Building a startup is hard enough without regulatory requirements slowing you down. The reality is clear: compliance isn't optional anymore. Enterprise customers, investors, and partners increasingly demand proof that you take security seriously before signing deals.
The good news? The right compliance automation platform can transform compliance from a months-long resource drain into a streamlined process that takes days, not months.
This guide breaks down every component of a modern compliance tech stack, helping you understand what tools you actually need and how they work together to get you audit-ready fast.

Why Do Startups Need a Compliance Tech Stack?
Before diving into specific tools, let's address the fundamental question: why invest in compliance infrastructure now?
How Compliance Certifications Drive Enterprise Revenue
Enterprise deals increasingly require compliance certifications. According to industry research, 60% of organizations will use cybersecurity risk as a primary determinant in conducting third-party transactions and business engagements by 2025.
This means a missing SOC 2 report or HIPAA certification can directly block revenue:
- Enterprise prospects often require SOC 2 Type II before procurement will approve vendors
- Healthcare customers mandate HIPAA compliance before any contract discussions
- European expansion requires GDPR compliance as a baseline
- Government contracts demand FedRAMP or StateRAMP certifications
The cost of delaying compliance isn't just the certification expense. It's the deals you lose while waiting. One startup reported losing access to over $500,000 in annual recurring revenue simply because they couldn't produce a SOC 2 report fast enough.
How Fast Can You Get Compliant With Automation?
Traditional compliance approaches take 6-12 months and consume significant engineering resources. Modern compliance tech stacks compress this timeline dramatically through automation. Understanding how long SOC 2 compliance takes helps you plan accordingly.
With the right tools, you can achieve:
→ SOC 2 Type I readiness in as little as 24 hours
→ Full Type II completion within 3-4 months (the minimum required observation period)
→ HIPAA readiness in under 7 days
→ ISO 27001 certification in as little as 14 days
This speed difference isn't just about convenience. It's about competitive advantage.
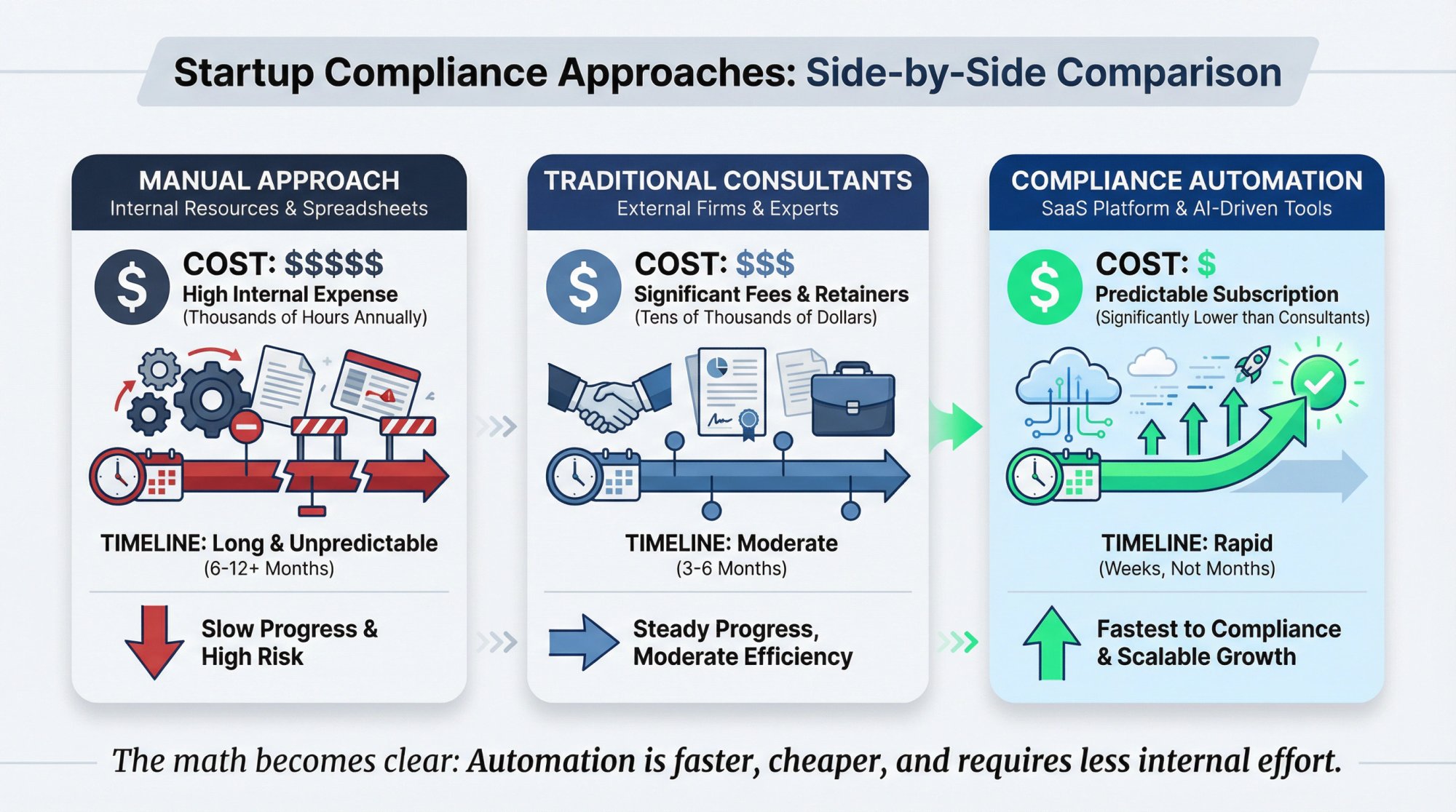
What Does Compliance Automation Cost vs Manual Processes?
Consider the alternative to automation:
| Approach | Cost | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Manual approach | 300-500+ hours of internal effort across engineering, legal, and operations teams | 6-12 months |
| Traditional consultants | $50,000-$150,000 in fees | 6-12 months + your team's time |
| Compliance automation | Under $15,000 annually | Days to weeks with minimal internal time |
The math becomes obvious when you factor in opportunity cost. Every hour your engineers spend on compliance documentation is an hour not spent building product features. Use a to understand your specific investment.
What Are the Core Components of a Compliance Tech Stack?
A comprehensive compliance tech stack consists of interconnected tools that handle different aspects of your security and compliance program. Here's how they fit together:
What Is a GRC Platform and Why Do You Need One?
What it does: Serves as the central hub for your entire compliance program, managing frameworks, controls, evidence, and audit workflows.
Key capabilities:
- Framework management (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)
- Control mapping across multiple frameworks
- Evidence collection and organization
- Audit preparation and management
- Compliance dashboard and reporting
Why it matters: Without a central GRC platform, you're managing compliance in spreadsheets and shared drives. This creates inconsistency, increases audit risk, and makes scaling to multiple frameworks nearly impossible.
Modern GRC platforms like Comp AI go beyond basic organization. We use AI to automate evidence collection, generate policies, and guide you through the compliance process step by step.
What to look for:
- Multi-framework support (you'll likely need more than one certification eventually)
- Integration depth with your existing tools
- Automation capabilities for evidence gathering
- Clear audit preparation workflows
- Responsive support when you have questions
How Does Identity and Access Management (IAM) Support Compliance?
What it does: Controls who has access to what within your organization and provides the audit trail to prove it.
Key capabilities:
- Single sign-on (SSO) for centralized authentication
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enforcement
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Automated user provisioning and deprovisioning
- Access review and certification workflows
Why it matters: Access control is fundamental to every compliance framework. Auditors will scrutinize how you manage user access, especially for sensitive systems and data.
The key requirement is demonstrating that:
- Only authorized users have access to systems
- Access is granted based on job function (least privilege)
- Access is removed promptly when employees leave
- You can prove all of the above with documentation
Having a strong access control policy is essential for any compliance program.
Popular options:
- Okta: Industry standard for enterprise SSO and identity management
- Google Workspace / Microsoft Entra ID: Built-in identity management for organizations already using these platforms
- JumpCloud: Good option for smaller teams needing directory, SSO, and device management in one
- Auth0: Developer-focused identity platform for application authentication
Integration tip: Make sure your IAM solution integrates with your GRC platform. This allows automated evidence collection of access reviews, MFA status, and user provisioning events.
Which Endpoint Management Tools Meet Compliance Requirements?
What it does: Manages and secures all devices (laptops, phones, tablets) that access company data.
Key capabilities:
- Device enrollment and inventory
- Security policy enforcement (encryption, passwords, screen lock)
- Patch management and software updates
- Remote wipe capability for lost or stolen devices
- Compliance status monitoring
Why it matters: Auditors want to see that you control the devices accessing your data. Unmanaged devices represent significant security and compliance risk.
At minimum, you need to demonstrate:
- All devices are encrypted
- Automatic screen lock is enabled
- Operating systems are kept updated
- You can remotely wipe devices if needed
- You know what devices exist in your environment
A comprehensive endpoint security policy documents these requirements.
Popular options:
- Jamf: Best-in-class for Apple device management
- Microsoft Intune: Strong choice for Windows-heavy environments
- Kandji: Apple-focused MDM with strong security features
- Mosyle: Cost-effective Apple MDM option
- Fleet: Open-source device management using osquery
Key consideration: Choose an MDM that matches your device mix. Forcing a Windows-focused tool on a Mac-first startup (or vice versa) creates friction and gaps.
What Is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
What it does: Monitors your cloud infrastructure for security misconfigurations and compliance violations.
Key capabilities:
- Continuous security assessment of cloud resources
- Misconfiguration detection and alerting
- Compliance benchmarking (CIS, SOC 2, etc.)
- Infrastructure-as-code scanning
- Remediation guidance and automation
Why it matters: Cloud misconfigurations are responsible for a significant portion of data breaches. Auditors will examine your cloud security posture closely.
For startups running on AWS, GCP, or Azure, a CSPM tool can automatically detect issues like:
- Publicly accessible storage buckets
- Overly permissive security groups
- Unencrypted databases
- Missing logging and monitoring
- Root account usage without MFA
Popular options:
- AWS Security Hub / Azure Security Center / Google Security Command Center: Native tools for single-cloud environments
- Wiz: Comprehensive cloud security platform
- Lacework: Cloud security with behavioral analysis
- Orca Security: Agentless cloud security scanning
- Prowler: Open-source AWS security assessment
Integration tip: Your CSPM should feed findings into your GRC platform. This creates an audit trail showing you identified and remediated security issues proactively.
How Do You Build a Vulnerability Management Program?
What it does: Identifies and tracks security vulnerabilities across your infrastructure and applications.
Key capabilities:
- Network vulnerability scanning
- Web application security testing
- Container and Kubernetes scanning
- Dependency and library scanning
- Vulnerability prioritization and tracking
Why it matters: Every major compliance framework requires you to identify and address vulnerabilities. You need a systematic approach with documentation.
The compliance requirements typically include:
- Regular vulnerability scanning (often quarterly minimum)
- Risk-based prioritization of findings
- Documented remediation timelines
- Evidence of vulnerability closure
A robust vulnerability management policy ensures you meet these requirements consistently.
Popular options:
- Qualys: Enterprise-grade vulnerability management
- Tenable / Nessus: Comprehensive scanning capabilities
- Rapid7 InsightVM: Vulnerability management with remediation guidance
- Snyk: Developer-focused application security
- Trivy: Open-source container and dependency scanning
- Dependabot: GitHub-native dependency vulnerability alerts
Pro TipIntegrate vulnerability scanning into your CI/CD pipeline. This catches issues before they reach production and demonstrates proactive security to auditors.
What SIEM and Log Management Tools Do Startups Need?
What it does: Aggregates, analyzes, and retains security logs from across your environment.
Key capabilities:
- Centralized log collection and storage
- Security event correlation and alerting
- Threat detection and investigation
- Log retention for compliance requirements
- Audit trail and forensic capabilities
Why it matters: Auditors will ask for evidence of security monitoring and logging. You need to demonstrate you can detect and investigate security incidents.
Key compliance considerations:
- Log retention periods (often 90 days to 1 year depending on framework)
- What events are being logged (authentication, access, changes, etc.)
- How you detect and respond to anomalies
- Tamper-evident log storage
Your logging and monitoring policy should address all these requirements.
Popular options:
- Datadog: Unified monitoring and security platform popular with startups
- Splunk: Enterprise-grade SIEM with extensive capabilities
- Elastic SIEM: Open-source based security analytics
- Panther: Cloud-native SIEM built for security teams
- Sumo Logic: Cloud SIEM with compliance-focused features
Startup reality check: Full SIEM deployments can be expensive and complex. Many startups start with centralized logging (like AWS CloudTrail, Datadog logs, or a simple ELK stack) and add SIEM capabilities as they scale.
What Security Awareness Training Do Compliance Frameworks Require?
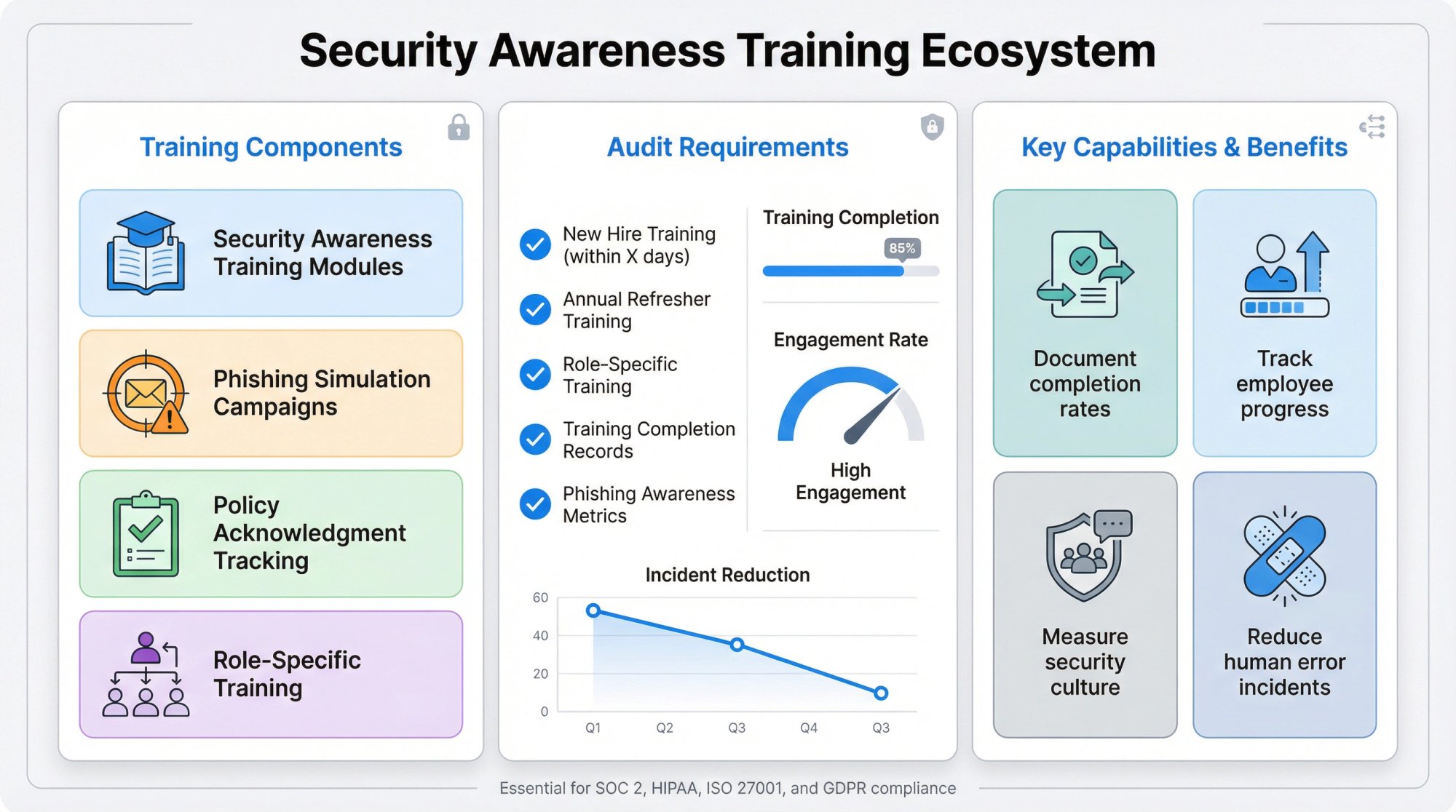
What it does: Educates employees on security best practices and compliance requirements.
Key capabilities:
- Security awareness training modules
- Phishing simulation campaigns
- Policy acknowledgment tracking
- Training completion reporting
- Compliance-specific training content
Why it matters: Human error remains a leading cause of security incidents. Every compliance framework requires evidence of employee security training.
What auditors look for:
- New hire security training within specified timeframe
- Annual refresher training for all employees
- Role-specific training for technical staff
- Training completion records and acknowledgments
- Phishing awareness metrics
Document your requirements in an awareness training policy.
Popular options:
- KnowBe4: Market leader in security awareness training
- Curricula: Engaging, story-based training content
- Hoxhunt: AI-powered phishing training
- Proofpoint Security Awareness: Integrated with email security
- Riot: Developer-focused security training
Budget-conscious alternative: Some compliance platforms include basic security awareness training modules. This can reduce the number of separate tools you need to manage.
Are Background Checks Required for Compliance?
What it does: Verifies the background of employees and contractors before granting access to systems and data.
Key capabilities:
- Criminal background checks
- Employment verification
- Education verification
- Reference checks
- Ongoing monitoring (for certain roles)
Why it matters: Compliance frameworks often require background checks for employees with access to sensitive data or systems.
What auditors look for:
- Documented background check policy
- Evidence that checks are performed consistently
- Clear criteria for what constitutes a passing check
- Procedures for handling adverse findings
Your HR security policy should cover these requirements.
Popular options:
- Checkr: API-first background checks popular with startups
- GoodHire: User-friendly background screening
- Sterling: Comprehensive enterprise background verification
- HireRight: Global background screening capabilities
Compliance tip: Your background check policy should clearly define which roles require checks and what types of checks are performed. This documentation is often requested during audits.
How Should Startups Handle Password Management for Compliance?
What it does: Secures and manages credentials across your organization.
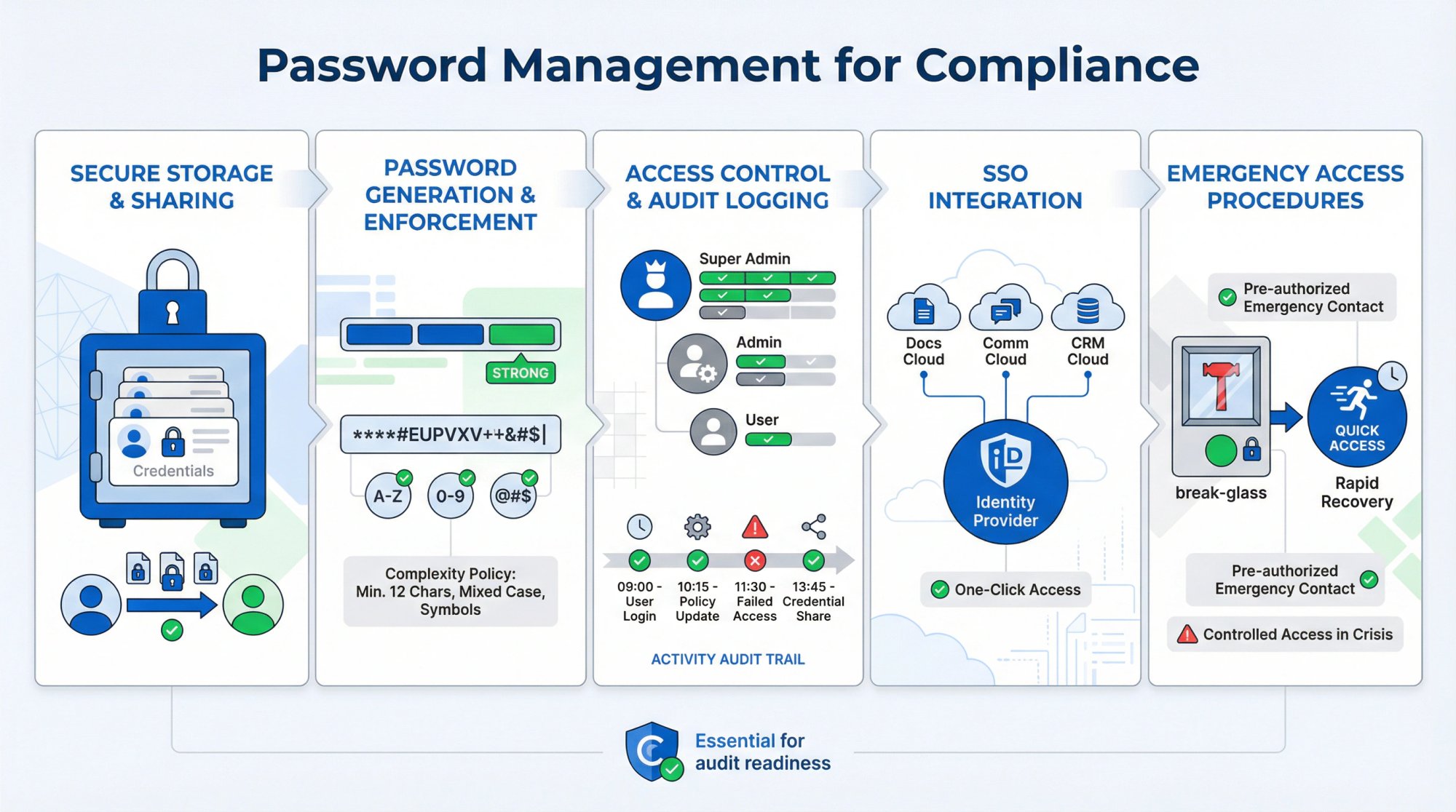
Key capabilities:
- Secure password storage and sharing
- Password generation and enforcement
- Access control and audit logging
- SSO integration
- Emergency access procedures
Why it matters: Password hygiene is a baseline security requirement. Auditors want to see that you have controls preventing weak or reused passwords.
Key compliance elements:
- Password complexity requirements
- Secure sharing mechanisms for team credentials
- Audit trail of password access
- Integration with SSO where possible
Your authentication and password policy defines these standards.
Popular options:
- 1Password Business: Strong team features and SSO integration
- Bitwarden: Open-source option with business features
- LastPass Teams: Established password management platform
- Dashlane Business: Password management with VPN included
Best practice: Wherever possible, use SSO instead of shared passwords. Password managers should be the fallback for systems that don't support SSO.
When Do Startups Need Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools?
What it does: Prevents sensitive data from leaving your organization through unauthorized channels.
Key capabilities:
- Data classification and discovery
- Policy-based data protection
- Endpoint DLP controls
- Cloud application monitoring
- Email and web filtering
Why it matters: Protecting sensitive data is central to every compliance framework. DLP tools help demonstrate you have controls preventing data exfiltration.
When you need DLP:
- You handle significant amounts of regulated data (PII, PHI, financial data)
- You're pursuing SOC 2 with the confidentiality trust service criteria
- Your customers require evidence of data protection controls
- You operate in highly regulated industries
Your data classification and handling policy should define what data requires protection.
Popular options:
- Microsoft Purview: Integrated with Microsoft 365
- Google Cloud DLP: Native to Google Cloud
- Netskope: Cloud-focused DLP
- Digital Guardian: Comprehensive DLP platform
- Code42 Incydr: Insider risk focused DLP
Startup perspective: Full DLP deployment can be overkill for early-stage startups. Start with basic controls (like disabling USB access and monitoring cloud storage sharing) and expand as your data handling requirements grow.
How to Build Your Stack for Different Compliance Frameworks
Different compliance frameworks have different emphases. Here's how to prioritize your tech stack based on what you're pursuing:
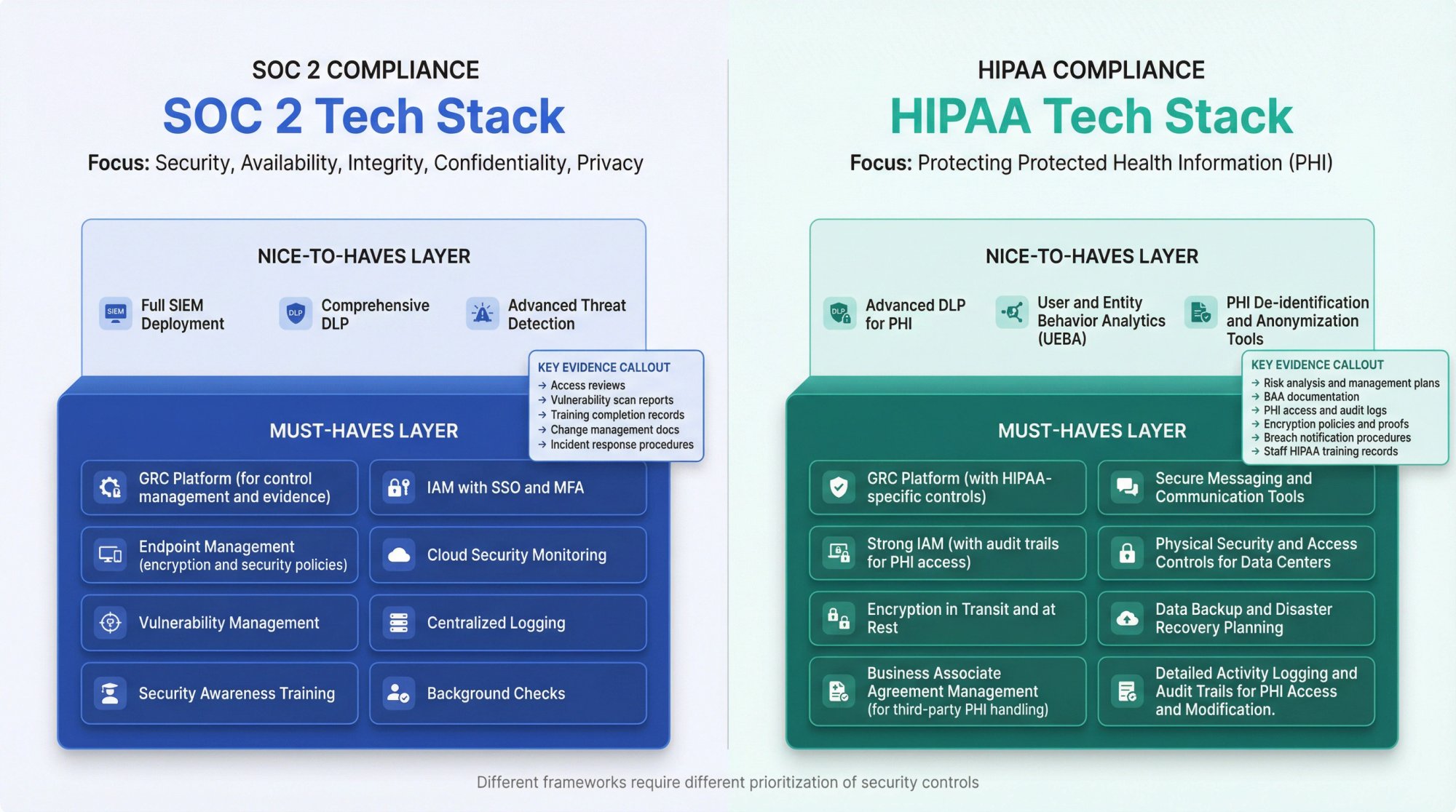
What Tools Do You Need for SOC 2 Compliance?
SOC 2 compliance focuses on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. A strong SOC 2 tech stack emphasizes:
Must-haves:
- GRC platform for control management and evidence
- IAM with SSO and MFA
- Endpoint management with encryption and security policies
- Cloud security monitoring
- Vulnerability management
- Centralized logging
- Security awareness training
- Background checks
Nice-to-haves:
- Full SIEM deployment
- Comprehensive DLP
- Advanced threat detection
Key evidence you'll need:
→ Access reviews showing appropriate permissions
→ Vulnerability scan reports showing remediation
→ Training completion records
→ Change management documentation
→ Incident response procedures and testing evidence
For a complete checklist, see our SOC 2 compliance checklist.
What Is the Best Tech Stack for HIPAA Compliance?
HIPAA compliance centers on protecting protected health information (PHI). Your tech stack must demonstrate safeguards for PHI throughout its lifecycle.
Must-haves:
- GRC platform with HIPAA-specific controls
- Strong IAM with audit trails for PHI access
- Endpoint encryption and management
- Encryption in transit and at rest
- Business Associate Agreements (BAA) with all vendors
- Security awareness training with HIPAA focus
- Incident response and breach notification capabilities
Critical considerations:
- Every tool that touches PHI needs a BAA
- Audit logs for PHI access are non-negotiable
- Encryption requirements are stricter than general security
Unique requirements:
→ PHI access logging and monitoring
→ Breach detection and notification procedures
→ Workforce training on PHI handling
Consider using HIPAA risk assessment tools to identify gaps in your program.
What Does an ISO 27001 Compliance Tech Stack Look Like?
ISO 27001 takes a risk-based approach to information security management. Your tech stack should support the entire ISMS (Information Security Management System).
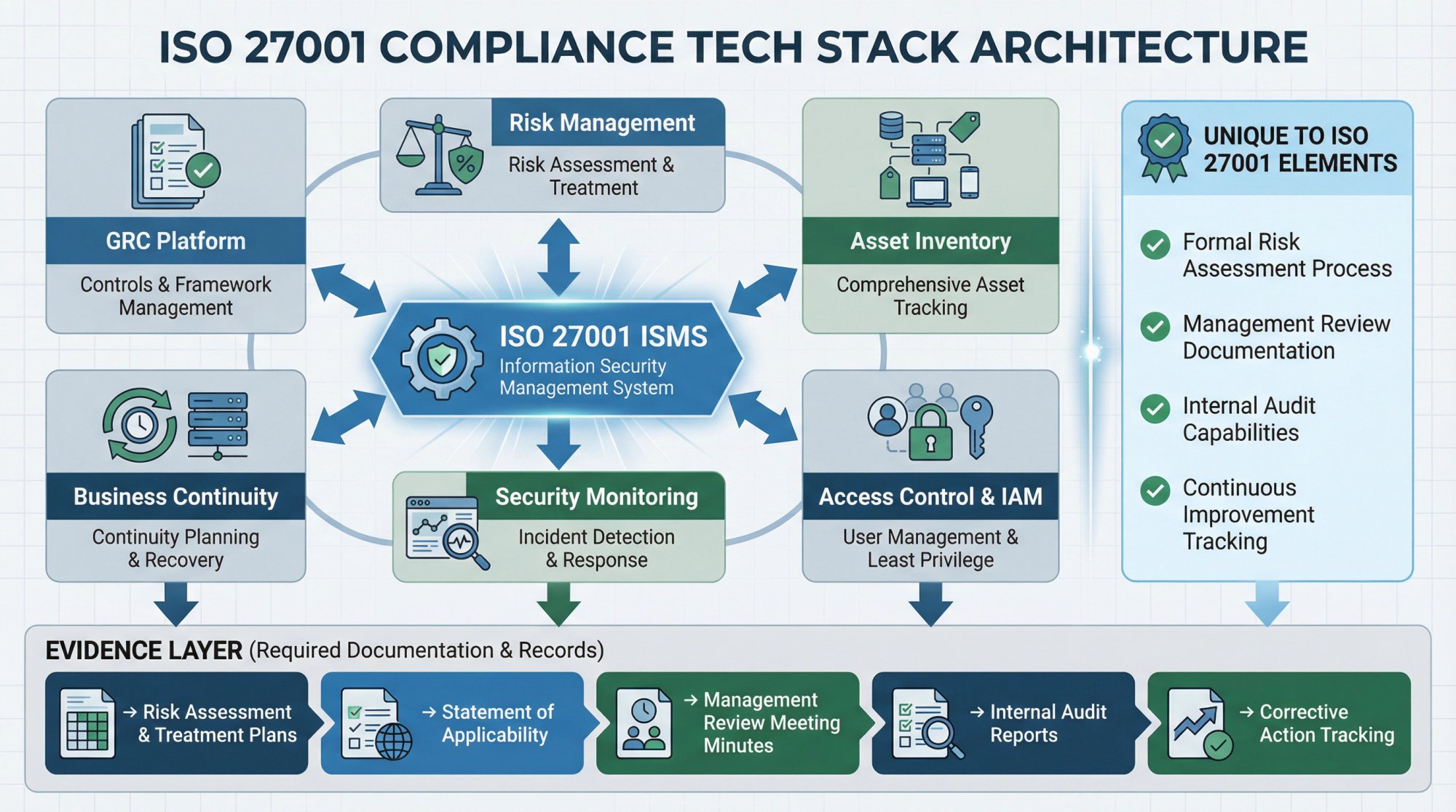
Must-haves:
- GRC platform supporting ISO 27001 controls
- Comprehensive risk management capabilities
- Asset inventory and management
- Access control and IAM
- Security monitoring and incident management
- Business continuity capabilities
Unique to ISO 27001:
- Formal risk assessment and treatment process
- Management review documentation
- Internal audit capabilities
- Continuous improvement tracking
Key evidence:
→ Risk assessment and treatment plans
→ Statement of Applicability
→ Management review meeting minutes
→ Internal audit reports
→ Corrective action tracking
Learn about the full ISO 27001 certification process for detailed guidance.
What Tools Support GDPR Compliance?
GDPR compliance focuses on protecting personal data of EU residents. Your tech stack must support data subject rights and demonstrate accountability.
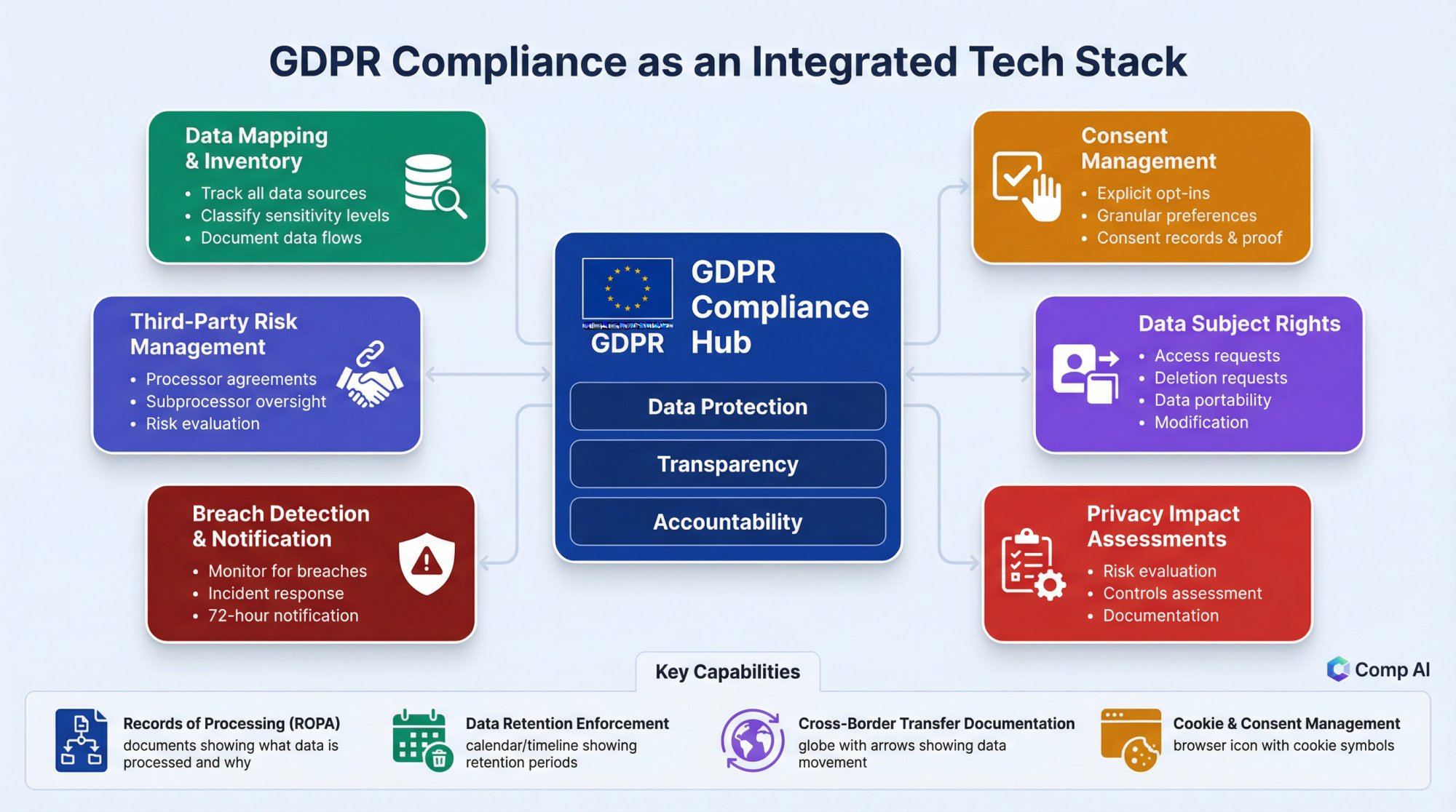
Must-haves:
- Data mapping and inventory capabilities
- Consent management
- Data subject request handling
- Privacy impact assessment tools
- Data breach detection and notification
- Third-party risk management for processors
Key capabilities:
→ Records of processing activities
→ Data retention enforcement
→ Cross-border transfer documentation
→ Cookie and consent management
A data retention policy is essential for GDPR compliance.
How to Integrate Your Compliance Tools Effectively
Having the right tools is only half the battle. They need to work together seamlessly. Here's how to think about integration architecture:
What Is the Hub-and-Spoke Integration Model?
Your GRC platform should be the hub, with other tools as spokes feeding into it:
This architecture ensures:
- Evidence flows automatically to your compliance platform
- Single source of truth for audit preparation
- Reduced manual effort maintaining documentation
- Consistent control status across tools
Which Integrations Should You Prioritize First?
1. Identity Provider to GRC
- Automates evidence of access reviews
- Tracks MFA enrollment status
- Documents user provisioning and deprovisioning
2. Cloud Provider to GRC
- Pulls infrastructure configurations automatically
- Documents security group changes
- Tracks encryption status
3. Code Repository to GRC
- Documents change management process
- Tracks code review requirements
- Links deployments to approvals
4. HR System to IAM
- Automates user provisioning on hire
- Triggers deprovisioning on termination
- Maintains access based on role changes
5. Vulnerability Scanner to GRC
- Tracks vulnerability status over time
- Documents remediation efforts
- Provides audit evidence automatically
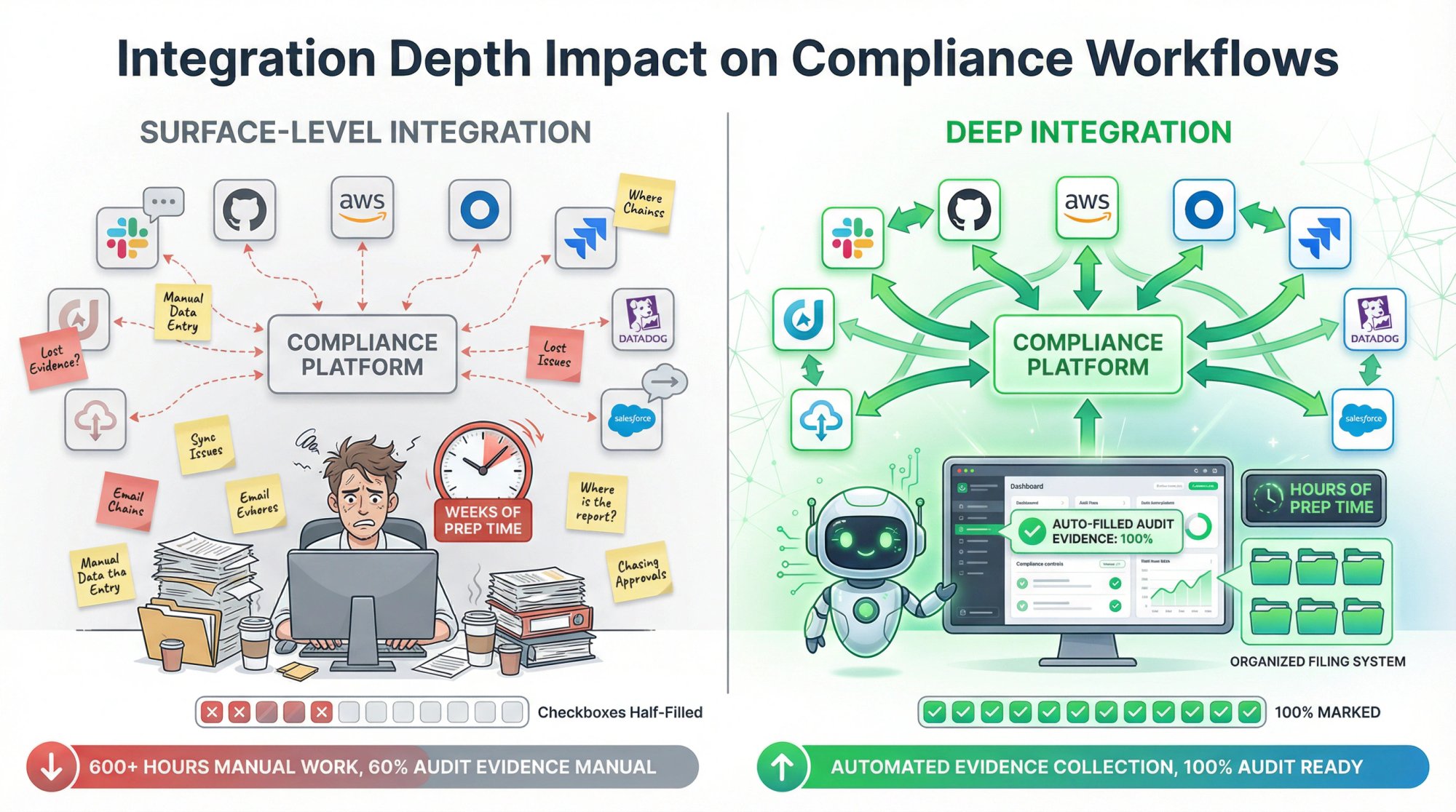
Why Does Integration Depth Matter for Compliance?
When evaluating tools, look beyond the checkbox of having an integration. Consider:
Surface-level integration: Tool shows up in a marketplace but only syncs basic data. You still do manual work for meaningful evidence.
Deep integration: Tool syncs comprehensive data automatically, maps to compliance controls, and generates audit-ready evidence without manual intervention.
The difference dramatically impacts how much time you spend preparing for audits. A well-integrated automated compliance software can reduce audit prep from weeks to hours.
How to Evaluate Compliance Software Vendors
When selecting tools for your compliance tech stack, use this evaluation framework:
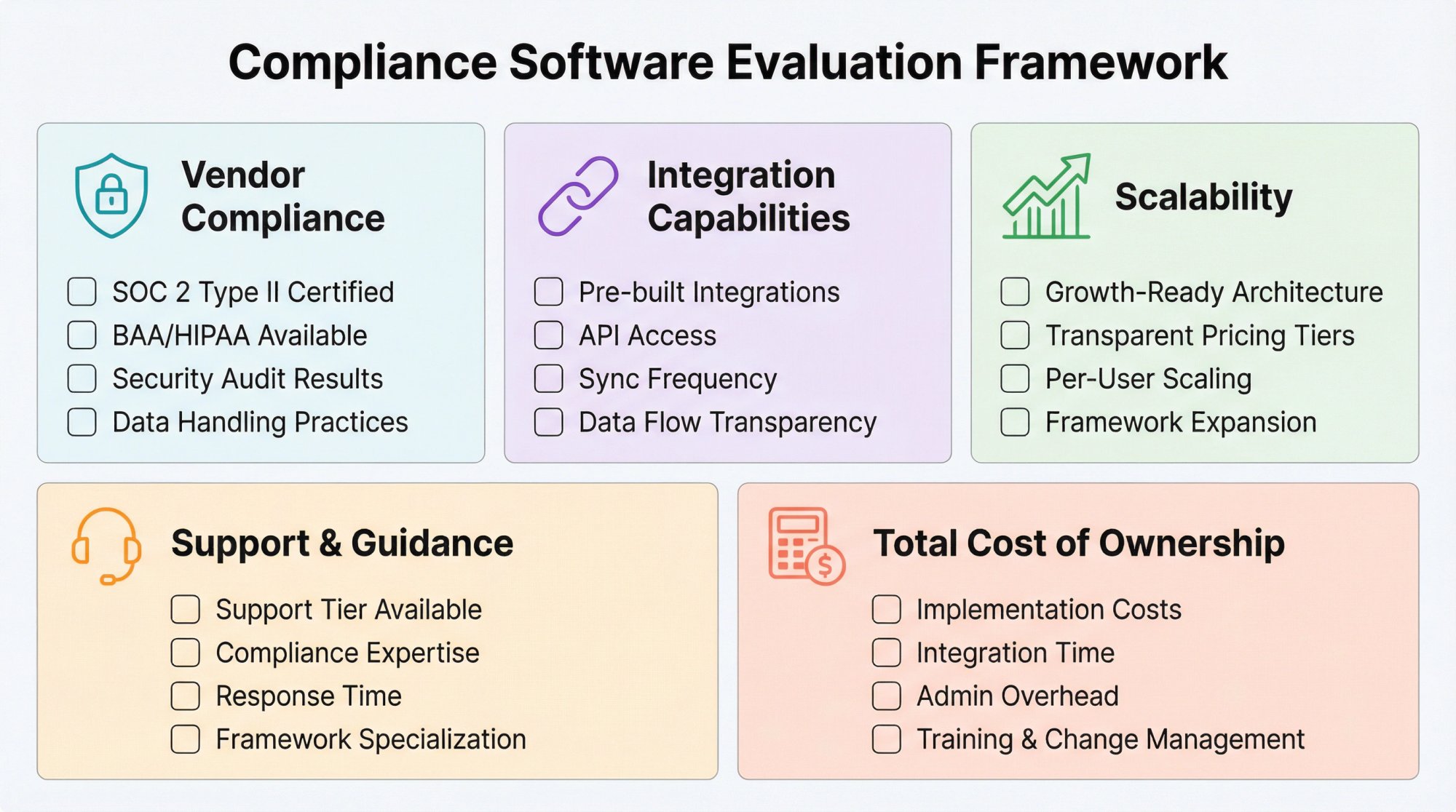
Is Your Compliance Vendor Actually Compliant?
Your compliance tools should themselves be compliant:
- Do they have SOC 2 Type II?
- Do they offer BAAs for HIPAA if needed?
- What's their security posture?
- How do they handle your data?
What Integration Capabilities Should You Look For?
- What pre-built integrations exist?
- Is there an API for custom integrations?
- How frequently do integrations sync?
- What data flows through the integration?
How Do You Assess Scalability?
- Will this tool scale with your growth?
- What are the pricing tiers?
- How does pricing change as you add users, assets, or frameworks?
What Level of Support Do Compliance Platforms Offer?
- What level of support is included?
- Do they provide compliance guidance or just software?
- How responsive is their support team?
- Do they have expertise in your specific frameworks?
How Do You Calculate Total Cost of Ownership?
Look beyond sticker price:
- Implementation and onboarding costs
- Integration development time
- Internal administration overhead
- Training and change management
- Time spent managing the tool vs. doing compliance work
How Much Should Startups Budget for Compliance Tools?
Let's be realistic about costs. Here's a framework for thinking about compliance tech stack budgeting
What Should Seed Stage Startups Spend on Compliance?
Budget reality: You're resource-constrained and compliance may not yet be blocking deals.
Recommended approach:
- Start with Comp AI that includes multiple capabilities
- Use built-in tools from your cloud provider and identity provider
- Use open-source options where appropriate
- Focus on getting compliant fast with minimal tooling
Estimated spend: $5,000-15,000 annually
What Is the Right Compliance Budget for Series A Startups?
Budget reality: Compliance is likely becoming a sales requirement. You can invest in proper tooling.
Recommended approach:
- Invest in a comprehensive GRC platform
- Add dedicated security tools where gaps exist
- Pursue multiple frameworks as customer needs require
- Consider tools that support scale
Estimated spend: $15,000-50,000 annually
How Do Series B+ Companies Approach Compliance Investment?
Budget reality: Compliance is a business function requiring dedicated resources and enterprise-grade tooling.
Recommended approach:
- Enterprise-grade tools across all categories
- Dedicated compliance and security team
- Multiple frameworks maintained simultaneously
- Advanced capabilities like DLP and threat detection
Estimated spend: $50,000-200,000+ annually
For detailed cost planning, use the SOC 2 cost breakdown as a starting point.
How to Implement Your Compliance Tech Stack Step by Step
Here's a phased approach to building your compliance tech stack:
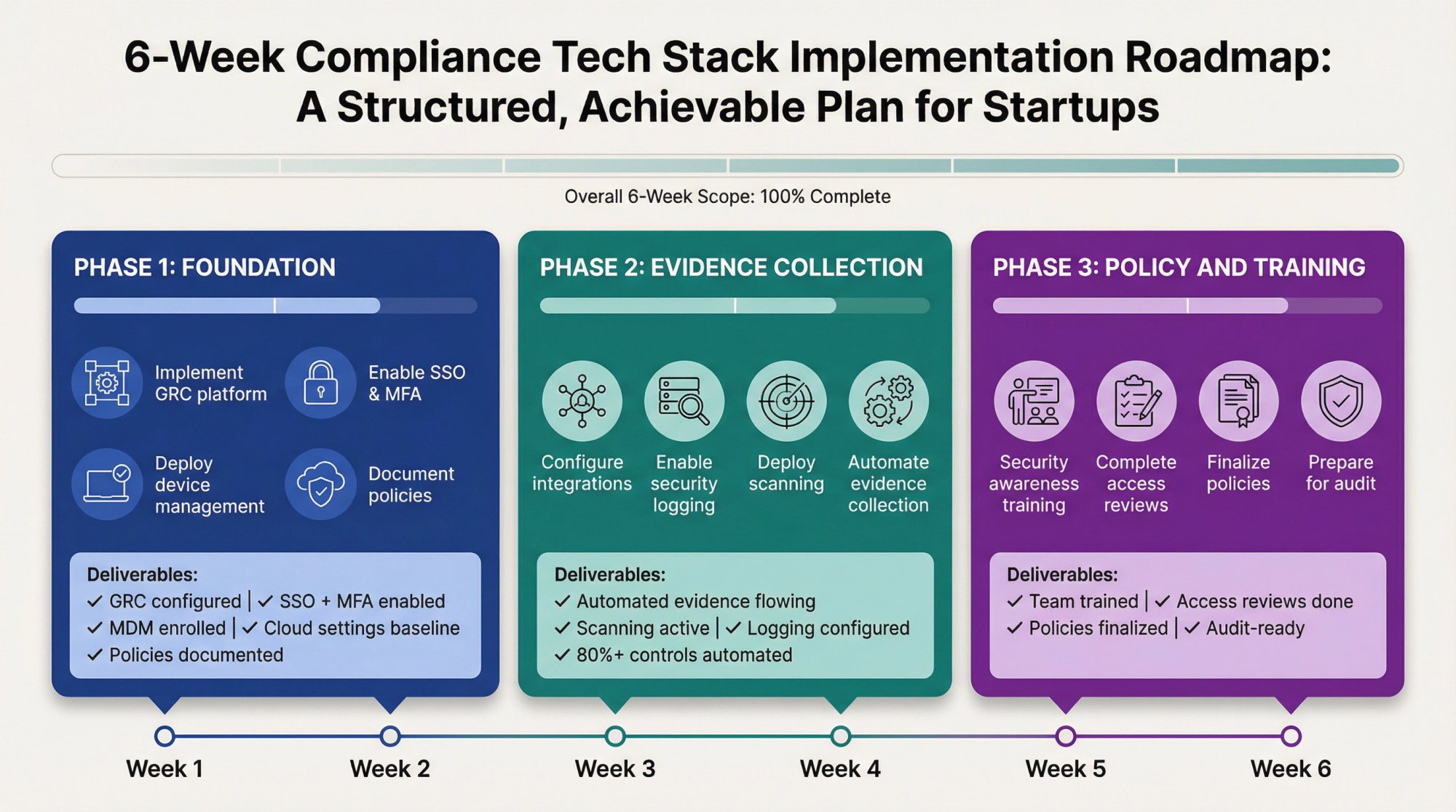
Phase 1: Foundation (Weeks 1-2)
Goal: Get core infrastructure in place
Actions:
- Select and implement GRC platform
- Make sure IAM has SSO and MFA enabled
- Deploy endpoint management to all devices
- Enable cloud security baselines in your cloud provider
- Document existing security policies
Deliverables:
- GRC platform configured with target framework
- All employees using SSO with MFA
- All devices enrolled in MDM
- Basic cloud security settings enabled
Phase 2: Evidence Collection (Weeks 3-4)
Goal: Automate evidence gathering
Actions:
- Configure integrations between tools and GRC platform
- Enable security logging in key systems
- Deploy vulnerability scanning
- Set up automated evidence collection workflows
Deliverables:
- Automated evidence flowing into GRC platform
- Vulnerability scanning operational
- Logging configured for key systems
- Evidence collection automated for 80%+ of controls
Phase 3: Policy and Training (Weeks 5-6)
Goal: Complete documentation and training requirements
Actions:
- Finalize all required policies and procedures
- Deploy security awareness training
- Conduct initial access reviews
- Complete risk assessment using top risk management software
Deliverables:
- All policies published and acknowledged
- Security training completed by all employees
- Initial access review documented
- Risk assessment completed
Phase 4: Audit Preparation (Weeks 7-8)
Goal: Prepare for audit or assessment
Actions:
- Complete gap assessment against framework
- Remediate any identified gaps
- Organize evidence for auditor review
- Conduct readiness review with a SOC 2 readiness assessment
Deliverables:
- All controls implemented and evidenced
- Gap remediation complete
- Evidence organized and accessible
- Ready for auditor engagement
Key InsightThe 8-week timeline assumes you're using automated tooling. Manual approaches can easily stretch to 6-12 months. The right tech stack doesn't just reduce cost; it compresses your time-to-compliance dramatically.
5 Compliance Tech Stack Mistakes to Avoid
Learn from others' mistakes:
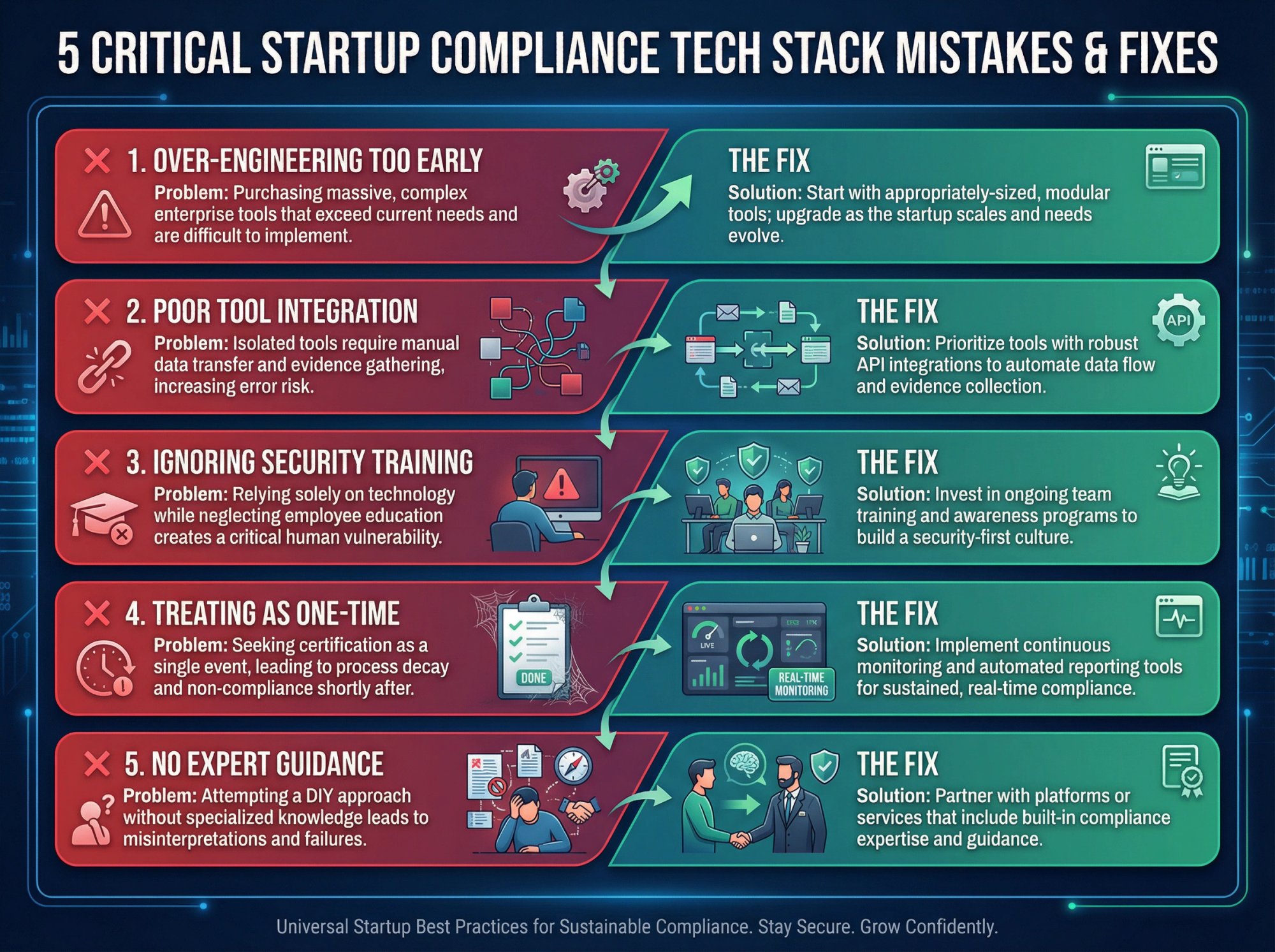
Mistake 1: Over-Engineering Your Stack Too Early
The mistake: Deploying enterprise-grade tools when startup-grade would suffice.
The fix: Start with tools appropriately sized for your stage. You can upgrade later.
Mistake 2: Under-Investing in Tool Integration
The mistake: Buying tools that don't talk to each other, creating manual work.
The fix: Prioritize integration capabilities. Manual evidence collection doesn't scale.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Security Training and Awareness
The mistake: Focusing only on tools and ignoring training and awareness.
The fix: Invest in training. Tools can't fix human behavior.
Mistake 4: Treating Compliance as a One-Time Project
The mistake: Getting certified and then letting things decay.
The fix: Choose tools that support continuous compliance, not just point-in-time audits.
Mistake 5: Not Getting Expert Compliance Guidance
The mistake: Trying to figure everything out without expert guidance.
The fix: Work with a platform or service that provides expertise, not just software. The right guidance can save months of trial and error.
How Do You Measure Compliance Tech Stack Success?
How do you know your compliance tech stack is working? Track these metrics:
What Efficiency Metrics Should You Track?
- Time to audit-ready: How long from zero to audit-ready?
- Evidence collection time: Hours spent gathering evidence for audits
- Control exceptions: Number of controls with issues at any time
- Remediation time: Average time to fix identified issues
What Effectiveness Metrics Matter for Compliance?
- Audit findings: Number and severity of audit findings
- Security incidents: Incidents prevented or detected by tools
- Compliance drift: Controls that fall out of compliance between audits
How Do You Measure Business Impact of Compliance?
- Deal velocity: Time from compliance request to certification provided
- Deals enabled: Revenue attributed to compliance certifications
- Cost of compliance: Total spend relative to company size and revenue
Frequently Asked Questions

What Is the Minimum Viable Compliance Tech Stack for Seed-Stage Startups?
At minimum, you need:
- A GRC platform or compliance automation tool
- SSO with MFA enabled (often included in Google Workspace or Microsoft 365)
- Basic endpoint management
- Cloud provider security features enabled
This gets you started without major investment. Add specialized tools as you grow.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Compliance Tech Stack From Scratch?
With modern automation, you can have a functional compliance tech stack in 2-4 weeks. The key is choosing integrated tools that work together out of the box rather than building custom integrations.
Can You Use the Same Tech Stack for Multiple Compliance Frameworks?
Yes, and you should plan for this. Most security controls overlap between frameworks. A well-designed tech stack supports SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR with minimal additional tooling. The key is choosing a GRC platform that handles multiple frameworks.
What Is the Biggest Mistake Startups Make With Compliance Tech Stacks?
The biggest mistake is treating tools as the solution rather than enablers. Tools without proper processes and expertise just create expensive shelfware. Look for platforms that provide guidance and support, not just software.
Should You Hire a Compliance Person Before Building Your Tech Stack?
Not necessarily. Modern compliance platforms are designed to guide founders and operators through the process without dedicated compliance headcount. You can often get through your first certification before hiring a dedicated person. That said, as you scale to multiple frameworks and customers, dedicated compliance expertise becomes valuable.
How Can You Tell If a Vendor Takes Security Seriously?
Ask for their SOC 2 report. If they don't have one, ask about their security practices and roadmap. A vendor handling your compliance data should have strong security themselves. Also check if they offer features like SSO, MFA, and audit logging for their platform.
What Are Your Next Steps?
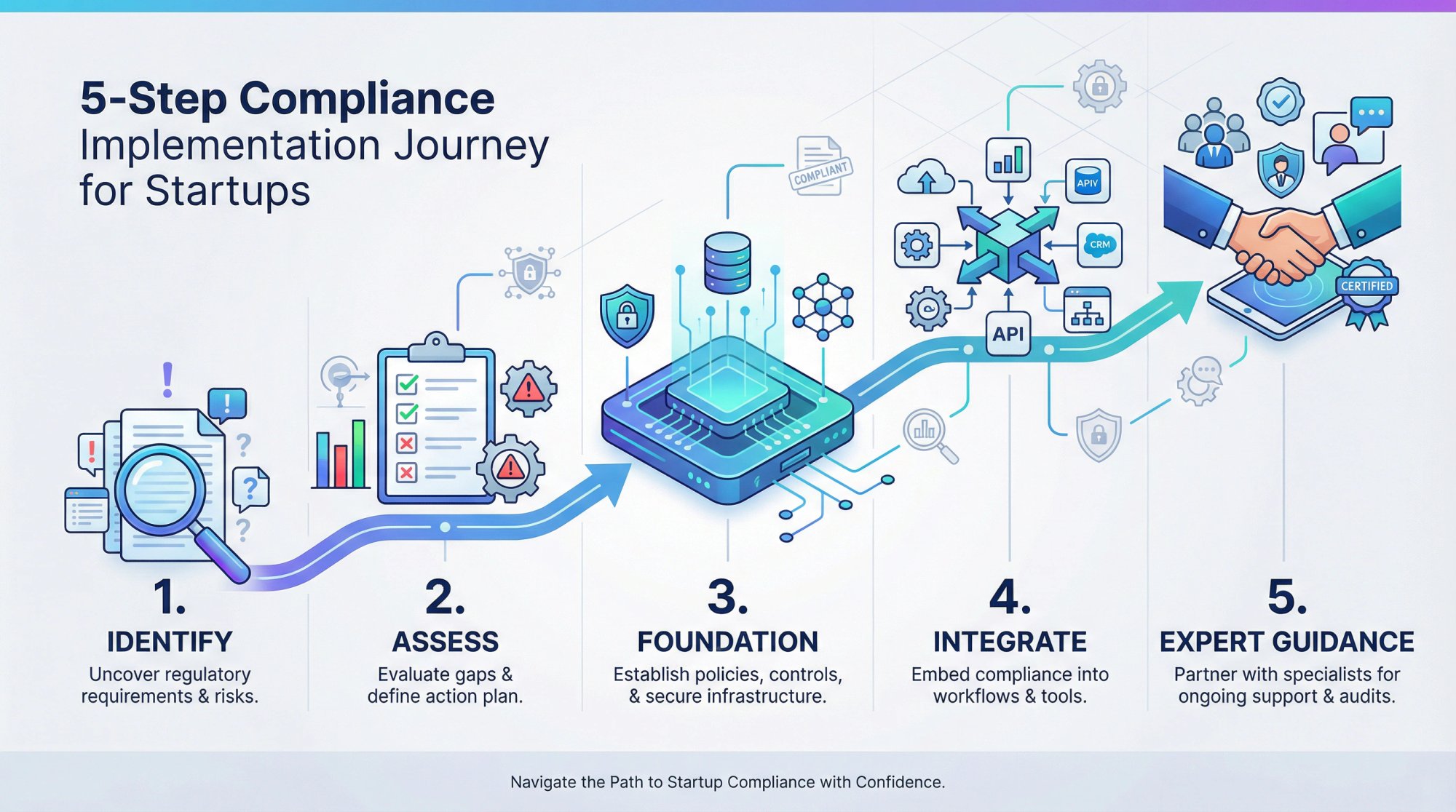
Building an effective compliance tech stack doesn't have to be overwhelming. Here's how to get started:
- Identify your immediate compliance needs: What frameworks do your customers require? What's blocking deals today?
- Assess your current state: What tools do you already have? Where are the gaps?
- Choose your foundation: Select a GRC or compliance platform that will serve as your hub.
- Prioritize integrations: Connect your existing tools to start automating evidence collection.
- Get expert guidance: Work with a platform or advisor who can accelerate your path to compliance.
The right compliance tech stack transforms a regulatory burden into a competitive advantage. With modern tools and automation, startups can achieve in weeks what used to take months, unlocking enterprise customers and demonstrating security maturity that builds trust.

Ready to build your compliance tech stack? Book a demo to see how Comp AI can help you get audit-ready in days, not months.
Share this article
Help others discover this content