant" in the meantime.
Post-Audit Best Practices
→ Address any audit findings: If the auditor noted exceptions or recommendations in the report, fix those as soon as possible. This might mean tightening a process or improving documentation. Auditors will follow up on past issues in the next audit.
→ Continuous monitoring: Keep your logging, alerting, and compliance monitoring running all year. It's wise to use continuous compliance tools or dashboards (many companies use automation platforms or build internal checks) so that if something drifts out of compliance (say a new user is created without proper access review) you catch it and remediate immediately.
For instance, Comp AI continuously tracks your controls and alerts you to any compliance drift, ensuring you can fix issues well before the next audit.
→ Regular internal reviews: Conduct periodic internal audits or reviews of controls. Many organizations do a quarterly compliance review, checking that all access reviews, trainings, patch updates happened on schedule. This prevents any nasty surprises at year-end. It can be as simple as running through a mini checklist every quarter.
→ Stay up-to-date: Keep an eye on updates to SOC 2 criteria or guidance. The AICPA occasionally updates the Trust Services Criteria (for example, they added more emphasis on risk assessment and vendor monitoring in recent years). Also track changes in your own business (new systems, new office locations, significant growth) and evaluate if your scope or controls need to adjust accordingly. It's easier to incorporate changes as you go than to scramble right before an audit.
→ Use your SOC 2: Finally, make use of the effort you put in! Use your SOC 2 report as a selling point with customers. Many companies create a summary or trust portal where prospects can see your compliance credentials (some even use automated trust center tools that answer security questionnaires based on your controls).
Having SOC 2 can reduce those endless security questionnaires and speed up deal cycles. Internally, use the momentum to further improve security in areas that might not have been required by SOC 2 but are good practice (like expanding to ISO 27001 or other certifications if needed).
How Comp AI Accelerates Your SOC 2 Journey
By following this checklist and building compliance into regular operations, you'll find that future SOC 2 audits become easier and faster. Instead of a frantic annual project, it will be an expected routine, with many tasks automated or already handled as part of normal business.
In fact, companies that invest in compliance automation and continuous monitoring often report spending 75-90% less time on subsequent audits compared to that first heavy lift.
The Traditional Compliance Burden
Traditional compliance consulting is built around manual work that should be automated. Companies typically spend months preparing for SOC 2 audits, with:
- Manual evidence collection across dozens of systems
- Endless back-and-forth with consultants
- Last-minute scrambles before audit deadlines
- High consultant fees (often $15,000+ for Type I audits, compared to $5,000-10,000 with Comp AI)
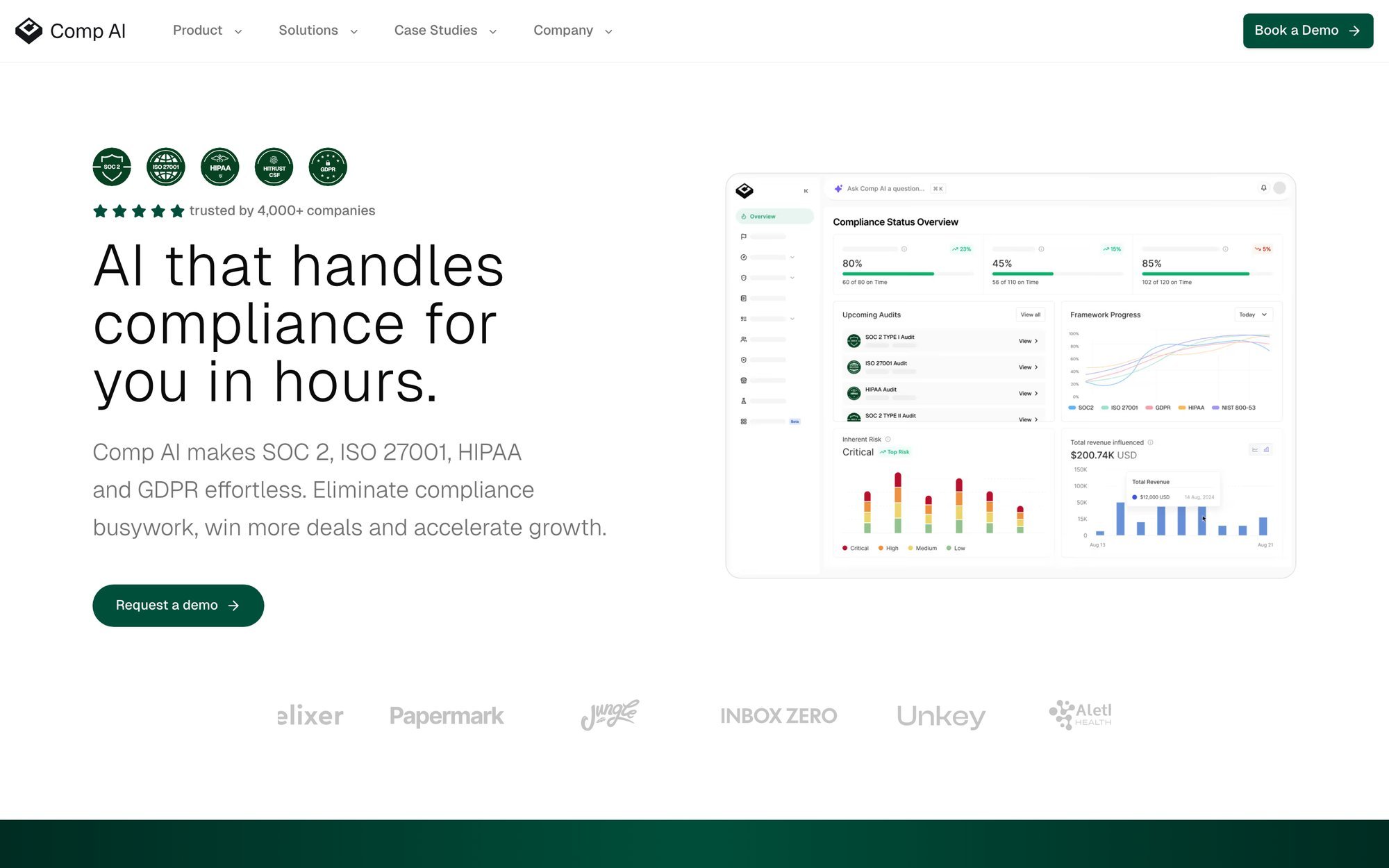
Comp AI's Automated Approach
Comp AI transforms this process through intelligent automation. The platform:
- Automatically collects evidence from 50+ integrated platforms
- Generates policies and documentation tailored to your tech stack
- Monitors controls continuously and alerts you to any drift
- Provides expert guidance when you need it
The result? You can achieve audit readiness in weeks instead of months, at a fraction of the cost:
| Cost Factor | Comp AI | Traditional Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| SOC 2 Type I | $5,000-10,000 | $15,000+ |
| SOC 2 Type II | $8,000-15,000 | $25,000+ |
| Time to Audit-Ready | 2-4 weeks | 3-6 months |
| Evidence Collection | 90%+ automated | Mostly manual |
With Comp AI, you're not just getting software. You're getting white-glove service combined with powerful automation. The platform handles the tedious work while security experts guide you through strategic decisions. Use our SOC 2 Cost Estimator and Timeline Calculator to see how fast you can get compliant.
Ready to accelerate your SOC 2 journey? Start with Comp AI and experience how compliance automation should work.
Frequently Asked Questions About SOC 2 Compliance
How long does it take to get SOC 2 compliant?
The timeline varies based on your starting point and whether you're pursuing Type I or Type II. With manual processes, most companies spend 3-6 months preparing for a Type I audit and 6-12 months for Type II (which requires an observation period). However, with compliance automation platforms like Comp AI, companies can become audit-ready in 2-4 weeks for Type I and complete the full Type II process in 4-6 months. Use our SOC 2 Timeline Calculator for a personalized estimate.
What's the difference between SOC 2 Type I and Type II?
SOC 2 Type I evaluates whether your controls are properly designed at a single point in time. Type II evaluates both the design and operating effectiveness of your controls over a period (typically 3-12 months). Type II provides stronger assurance because it proves your controls work consistently over time. Most enterprise customers ultimately expect Type II, though some companies start with Type I for faster initial compliance. For a detailed comparison, see our guide on SOC 2 Type 1 vs Type 2.
Do I need to be SOC 2 compliant to sell to enterprise customers?
While SOC 2 isn't legally required, it's become a de facto requirement for B2B SaaS companies selling to enterprise customers. Most security-conscious organizations require SOC 2 reports before signing contracts, and sales cycle delays can be significant without it. Some companies report losing deals entirely because they lack SOC 2 certification.
Can I get SOC 2 certified if I'm a small startup?
Yes. SOC 2 is designed to be flexible and scalable to organizations of different sizes. The key is setting up controls appropriate to your environment. Small startups can achieve SOC 2 compliance by using cloud infrastructure (which handles many physical security controls), setting up strong access controls, documenting policies, and using automation tools to handle evidence collection efficiently. Check out our SOC 2 Checklist for SaaS Startups.
How much does SOC 2 compliance cost?
Costs vary widely depending on your approach. Traditional consulting can run $15,000+ for Type I and $25,000+ for Type II, plus ongoing costs for consultants and manual processes. With Comp AI's automated platform, you're looking at $5,000-10,000 for Type I and $8,000-15,000 for Type II, with significantly reduced ongoing maintenance costs due to automation. Use our SOC 2 Cost Estimator for a personalized quote.
What happens if I fail a SOC 2 audit?
SOC 2 isn't technically pass/fail. The auditor issues a report that may include exceptions or findings where controls didn't meet expectations. Minor exceptions might not prevent you from receiving a report, but significant exceptions could result in a qualified opinion that reduces the report's value to customers. If major issues are found, you may need to remediate and extend the audit period before receiving a clean report.
Which Trust Services Criteria should I include in my SOC 2 audit?
Security is mandatory for all SOC 2 audits. The other four criteria (Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, Privacy) are optional and should be chosen based on your business model and customer expectations. Most SaaS companies include Security, Availability, and Confidentiality. If you handle particularly sensitive data or have specific regulatory requirements, you might add Privacy or Processing Integrity. Review our full SOC 2 Compliance Requirements guide.
How often do I need to renew my SOC 2 report?
SOC 2 reports are typically valid for 12 months. To maintain continuous compliance, most companies conduct annual audits. For Type II reports, each audit covers a 6-12 month observation period, so planning ahead ensures continuous coverage without gaps. Some companies time their audits to overlap slightly, ensuring they always have a current report available for customers.
Can I use my cloud provider's SOC 2 report instead of getting my own?
No. While you can (and should) reference your cloud provider's SOC 2 report as part of your vendor management, it only covers their infrastructure. You still need your own SOC 2 audit to attest to your application-level controls, policies, and procedures. However, using your cloud provider's physical security controls can significantly reduce your audit scope.
What's the difference between SOC 2 and ISO 27001?
SOC 2 is a reporting framework (you receive an attestation report from an auditor), while ISO 27001 is a certifiable standard (you can become ISO 27001 "certified"). SOC 2 is more common in North America, particularly for SaaS companies, while ISO 27001 is globally recognized. Many companies pursue both certifications as they serve different markets. The good news is that many controls overlap, so achieving one makes the other easier. Learn more about ISO 27001 certification requirements and the ISO 27001 certification process.
Conclusion: Making SOC 2 Compliance Achievable
Achieving SOC 2 compliance is a significant accomplishment. It demonstrates to your customers, partners, and stakeholders that you take data security seriously and have the internal controls to prove it. While the journey involves substantial effort, the trust and market access it unlocks make it well worth it.
By using the checklist above, you can approach SOC 2 in a systematic way, avoid common pitfalls, and get to the finish line with confidence. And remember, you don't have to do it all alone.
Modern platforms like Comp AI can automate a huge portion of the workload (evidence collection, control tracking, documentation), helping companies become audit-ready in weeks instead of months, at a fraction of traditional consulting costs.
Whether you go manual or automated, thorough preparation and a proactive mindset are your best assets. Good luck on your SOC 2 journey, and welcome to the club of security-conscious organizations.
Ready to start your SOC 2 compliance journey with expert guidance and powerful automation? Get started with Comp AI today and experience the fastest path to SOC 2 certification. Want to see how we compare to other solutions? Check out our alternative pages for Vanta, Drata, Scrut, and Delve.
Share this article
Help others discover this content
More from Compliance Hub
Explore more insights and stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
Cloud Security Compliance Guide for SaaS Teams (2025)
Complete guide to cloud security compliance for startups: 12 essential controls, framework comparisons, and a 30-day audit readiness roadmap.
NIST Compliance Guide : CSF 2.0, 800-171, 800-53 (2025)
Complete NIST compliance guide: CSF 2.0, 800-171, 800-53 explained. Implementation roadmaps, ready-to-use templates, and Comp AI automation.
CCPA Compliance Requirements: Complete Guide (2025)
Complete CCPA compliance guide for B2B SaaS: consumer rights handling, opt-out infrastructure, vendor contracts, and defensible documentation.