If you're running a SaaS company in 2025, you've probably heard both terms thrown around in sales calls, security questionnaires, and late-night compliance research sessions. SOC 2 keeps coming up when enterprise prospects ask about your security posture. GDPR surfaces the moment you have users in Europe (or even just visitors to your website from the EU).
These two frameworks seem unrelated at first glance. One's a voluntary audit standard from American accountants. The other's a legally binding regulation from the European Union. But they overlap just enough to cause confusion, and differ enough to create separate workloads for your team.
Getting the SOC 2 vs GDPR question wrong can mean lost deals on one side and hefty fines on the other. This guide breaks down exactly what each framework requires, where they intersect, and how you can tackle both without duplicating effort. By the end, you'll understand the "map once, comply twice" approach that lets fast-growing companies handle multiple frameworks efficiently.
What is the Difference Between SOC 2 and GDPR?
Here's what you need to know:
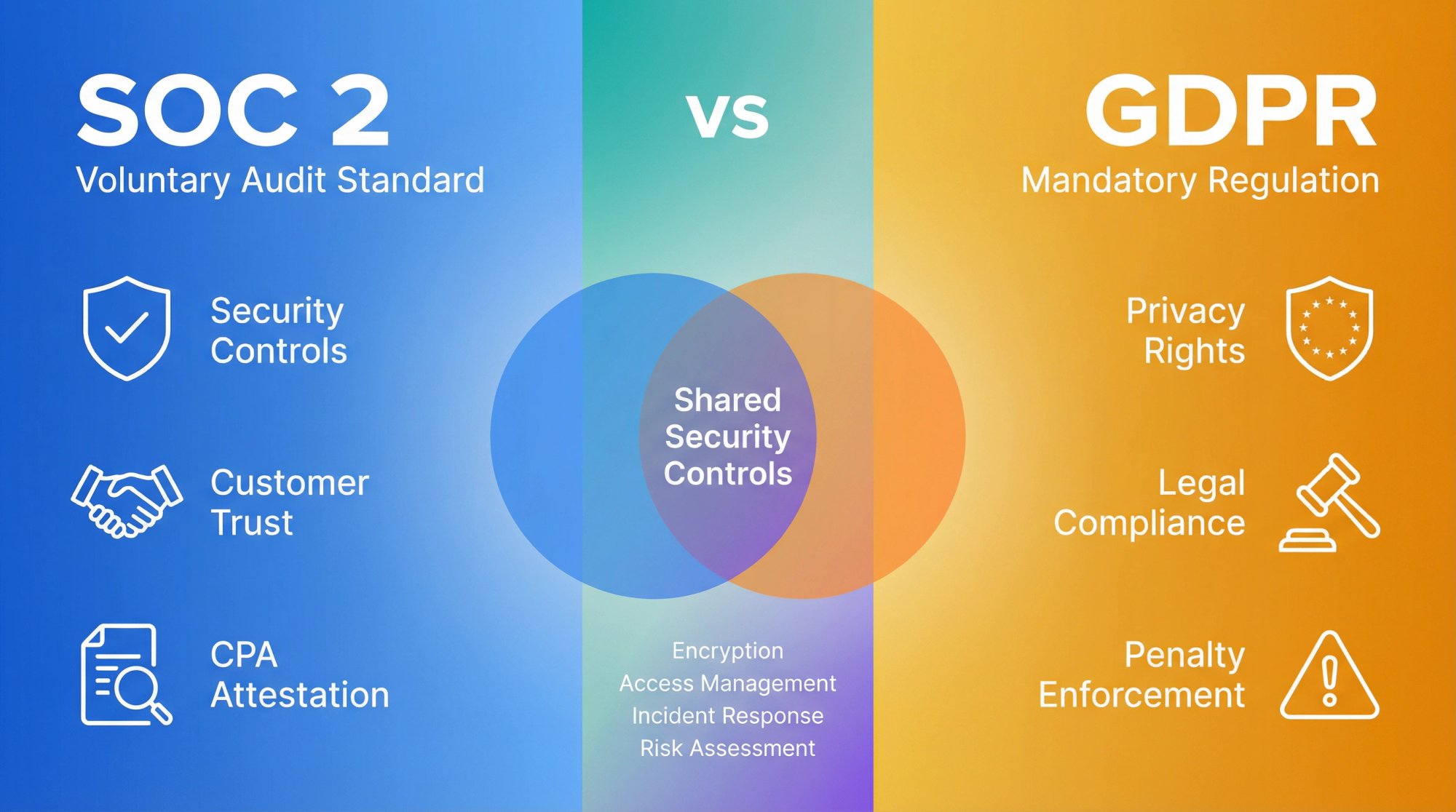
SOC 2 is a voluntary compliance framework (technically an audit report) that proves your organization's security controls meet the Trust Services Criteria. It's what enterprise customers demand before signing contracts with your SaaS company. Think of it as your ticket to B2B deals.
GDPR is a legally binding EU regulation on personal data protection. If you process any personal data from people in the EU (customers, users, even website visitors), you must comply. Violations can result in fines up to 20 million euros or 4% of your global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
The key insight? They're complementary, not mutually exclusive. Both require strong security measures like encryption, access controls, and incident response. A smart compliance strategy sets up shared controls once to satisfy both frameworks. Treating them as completely separate silos leads to duplicate work and inconsistent policies.
If you need both SOC 2 and GDPR (which is common for SaaS companies handling global data), don't build two separate programs. Unify your compliance effort by mapping overlapping requirements and using automation to collect evidence continuously. At Comp AI, we've built our platform specifically for this scenario, with pre-mapped controls for SOC 2, GDPR, and 25+ other frameworks so you can set up one set of security policies and cover multiple standards.
What is SOC 2 Compliance?
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) is a compliance reporting framework developed by the AICPA (American Institute of CPAs) that evaluates how well a service organization protects customer data. It's not a law or certification in the traditional sense. It's an independent audit that results in a formal report attesting that your company meets specified security criteria. For a detailed breakdown of what auditors look for, see our SOC 2 compliance requirements guide.
SOC 2 audits focus on five Trust Services Criteria:
- Security (mandatory for every SOC 2): Protection of information and systems against unauthorized access
- Availability: Systems are available for operation and use as committed
- Processing Integrity: System processing is complete, accurate, timely, and authorized
- Confidentiality: Information designated as confidential is protected as committed
- Privacy: Personal information is collected, used, retained, and disclosed in conformity with commitments
Security is always required. The others are optional depending on your services and what your customers need to see.
In practice, SOC 2 compliance means setting up robust internal controls and security policies, then having an accredited CPA firm audit those controls. If you pass, you get a SOC 2 report you can share with customers. It's become the standard for B2B SaaS and cloud companies to prove their data security.
Here's the catch: SOC 2 is technically voluntary. No regulator will fine you for not having it. But market expectations make it practically mandatory. Enterprise customers (especially in North America) won't do business with a vendor lacking a SOC 2 report. If you're selling to Fortune 500 companies, financial institutions, or healthcare organizations, the conversation usually stops right there without SOC 2.
Type I vs Type II: A quick distinction that matters. Type I is a point-in-time audit of control design (your controls are properly set up as of a specific date). Type II observes control effectiveness over a period of at least three months. Startups often get Type I first because it's faster, then progress to Type II. Most enterprise customers ultimately require Type II because it shows your controls actually work over time, not just that they exist on paper. Understanding the differences between SOC 2 Type 1 vs Type 2 helps you plan your compliance roadmap strategically.
What is GDPR Compliance?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It's the landmark data privacy law in the European Union that's been in effect since May 2018. GDPR governs how organizations worldwide collect, use, store, and transfer personal data of individuals in the EU and EEA.
Unlike SOC 2, GDPR is a law. If you handle personal data of EU residents (whether they're customers, users, or even just visitors to your website), GDPR applies to you regardless of where your company is based. A startup in San Francisco serving EU users must comply just like a company headquartered in Berlin.
GDPR enshrines several key principles:
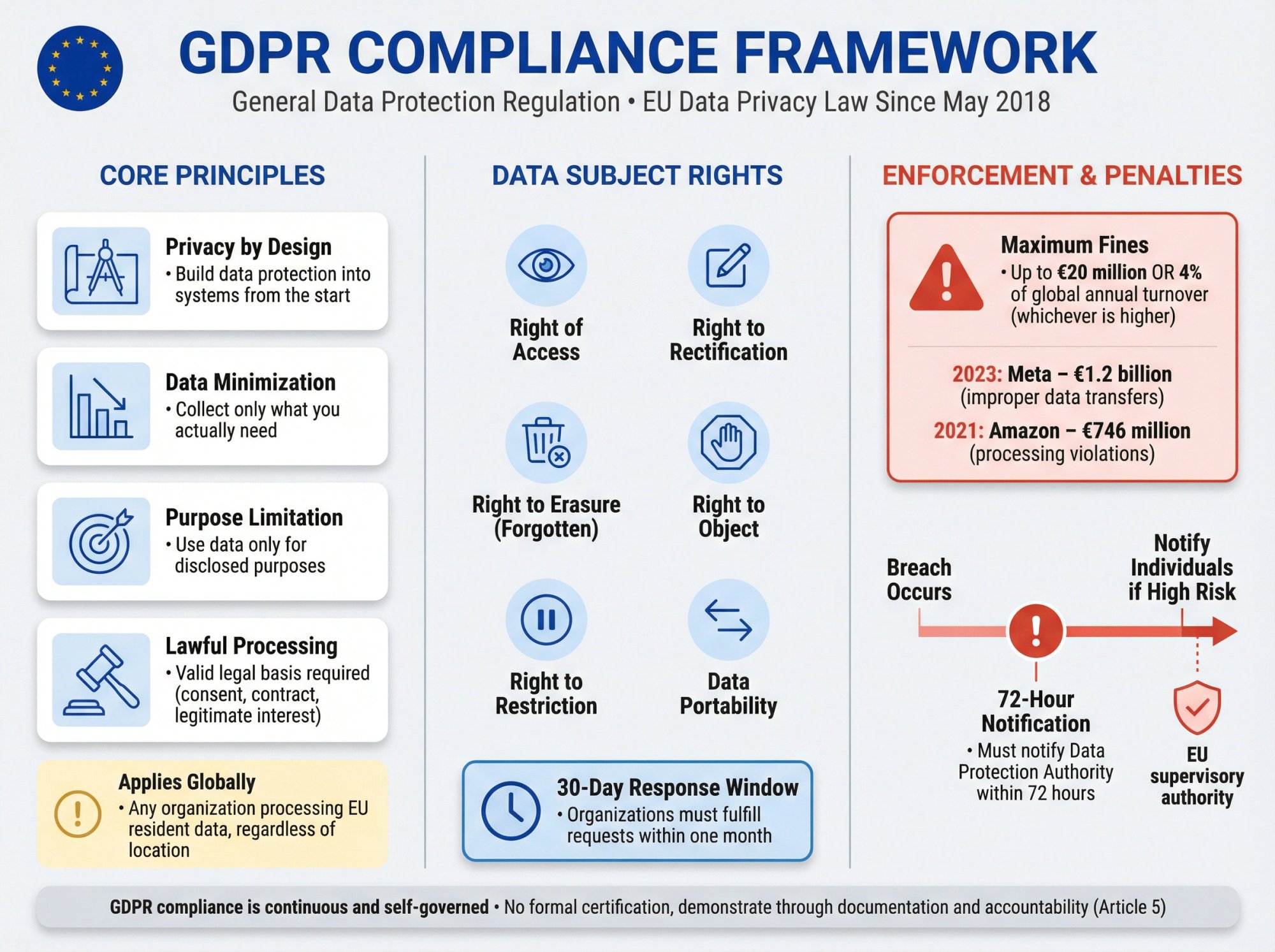
- Privacy by design: Build data protection into your systems from the start, not as an afterthought
- Data minimization: Collect only the personal data you actually need
- Purpose limitation: Use data only for the specific purposes you disclosed
- Lawful processing: Have a valid legal basis for processing personal data (consent, contract necessity, legitimate interest, etc.)
The regulation also grants individuals strong rights over their data. People can request access to see what data you have on them, correct inaccuracies, delete their data entirely (the "right to be forgotten"), withdraw consent, and port their data to another service. You must have processes to fulfill these requests, typically within 30 days.
The enforcement teeth are real. GDPR fines can reach up to 20 million euros or 4% of annual global turnover (whichever is higher) according to GDPR Article 83. These aren't theoretical threats. In 2023, Meta (Facebook) received a 1.2 billion euro fine for improper data transfers. Amazon was hit with a 746 million euro penalty in 2021. Smaller companies have faced fines too, often for seemingly basic violations like inadequate consent mechanisms or failing to notify breaches promptly.
One critical requirement: if a personal data breach occurs, you must notify the relevant Data Protection Authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of it. If the breach poses high risk to individuals, you must also notify them directly. This 72-hour window is strict, and failure to comply is itself a violation.
There's no "GDPR certification" to hang on your wall. Compliance is continuous and self-governed. You must maintain evidence (policies, records, assessments, Data Protection Impact Assessments) to demonstrate compliance if regulators investigate or customers ask questions.
How Do SOC 2 and GDPR Requirements Overlap?
Despite coming from different worlds (one from U.S. auditing standards, the other from EU regulation), SOC 2 and GDPR share fundamental principles when it comes to keeping data secure. Recognizing these overlaps can save your team significant effort.
Do SOC 2 and GDPR Both Require Risk Assessments?
Both frameworks are risk-based. Neither hands you a rigid checklist of specific controls. Instead, they expect you to set up measures appropriate to your specific risks. GDPR explicitly calls for measures "appropriate to the risk" considering the likelihood and severity of data breaches. SOC 2 likewise requires you to assess your threat landscape and apply controls accordingly.
What this means practically: a unified risk assessment can satisfy both. You evaluate risks to personal data (for GDPR) and risks to system security (for SOC 2) in the same exercise. There's no need for two separate risk management processes.
What Security Controls Satisfy Both SOC 2 and GDPR?
Security is baked in by default under both regimes. GDPR mandates "privacy and security by design and by default," meaning you should design systems with data protection in mind from day one. SOC 2's criteria similarly examine whether security is integrated into every layer of your operations. A compliance automation platform can help you embed security controls directly into your workflows rather than bolting them on after the fact.
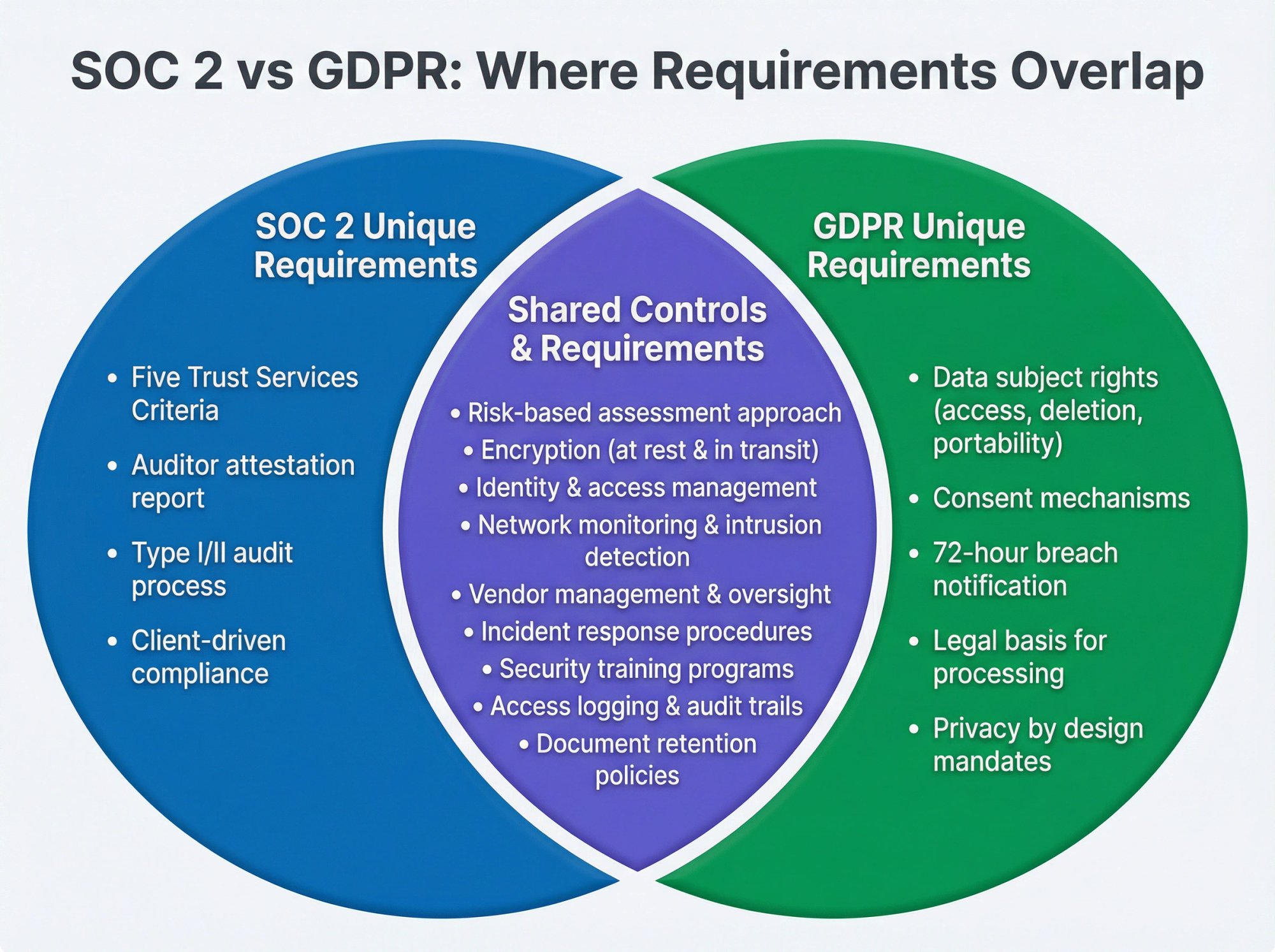
Common baseline controls like these satisfy both SOC 2 and GDPR:
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit
- Strong identity and access management (IAM)
- Network monitoring and intrusion detection
- Secure software development practices
- Endpoint protection
If you're encrypting databases, enforcing multi-factor authentication, logging activity, and hardening servers for your SOC 2 audit, you're also fulfilling GDPR's expectation for "appropriate technical measures" to protect personal data under Article 32.
How Do SOC 2 and GDPR Handle Third-Party Vendors?
Both frameworks care deeply about how you manage third-party risk. Under GDPR, whenever you use a data processor (a cloud vendor, SaaS sub-processor, etc.), you must vet them for security and sign Data Processing Agreements. You remain responsible for ensuring your vendors protect EU personal data.
SOC 2 audits evaluate your vendor management controls too: how you authorize and monitor service providers, ensure they meet your security requirements, and maintain oversight. One vendor risk management program covers both. Maintain an inventory of processors, assess their security (and get their SOC 2 reports), put proper contracts in place. Both frameworks give you credit for that single robust process.
What Do SOC 2 and GDPR Require for Incident Response?
When a security incident occurs, both frameworks require swift and systematic response. SOC 2's Security criteria ask whether you have incident response plans, conduct investigations, and take corrective actions. GDPR adds the legal requirement for breach notifications within 72 hours to regulators, and to affected individuals if there's high risk.
While SOC 2 doesn't impose a specific notification timeframe, your auditor will check that your incident response policy is sound and that serious incidents would be communicated appropriately. The overlap: have one solid incident response process. Include detecting incidents, preserving logs, analyzing impact, and communicating to stakeholders. You'll meet SOC 2 requirements and be prepared for GDPR's notification rules.
How Can Shared Documentation Satisfy Both Frameworks?
Both demand a "prove it" culture. You need to not only set up controls but also document and demonstrate compliance. GDPR's accountability principle (Article 5) means maintaining records, policies, and assessments to show a regulator how you comply at any time. SOC 2 audits hinge on evidence: auditors examine your policies, logs, screenshots, and tickets to verify controls are working.
The practical result: maintaining an access log serves both SOC 2 (proof of access control) and GDPR (demonstrating who accessed personal data). Both expect ongoing monitoring and periodic review, not a one-and-done effort. A unified evidence repository can feed your SOC 2 audit and satisfy GDPR regulators simultaneously. Using automated evidence collection tools eliminates the manual burden of gathering this documentation for both frameworks.
Make the overlap work for you. Perform one risk assessment covering both. Set up shared controls that fulfill both sets of requirements. Maintain one set of evidence and documentation. You avoid reinventing the wheel and run a leaner compliance program.
SOC 2 vs GDPR: What Are the Key Differences?
While the overlaps are significant, SOC 2 and GDPR diverge in important ways. Understanding these differences ensures no requirements fall through the cracks.

Is SOC 2 Voluntary or Mandatory Compared to GDPR?
SOC 2 is voluntary. It's a compliance framework and auditing procedure that organizations choose to undergo, typically to meet customer or market demands.
GDPR is mandatory law. It's a regulation enacted by the EU that organizations must obey if it applies to them.
Put simply: SOC 2 is customer-driven trust, GDPR is regulator-driven legal obligation.
What Happens if You Fail SOC 2 vs GDPR Compliance?
Failing SOC 2 (or not having it) isn't illegal. The risk is commercial. You might lose sales, fail security questionnaires, or fall behind competitors that have a SOC 2 report. There's no "SOC 2 police" issuing fines.
Failing GDPR is a legal violation. Regulators can investigate and impose fines, sanctions, or even ban you from processing data. The penalties are substantial: up to 4% of global revenue or 20 million euros. Amazon's 746 million euro fine and Meta's 1.2 billion euro fine show these aren't empty threats.
SOC 2 enforcement happens through the market (lost contracts). GDPR enforcement happens through supervisory authorities (formal penalties). Understanding the SOC 2 cost breakdown helps you budget appropriately for compliance while recognizing that GDPR non-compliance carries far steeper financial penalties.
Which Companies Need SOC 2 vs GDPR Compliance?
SOC 2 primarily applies to B2B technology service companies: SaaS providers, cloud hosts, fintech platforms, and similar organizations handling sensitive customer data. It's commonly needed for U.S. enterprise sales but isn't tied to any specific region or user citizenship.
GDPR applies to any organization (any industry, any size, anywhere in the world) that processes personal data of people in the EU. This includes consumer apps, e-commerce stores, hospitals, and B2B SaaS alike. A brick-and-mortar retailer with EU customers falls under GDPR, even if they'd never need SOC 2.
How Does SOC 2 Focus Differ from GDPR Focus?
SOC 2's focus is on internal controls and security processes. It asks: Do you have proper controls to secure data and systems? Are they documented and effective? It's very much an operations and IT security examination.
GDPR's focus is on personal data and individual privacy rights. It asks: Do you have a legitimate basis to collect personal data? Are you respecting user consent and rights? Are you limiting data collection to what's necessary?
GDPR cares about why and how you collect data, not just whether it's stored securely. You could have excellent security and still violate GDPR if you're collecting personal information without proper consent or keeping it longer than needed. SOC 2 wouldn't flag that issue because it doesn't mandate the legal basis for data collection.
Does SOC 2 Cover Data Subject Rights Like GDPR?
This is one of the starkest differences.
GDPR grants enforceable rights to individuals over their personal data. You must allow people to access their data, correct inaccuracies, delete their data on request, and easily withdraw consent. Features like GDPR consent forms, privacy preference centers, and Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) workflows are required.
SOC 2 has no concept of user consent or data subject rights. SOC 2's optional Privacy criterion checks that you disclose what data you collect and have a mechanism to address inquiries, but it doesn't mandate giving users rights to delete or export their data.
This means achieving SOC 2 alone doesn't make you GDPR compliant. You could have great security controls and still face GDPR fines for ignoring user rights or collecting data without lawful basis.
How Do Breach Notification Rules Differ?
Both frameworks expect incident response, but only GDPR imposes a strict notification timeline. Under GDPR, you have 72 hours to report a personal data breach to the Data Protection Authority (unless it's unlikely to pose risk), and you may need to notify affected individuals if there's high risk.
SOC 2 has no such notification rule. It requires you to have a process to handle incidents, but you won't "fail" SOC 2 for not telling a regulator about a breach within 72 hours. Your GDPR incident response plan must include regulatory notification steps that your SOC 2 plan may not require.
SOC 2 vs GDPR Comparison Table
| Aspect | SOC 2 | GDPR |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Framework | Voluntary audit standard (CPA attestation report) | Legally mandated regulation (EU law) |
| Geographic Scope | Not tied to region (originated in U.S., now global for cloud/SaaS) | European Union (applies globally to orgs processing EU resident data) |
| Primary Focus | Internal security controls and system reliability | Personal data privacy and individual rights |
| Applicable To | Service organizations (B2B SaaS, cloud, fintech). Client-driven. | Any organization processing EU personal data (B2B or B2C, any sector). Regulatory-driven. |
| Compliance Mechanism | Annual audit by independent CPA firm, results in SOC 2 report (Type I or II) | Continuous self-managed compliance. No formal certificate, demonstrate through documentation. |
| Enforcement | Market enforcement: loss of business and trust, no legal penalties | Legal enforcement: regulators investigate, issue orders, levy fines |
| Penalties | No direct fines. Biggest "penalty" is losing enterprise contracts. | Fines up to 20 million euros or 4% of global annual turnover |
| Security Requirements | Broad, based on Trust Services Criteria: access controls, network security, monitoring, incident management | "Appropriate technical and organizational measures" (Article 32): encryption, access control, resilience |
| Privacy and Data Use | Does not dictate how you collect/use personal data. Privacy criterion optional. | Core focus: need legal basis, collect minimum necessary, privacy by design/default (Article 25) |
| Individual Rights | Not addressed. No requirement to provide data access, deletion, or correction to individuals. | Mandated: Right of access, rectification, erasure, objection, restriction, data portability |
| Breach Notification | No formal requirement or timeframe. Expected to have incident response plan. | Mandatory: Notify supervisory authority within 72 hours, notify individuals if high risk |
| Proof of Compliance | SOC 2 report from auditor serves as proof. Maintain evidence for auditor review. | Documentation: records of processing (Article 30), DPIAs, consents, training records. Audit-ready at all times. |
Bottom line: If you're in scope for GDPR, SOC 2 alone is not enough. You could pass a SOC 2 audit yet still face GDPR fines for unlawful data collection. Conversely, you could be GDPR compliant in terms of privacy law but fail a SOC 2 audit if your security controls are weak. Each framework plugs a different gap: SOC 2 gives assurance to business customers, GDPR ensures compliance with privacy law.

Do You Need Both SOC 2 and GDPR Compliance?
For many SaaS and tech companies operating internationally, it's not SOC 2 or GDPR. You likely need both. Here's when each becomes necessary:
You handle personal data of EU residents. This is the trigger for GDPR. If you have any users, customers, or end-users in the EU (or UK, which maintains similar requirements), GDPR compliance is mandatory regardless of where your company is headquartered. This could be as simple as an EU citizen signing up for your app or storing EU employee data in your HR system. In today's connected world, even early-stage startups often have some EU data.
You sell to enterprise or B2B customers. If your sales pipeline involves businesses, someone will eventually ask for your SOC 2 report. It's become a de facto requirement for enterprise B2B deals. Security questionnaires and RFP checklists routinely include SOC 2 as a checkbox item. Many larger companies (financial institutions, Fortune 500s, healthcare organizations) won't sign a contract or integrate with your systems unless you have SOC 2 Type II or are actively working toward it. If you're unsure where to start, our guide on how to get SOC 2 certification walks through the process step by step.
You use cloud infrastructure and process customer data. Both SOC 2 and GDPR scrutinize cloud and data infrastructure. If you're a SaaS company using AWS, GCP, or Azure and storing customer data, SOC 2 audits your cloud security configurations while GDPR requires that personal data in the cloud is protected and that your cloud providers have proper agreements in place. A SaaS delivering services via the cloud sits squarely in the intersection of both.

You plan to expand to new markets or industries. Compliance requirements become gateways. GDPR is the price of admission to European markets since EU customers and partners will insist you comply. SOC 2 (or ISO 27001) is often needed to enter sectors like finance, healthcare, or enterprise technology. If you're evaluating multiple frameworks, understanding the comparison between ISO 27001 vs SOC 2 can help you prioritize based on your target markets. Instead of asking "one or the other?", recognize that as you grow, both become essential to avoid roadblocks.
You want to minimize both legal and business risk. SOC 2 mitigates the risk of security failures eroding customer trust or causing data breaches. GDPR mitigates the risk of legal non-compliance and penalties. Ignoring either leaves a flank unprotected. A data breach without SOC 2-level controls could be catastrophic (and likely also a GDPR violation). A lack of GDPR compliance could mean a well-secured company still faces fines or orders to stop processing data.
In summary, SaaS and tech companies with global reach almost always need both. SOC 2 is about earning trust through security assurance. GDPR is about meeting legal obligations to protect individuals' privacy. If you check the typical profile (cloud-based, data-heavy, international ambition), pursuing both isn't just best practice. It's a strategic imperative.
How to Comply with Both SOC 2 and GDPR Efficiently
Managing two major frameworks can feel overwhelming if you approach them separately. The key to efficiency is smart control mapping: identifying where one control or process fulfills requirements for both SOC 2 and GDPR, then using automation to manage those controls centrally.
How Do Shared Controls Eliminate Redundant Work?
Start by listing controls and tasks required by each framework, then find the overlaps. You'll discover substantial common ground: encryption, endpoint security, access management, incident response, vendor assessments, employee training. Do them once, use for both.
For example, you don't need two separate encryption implementations. One encryption-at-rest setup satisfies SOC 2's Confidentiality criterion and GDPR's Article 32 requirements. Instead of parallel compliance projects, create a master control set and map each control to the frameworks it covers. Set up one control to meet many requirements. It reduces operational drag and ensures consistency.
What is a Common Control Framework for SOC 2 and GDPR?
A Common Control Framework (CCF) is a centralized set of controls cross-mapped to multiple standards. Define a control like "All company laptops are encrypted and have device management," then map it to SOC 2 (Security criterion) and GDPR (encryption as an expected measure) automatically.
By using a CCF, you avoid maintaining separate spreadsheets for each framework. Changes to a control (like improving password policy) get reflected in all mappings. This one-to-many mapping ensures you don't miss applying a control to one framework, and it highlights any requirement not yet met. The result: you manage, test, and update one set of controls that keeps you compliant with both SOC 2 and GDPR.
How Does Automated Evidence Collection Help with Both?
Collecting evidence is one of the most time-consuming parts of compliance: screenshots, logs, policy documents, training records. Doing this separately for SOC 2 and GDPR would be exhausting and unnecessary.
Instead, use automation tools that continuously collect evidence once and map it to any framework. Connect to your cloud provider to pull config snapshots, link to your HR system for training completion records, integrate with your identity provider for access logs. Tag those evidence pieces as satisfying SOC 2 control X and GDPR requirement Y. Automation ensures you're not scrambling to gather the same information twice and reduces errors since evidence is captured in real-time.
When audit time comes or you need to demonstrate GDPR compliance, you have a central evidence vault already mapped to each requirement. A single log extract might show user access reviews (for SOC 2) and also act as proof of access governance for GDPR's accountability principle.
Why Should You Use a Unified Compliance Dashboard?
Rather than tracking SOC 2 controls in one spreadsheet and GDPR activities in another, consolidate your monitoring. A unified compliance dashboard tracks the status of all controls and obligations continuously. If a control drifts out of compliance (say, an S3 bucket becomes public), the system flags it. That single alert is relevant to both SOC 2 and GDPR since it's a security issue affecting both.
This lets your team respond to issues before they escalate into audit findings or GDPR incidents. Continuous monitoring might catch that an employee account wasn't deactivated when they left (a SOC 2 access control violation and a GDPR risk). Fix it once, close the gap for both frameworks.
How Do You Scale to Multiple Compliance Frameworks?
By mapping and automating in this unified way, adding frameworks becomes much easier. Many companies start with SOC 2 and GDPR, then later need ISO 27001, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. If you've done the groundwork to harmonize controls for two, extending to a third or fourth is less painful because you already have a strong core of security and privacy controls. You can explore additional resources in our compliance hub to prepare for future framework requirements.
Think of SOC 2 and GDPR as the impetus to build a scalable compliance foundation that can absorb new requirements with minimal rework. This "build once, comply with many" philosophy is how fast-growing companies handle compliance without a massive team.
How Comp AI Streamlines SOC 2 and GDPR Compliance
Getting SOC 2 and GDPR done in parallel might sound daunting, but the right approach and tools make it achievable. The goal is to reduce duplication, map overlapping requirements, and automate wherever possible. This is exactly what we built Comp AI to do: a unified compliance automation platform that enables startups and enterprises to handle multi-framework compliance efficiently.
Comp AI takes the pain out of managing SOC 2 and GDPR together by providing a single, intelligent solution for both. Here's how we help you streamline compliance:
All-in-One Compliance Hub
Comp AI comes with out-of-the-box support for 25+ leading frameworks, including SOC 2, GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and more. You can instantly launch compliance programs for SOC 2 and GDPR without building everything from scratch. Our platform includes auditor-grade policy templates, controls, and guidance tailored to each framework. From day one, you have a roadmap for both SOC 2 and GDPR requirements in one place.
Pre-Mapped Controls
Our platform features pre-mapped common controls that link SOC 2 criteria with corresponding GDPR requirements. Comp AI knows that your access control policy and MFA setup address both SOC 2 Security and GDPR Article 32, or that your vendor management process maps to SOC 2 CC9 and GDPR's processor due diligence. You don't have to manually map which control covers what. We intelligently link overlapping controls across frameworks.
The benefit: you set up a control one time in Comp AI and it automatically applies and tracks for all relevant standards. Nothing falls through the cracks, and you eliminate duplicative work.
Automated Evidence Collection and Continuous Monitoring
Comp AI uses AI agents to continuously monitor your compliance posture and collect evidence across your tech stack, 24/7. We integrate with 100+ systems (cloud providers, code repos, HR systems, identity providers, and more) to auto-gather audit evidence and check configurations. All evidence is stored in a centralized repository and mapped to respective SOC 2 and GDPR controls.
Whether it's a SOC 2 auditor or a GDPR regulator inquiry, you can pull up real-time evidence of compliance in seconds. We also send alerts before issues become problems. If an S3 bucket becomes public or an employee fails to complete security training, Comp AI flags it so you can fix it before it leads to a compliance failure.
Unified Audit and Privacy Documentation
Comp AI provides audit-ready dashboards and reports that cover both frameworks. All your policies, risk assessments, and control evidence are organized in one portal. When it's time for your SOC 2 audit, you can grant your auditor access to our workspace where they'll find all evidence neatly mapped to each Trust Services Criterion.
Similarly, if you need to demonstrate GDPR compliance to a client or as part of a Data Protection Impact Assessment, you have the necessary records (Article 30 processing records, consent logs, etc.) available. The platform acts as a single source of truth for compliance, simplifying responses to both auditors and regulators.
Expert Support When You Need It
Beyond technology, Comp AI offers one-on-one support from compliance experts via Slack with rapid response times. Our team includes experienced SOC 2 auditors and GDPR consultants who can answer questions like "Does this control meet GDPR Article 25?" or "How do I handle this auditor request?" in minutes.
We guide you through tricky edge cases: how to handle a Data Subject Access Request in a way that satisfies GDPR yet doesn't compromise security, or how to scope your SOC 2 audit to include your GDPR-relevant systems. With Comp AI, you get advanced automation and personalized guidance when you need it.
Fast-Track to Compliance
Thanks to automation and pre-built mappings, Comp AI dramatically reduces the time to achieve compliance. Companies have gotten SOC 2 Type I audit-ready in days rather than the typical three to six months. One startup was only 30% through SOC 2 after four months using a traditional approach. After switching to Comp AI, they were audit-ready in a couple of days, all while maintaining GDPR-aligned practices throughout.
We also connect you with pre-vetted auditors familiar with our platform to further speed up the SOC 2 audit and ensure it covers any GDPR-related scope appropriately.
Pricing comparison: Traditional compliance approaches (consultants plus manual processes) can run $30,000 to $100,000+ for SOC 2 alone. Add GDPR consulting and the costs climb further.
Price with Comp AI: Starting around $8,000 for full SOC 2 and GDPR coverage
Price with traditional approaches: $30,000-$100,000+
You get expert support, AI-powered automation, and multi-framework coverage at a fraction of the cost.
SOC 2 vs GDPR: Frequently Asked Questions
Is SOC 2 Compliance Enough to Satisfy GDPR?
No. SOC 2 and GDPR address different areas. SOC 2 verifies your organization has strong security controls, but GDPR includes many legal and privacy obligations that SOC 2 doesn't cover. These include obtaining consent, honoring individual data deletion requests, and restricting data use to specific purposes.
You could pass a SOC 2 audit yet still violate GDPR (for example, if you collect personal data without proper consent or fail to notify a breach within 72 hours). Think of SOC 2 as proving security, and GDPR as requiring privacy and lawfulness. The security measures you set up for SOC 2 (encryption, access controls) will definitely help with GDPR compliance as part of "appropriate security measures," but SOC 2 alone won't protect you from GDPR fines.
Which is Mandatory: SOC 2 or GDPR?
GDPR is mandatory by law whenever it applies (meaning you process personal data of EU residents). Compliance isn't optional and is enforced by government authorities with penalties.
SOC 2 is voluntary from a legal standpoint, but it's often mandatory in practice due to customer and market expectations. You won't face regulatory fines for lacking SOC 2, but you might lose business opportunities. Many companies treat SOC 2 as a must-have because without it they can't sign enterprise deals.
Legally speaking: GDPR is compulsory. SOC 2 is contractually or commercially compelled.
Do SOC 2 Controls Help with GDPR Compliance?
Yes, there's significant overlap. Many SOC 2 controls (especially those under the Security Trust Services Criteria) directly support GDPR's requirements for protecting personal data under Article 32.
For example, a control like "All customer data is encrypted at rest with AES-256 and in transit via TLS 1.2+" satisfies both SOC 2 auditors and GDPR expectations. "Quarterly user access reviews conducted to ensure least privilege" aligns with GDPR's principle of data protection by design.
Most SOC 2 security controls can be used for GDPR, but you'll have some extra GDPR-specific requirements to add: legal procedures, consent management, and data subject rights workflows that SOC 2 doesn't address.
How Long Does It Take to Achieve SOC 2 and GDPR Compliance?
With traditional approaches using consultants and manual processes, SOC 2 typically takes three to six months for the initial audit. GDPR compliance can take similar timeframes to set up properly.
With automation platforms like Comp AI, companies have achieved SOC 2 audit-readiness in days to weeks rather than months. Because our platform handles both frameworks with pre-mapped controls, you can work toward SOC 2 attestation and bolster GDPR compliance simultaneously in a fraction of the traditional timeframe.
Can One Platform Handle Both SOC 2 and GDPR?
Yes, and that's exactly the approach we recommend. Comp AI supports 25+ frameworks including both SOC 2 and GDPR with pre-mapped controls that link overlapping requirements. Instead of managing separate compliance programs, you set up unified controls that satisfy both frameworks.
This "map once, comply twice" approach eliminates duplicate effort, maintains consistency across frameworks, and makes adding future frameworks (like ISO 27001 or HIPAA) much easier since you've already built a strong foundation.
SOC 2 and GDPR may come from different worlds, but they share the same goal: ensuring you protect sensitive data properly. The smartest approach isn't treating them as separate burdens. It's building a unified compliance program that addresses both through shared controls, automated evidence collection, and continuous monitoring.
If you're ready to tackle SOC 2 and GDPR without the typical headaches, Comp AI can help you map once and comply with both frameworks efficiently. Our platform and team are built specifically for fast-growing companies that can't afford to spend months on compliance or hire large internal teams. Book a demo to see how you can get audit-ready faster than you thought possible.
Share this article
Help others discover this content